section 3, chapter 9 cross-bridge cycling
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
11 likes•10,147 views
cross-bridge cycling
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Similar to section 3, chapter 9 cross-bridge cycling
Similar to section 3, chapter 9 cross-bridge cycling (20)
Molecular mechanism of Skeletal muscle contraction.2022.pptx

Molecular mechanism of Skeletal muscle contraction.2022.pptx
More from Michael Walls
More from Michael Walls (20)
Recently uploaded
This presentation was provided by William Mattingly of the Smithsonian Institution, during the fourth segment of the NISO training series "AI & Prompt Design." Session Four: Structured Data and Assistants, was held on April 25, 2024.Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: Structured Data, Assistants, & RAG"

Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: Structured Data, Assistants, & RAG"National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
APM Welcome
Tuesday 30 April 2024
APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across Sectors
Presented by:
Professor Adam Boddison OBE, Chief Executive Officer, APM
Conference overview:
https://www.apm.org.uk/community/apm-north-west-branch-conference/
Content description:
APM welcome from CEO
The main conference objective was to promote the Project Management profession with interaction between project practitioners, APM Corporate members, current project management students, academia and all who have an interest in projects.APM Welcome, APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across Sectors

APM Welcome, APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across SectorsAssociation for Project Management
Recently uploaded (20)
9548086042 for call girls in Indira Nagar with room service

9548086042 for call girls in Indira Nagar with room service
Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: Structured Data, Assistants, & RAG"

Mattingly "AI & Prompt Design: Structured Data, Assistants, & RAG"
Call Girls in Dwarka Mor Delhi Contact Us 9654467111

Call Girls in Dwarka Mor Delhi Contact Us 9654467111
Interactive Powerpoint_How to Master effective communication

Interactive Powerpoint_How to Master effective communication
APM Welcome, APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across Sectors

APM Welcome, APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across Sectors
Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...

Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...
Measures of Dispersion and Variability: Range, QD, AD and SD

Measures of Dispersion and Variability: Range, QD, AD and SD
Beyond the EU: DORA and NIS 2 Directive's Global Impact

Beyond the EU: DORA and NIS 2 Directive's Global Impact
Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi

Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi
Kisan Call Centre - To harness potential of ICT in Agriculture by answer farm...

Kisan Call Centre - To harness potential of ICT in Agriculture by answer farm...
section 3, chapter 9 cross-bridge cycling
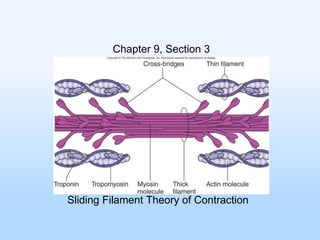
- 1. Chapter 9, Section 3 Sliding Filament Theory of Contraction
- 2. The Sliding Filament Model of Muscle Contraction During a muscle contraction Thick (myosin) filaments and thin (actin) filaments slide across one another The filaments do not change lengths Z-bands move closer together causing the sarcomere to shorten. I bands appear narrow Figure 9.11a. Individual sarcomeres shorten as thick and thin filaments slide past one another.
- 3. Cross Bridge Cycling 1. When a muscle is relaxed, tropmyosin covers the binding sites on actin. A molecule of ADP and Phosphate remains attached to myosin from the previous contraction.
- 4. Cross Bridge Cycling 2. During a contraction, Calcium binds to troponin. Tropomyosin is repositioned, exposing the myosin binding sites on actin filaments
- 5. Cross Bridge Cycling 3. Myosin heads bind to actin filaments. The phosphate is released.
- 6. Cross Bridge Cycling 4. Myosin heads spring forward “Power Stroke” pulling the actin filaments. ADP is released from Myosin
- 7. Cross Bridge Cycling 5. Myosin is released from actin. A new molecule of ATP binds to myosin, causing it to be released from the actin filament. • ATP is not yet broken down, but it is essential to release the crossbridges.
- 8. Cross Bridge Cycling 6. ATP is broken down, providing the energy to “cock” the myosin filaments (recovery stroke). 7. Steps 1-6 are repeated several times.
- 9. Figure 9.10. The cross-bridge cycle. The cycle continues as long as ATP is present, and nerve impulses release Acetylcholoine. Watch the You-Tube video “Sliding Filament” to view cross-bridge cycling in action.
- 10. Relaxation When a nerve impulse ceases, two events relax muscle fibers. 1. Acetylcholinesterase breaks down Ach in the synapse. • Prevents continuous stimulation of a muscle fiber. 2. Calcium Pumps (Ca2+ATPase) remove Ca2+ from the sarcoplasm and returns it to the SR. • Without calcium, tropomyosin covers the binding sites on actin filaments.
- 11. Relaxation Rigor Mortis is a partial contraction of skeletal muscles that occurs a few hours after death. • After death calcium leaks into sarcoplasm, triggering the muscle contractions. • But ATP supplies are diminished after death, so ATP is not available to remove the cross-bridge linkages between actin and myosin. • muscles do not relax*. • Contraction is sustained until muscles begin to decompose. * Notice that ATP is required for muscle relaxation!
- 12. End of Chapter 9, Section 3