Female Reproductive System Lecture
- 1. Medical and Surgical Nursing Lecture Notes on Female Reproductive System System Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R Abejo R.N, MAN Medical and Surgical Nursing Abejo1 MEDICAL AND SURGICAL NURSING Female Reproductive System Lecturer: Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MAN Anatomy and Physiology of the Female Reproductive System
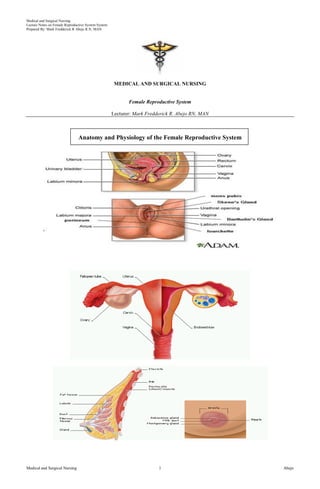
- 2. Medical and Surgical Nursing Lecture Notes on Female Reproductive System System Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R Abejo R.N, MAN Medical and Surgical Nursing Abejo2 Internal Female Reproductive System Vagina Birth canal Muscular tube (8 cm) Connects cervix of the uterus to the exterior Receives erect stimulus during sexual intercourse Opens to outside Cervix Neck-like part Entrance to uterus Capable of very wide dilation during childbirth Uterus (womb) Virtually at a right angle to the vagina Specialized to allow the embryo to become implanted in its inner wall and to nourish the growing fetus from the maternal blood 3 layers: Peritoneum (outer) Myometrium (middle) – labour, cramps Endometrium (inner) – sloughed off every 28 days during menstrual cycle Fallopian Tube (oviducts) Found at the top of the uterus on each side Function is to conduct ova (eggs) from the ovary to the uterus Not physically attached to the ovaries Fimbraie (finger-like projections) help draw the egg into the fallopian tubes Right arm = fallopian tube, right hand = fimbraie, left fist = ovary Fertilization occurs near the ovarian end of the fallopian tube (must take place within 24 hours of ovulation) Movement of the egg down the fallopian tube is through peristalsis Ampulla: site for fertilization Isthmus : site for tubal ligation Ovaries (female gonads) Main female reproduction organs Produces egg cells which are nonmotile Produces steroid hormones (estrogen and progesterone) Held in place by ligaments Each ovary contains numerous follicles (“shell”) each containing an egg Follicle serves as the endocrine gland All immature eggs are produced before birth 30th week of gestation – 7 million eggs At birth – 2 million Puberty – 300 000 – 400 000 300 to 400 mature eggs released in a life time At puberty, 1 mature egg is released every 28 days Will occur usually until the age of 45-50 When female has no more eggs to release she goes into menopause (physiological) Fertilization must take place to complete meiosis II As many as 20 follicles can begin development at the beginning of the menstrual cycle Older eggs have more chances of having problems with the baby External Female Reproductive Parts Mons Pubis Soft fatty tissue, lies directly over symphysis pubis & becomes covered w/ hair just before puberty It is where the pubic hair grows. Labia Majora W/ hair outside but smooth inside fatty skin folds from MONS PUBIS to PERINEUM and protects the labia minora , urinary meatus & vagina Labia Minora Thin, pink, smooth, hairless, extremely sensitive to pressure, touch and temperature. The glands of labia minora lubricate the vulva. It is formed by the frenulum and the prepuce of the clitoris which is also very sensitive Clitoris Composed of glans & shaft that is partially covered by prepuce GLANS is small and round and is filled w/ many nerve endings and rich blood supply SHAFT is a cord connecting the glans to the pubic bone; w/in it is the major blood supply of clitoris Urethral Meatus Entrance of urethra, opens approximately 1cm below clitoris Skenes Gland lubricates the external genitalia Bartholins Gland alkaline in ph, helps improve sperm survival FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE DISORDER OVARIAN CYSTS Cysts are nonneoplastic sacs that contain fluid or semisolid material. Ovarian cysts are usually small and produce no symptoms, ovarian cysts should be thoroughly investigated as possible sites of malignant change. Common types include: Follicular,cysts, which are usually very small, semitransparent, and fluid-filled Lutein cysts, including corpus luteum cysts, which are functional, nonneoplastic enlargements of the ovaries Theca-lutein cysts, which are commonly bilateral and filled with clear, straw-colored fluid Polycystic (or sclerocystic) ovary disease is part of the Stein-Leventhal syndrome. Ovarian cysts can develop any time between puberty and menopause, including during pregnancy. Corpus luteum cysts occur infrequently, usually during early pregnancy.
- 3. Medical and Surgical Nursing Lecture Notes on Female Reproductive System System Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R Abejo R.N, MAN Medical and Surgical Nursing Abejo3 Cause / Risk Factors Follicular cysts arise from follicles that over distend instead of going through the atretic stage of the menstrual cycle. Corpus luteum cysts are caused by excessive accumulation of blood during the hemorrhagic phase of the menstrual cycle. Theca-lutein cysts are commonly associated with hydatidiform mole, choriocarcinoma, or hormone therapy. Polycystic ovary disease results from endocrine abnormalities. Clinical Manifestation Usually small cysts produces no symptoms, unless torsion or rupture causes signs of acute abdomen. Low back pain Mild pelvic discomfort Dyspareunia ( difficult and or painful intercourse) Abnormal uterine bleeding Acute abdominal pain (similar to that of appendicitis) -in ovarian cysts with torsion In corpus luteum cysts appearing early in pregnancy, the patient may develop unilateral pelvic discomfort and (with rupture) massive intraperitoneal hemorrhage. In polycystic ovary disease, the patient may develop amenorrhea ( abnormal absence or stoppage of menses), Oligomenorrhea (abnormally infrequent menstruation), or infertility secondary to the disorder as well as bilaterally enlarged ovaries. Collaborative Management Follicular cysts usually don't require treatment because they tend to disappear spontaneously within 60 days. If they interfere with daily activities, Clomiphene citrate P.O. for 5 days or progesterone I.M. for 5 days, reestablishes the ovarian hormonal cycle and induces ovulation. Oral contraceptives may also accelerate involution of functional cysts (including both types of lutein cysts and follicular cysts). Treatment for corpus luteum cysts that occur during pregnancy is symptomatic because these cysts diminish during the third trimester and rarely require surgery. Theca-lutein cysts disappear spontaneously after elimination of hydatidiform mole or choriocarcinoma, or discontinuation of HCG or clomiphene citrate therapy. Polycystic ovary disease treatment may include; drugs, such as clomiphene citrate to induce ovulation or if drug therapy fails to induce ovulation, surgical wedge resection of one-half to one-third of the ovary. Surgery may become necessary for both diagnosis and treatment. ENDOMETRIOSIS Endometrial tissue appears outside the lining of the uterine cavity. This ectopic tissue usually remains in the pelvic area, most commonly around the ovaries, uterovesical peritoneum, uterosacral ligaments, and the cul-de-sac, but it can appear anywhere in the body. Active endometriosis usually occurs between ages 30 and 40, more so in women who postpone child-bearing. Endometriosis usually becomes progressively severe during the menstrual years, and subsides after menopause. Infertility is the primary complication. Spontaneous abortion may also occur. Cause / Risk Factors Trasportation---during menstruation, the fallopian tubes expel endometrial fragments that implant of the ovaries or pelvic peritoneum Formation in situ--inflammation or a hormonal change triggers metaplasia (differentiation of coelomic epithelium to endometrial epithelium) Induction--this is a combination of transportation and formation in situ and is the most likely cause. The endometrium chemically induces undifferentiated mesenchyma to form endometrial epithelium Clinical Manifestation Dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation)-- Pain usually begins 5 to 7 days before menses reaches its peak and last for 2 to 3 days. It is less cramping and less concentrated in the abdominal midline than primary dysmenorrheal pain. Lower abdominal pain and in the vagina -- Pain to posterior pelvis and back Multiple tender nodules on uterosacral ligaments or in the rectovaginal system. They enlarge and become more tender during menses. Ovarian enlargement may also be evident. Other symptoms depend on the location of the ectopic tissue: Ovaries and oviducts--infertility and profuse menses Ovaries or cul-de-sac--deep-thrust dyspareunia (painful intercourse) Bladder--suprapubic pain, dysuria (painful or difficulty urinating), hematuria (Presence of blood in the urine) Rectovaginal septum and colon--painful defecation, rectal bleeding with menses, pain in the coccyx or sacrum Small bowel and appendix--nausea and vomiting, which worsen before menses, and abdominal cramps Cervix, vagina, and perineum--bleeding from endometrial deposits in these areas during menses Diagnostic Test Laparoscopy may confirm the diagnosis and determine the stage of the disease Barium enema rules out malignant or inflammatory bowel disease. Collaborative Management For young women who want to have children includes: androgens, such as danazol, which produce a temporary remission in Stages I and II. Oral contraceptives and progestins also relieve symptoms. Stage III and IV (when ovarian masses are present), they should be removed to rule out cancer. The patient may undergo conservative surgery, but the treatment of choice for women who don't want to bear children or who have extensive disease (StageIII and IV) is a total abdominal hysterectomy performed with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. UTERINE LEIOMYOMAS ( Myomas / Fibromyomas ) These neoplasms (tumor; any new and abnormal growth) art the most common benign tumors in women. They usually occur in the uterine corpus, although they may appear on the cervix or on the round or broad ligament. Cause / Risk Factors Uterine Leiomyomas are usually multiple and usually occur in women over age 35 They affect blacks three times more often than whites. The cause is unknown, but excessive levels of estrogen and human growth hormone (HGH) probably influence tumor formation by stimulating susceptible fibromuscular elements. Large doses of estrogen and the later stages of pregnancy increase both tumor size and HGH levels.
- 4. Medical and Surgical Nursing Lecture Notes on Female Reproductive System System Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R Abejo R.N, MAN Medical and Surgical Nursing Abejo4 When estrogen production decreases, uterine leiomyomas usually shrink or disappear (usually after menopause) Clinical Manifestation Pain Submucosal hypermenorrhea (excessive menstrual bleeding, but occurring at regular intervals and being of usual duration) Possibly other forms of abnormal endometrial bleeding Dysmenorrhea (abnormally painful menses) If tumor is large, the patient may develop a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen; Increasing pain Intestinal obstruction Constipation Urinary frequency or urgency Irregular uterine enlargement Diagnostic Test Blood studies/ anemia will support the diagnosis D&C (dilatation and curettage) Submucosal hysterosalpingoraphy - detects submucosal leiomyomas Laparoscopy - visualizes subserous leiomyomas on the uterine surface Collaborative Management Treatment of choice for women who desire to have children - A surgeon may remove small leiomyomas that have caused problems in the past or that appear likely to threaten a future pregnancy Tumors that twist or grow large enough to cause intestinal obstruction require a hysterectomy, with preservation of the ovaries if possible Pregnant patient: If a patient uterus no larger than a 6 month normal uterus by the 16th week of pregnancy, the outcome for the pregnancy remains favorable, and surgery is usually unnecessary. However if a pregnant woman has a leiomyomatous uterus the size of a 5 to 6 month normal uterus by the 9th week of pregnancy, spontaneous abortion will probably occur, especially with a cervical leiomyoma. If surgery is necessary, a hysterectomy is usually performed 5 to 6 months after delivery (when involution is complete), with preservation of the ovaries if possible Appropriate intervention depends on the severity of symptoms, the size and location of the tumors, and the patient's age, parity, pregnancy status, desire to have children, and general health. Call your doctor immediately if there is any abnormal bleeding or pelvic pain PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE (PID) Recurrent, acute, subacute, or chronic infection of the oviducts and ovaries, with adjacent tissue involvement. PID may refer to inflammation of the cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, which can extend to the connective tissue lying between the broad ligaments (parmetritis). Early diagnosis and treatment prevent damage to the reproductive system. Complications of PID may include potentially fatal septicemia, pulmonary emboli, shock and infertility. Untreated PID may be fatal. Clinical Manifestation Clinical features vary with the affected area. They may include profuse, purulent vaginal discharge Low-grade fever Malaise Lower abdominal pain Three Types of PID Salpingo-oophoritis (fallopian tubes, and ovaries): Acute: sudden onset of lower abdominal and pelvic pain, usually after menses, increased vaginal discharge fever malaise lower abdominal pressure and tenderness tachycardia pelvic peritonitis Chronic: recurring acute episodes Cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix): Acute- purulent, foul-smelling vaginal discharge; Vulvovaginitis, with itching or burning Red, edematous cervix Pelvic discomfort Sexual dysfunction Metrorrhagia; infertility; spontaneous abortion Chronic- cervical dystocia, laceration or eversion of the cervix, ulcerative vesicular lesion (when cervicitis results from herpes simplex virus type II) Endometritis (inflammation of the uterus): Acute- mucoopurulent or purulent vaginal discharge oozing from cervix Edematous, hyperemic endometrium, possible leading to ulceration and necrosis Lower abdominal pain and tenderness Fever Rebound pain Abdominal muscle spasm thrombophlebitis of uterine and pelvic vessels Chronic- recurring acute episodes (more common from multiple sexual partners and sexually transmitted infections) Cause / Risk Factors PID can result from infection with aerobic or anaerobic organisms. Any sexually transmitted infection More than one sex partner Conditions or procedures, such as cauterization of the cervix, that alter or destroy cervical mucus, allowing bacteria to ascend into the uterine cavity Any procedure that risks transfer of contaminated cervical mucus into the endometrial cavity by instrumentation such as use of a biopsy curet Infection during or after pregnancy Infectious foci within the body, such as drainage from a chronically infected fallopian tube Treatment: Effective management eradicates the infection, relieves symptoms, and avoids damaging the reproductive system. Aggressive therapy with multiple antibiotics begins immediately after culture specimens are obtained. Infection may become chronic if treated inadequately Supplemental treatment of PID may include bed rest, analgesics, and I.V. therapy Narcotics may be needed, NSAID's are preferred for pain relief. Development of a pelvic abscess requires adequate drainage. A ruptured pelvic abscess is a life-threatening condition. If this complication develops, the patient may need a total abdominal hysterectomy, with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy
- 5. Medical and Surgical Nursing Lecture Notes on Female Reproductive System System Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R Abejo R.N, MAN Medical and Surgical Nursing Abejo5 VAGINAL PROBLEMS Vaginitis Inflammation of the vagina Most common: Candida vaginitis (yeast infection): Studies shows approximately 75% of all women will have a yeast infection at least once in their lifetime. Some will suffer form recurring yeast infections. Vaginal yeast infections may cause pain during urination and or during sexual intercourse. Symptoms of yeast infection - itching, soreness and may have a white, cottage-cheese-like discharge. Bacterial vaginosis: For reasons unknown there may be a change in the balance of naturally occurring bacteria in the vagina that allows disease causing bacteria to dominate. It occurs commonly during reproductive years. Symptoms - Many women with this infection exhibit no symptoms, but the predominate sign of this condition is a fishy smelling gray discharge. Trichomonas vaginitis: (produces a refractory vaginal discharge and puritis) - causes itching and irritation of the vulva with increased vaginal discharge that may be green and frothy. Vaginismus: involuntary spastic constriction of the lower vaginal muscles, usually from fear of vaginal penetration. If severe, this disorder may prevent intercourse ( a common cause of unconsummated marriages). Vaginismus affects females of all ages and backgrounds. Patients usually experience muscle spasm with constriction and pain on insertion of any object into the vagina, such as a vaginal tampon, speculum or diaphragm. *Note - Vaginismus usually has a psychological origins. It occurs usually after sexual trauma such as rape or incest. Please seek counseling and see your doctor. Vaginal cancer: usually occurs primarily in women over the age of 50, vaginal cancer is very rare, studies shows approximately 2% of all gynecological cancers. Once cancer appears on the vagina, it may spread to surrounding tissues, including the bladder, rectum, vulva and the pubic bone. Diagnosis is made by your doctor with thorough examination with a colposcope and biopsy of any suspicious-looking areas. Vulvitis: Inflammation of the vulva. May cause itching, burning and or pain. Pelvic examination and blood test or tests to check for any STD ( sexually transmitted disease ) Symptoms: Vaginitis: Increased vaginal discharge with an offensive odor, burning, itching and pain Vaginal Cancer: Abnormal discharge and bleeding, firm lesion on any part of the vagina (possible cancer) Vaginismus: muscle constriction, spasm and pain on insertion of any object into the vagina Vulvitis: if your vulva is inflamed and itches Treatment: Your doctor will determine the course of treatment. Treatment for most vaginal disorders is aimed at maintaining proper bacterial balance and treating your irritation and discomfort. Bacterial vaginitis and trichomonas: Your doctor may prescribe a topical cream and or oral medication Vaginismus: Your doctor may want to refer you to a doctor who specialize in psychology, and or one who specialize in sexual therapy. Candida vaginitis (yeast infection) topical cream . PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME: Also called PMS -The effects of this disorder ranges from minimal discomfort to severe, disruptive behavioral and somatic changes. Symptoms usually appear 7 to 14 days before menses and usually subside with its onset. Cause: Direct cause unknown, PMS may result from a progesterone deficiency in the luteal phase ot the menstrual cycle or from an increased estrogen-progesterone ratio. Approximately 10% of patients with PMS have elevated prolactin levels Symptoms: Behavioral changes: Mild to severe personality changes Nervousness Hostility Irritability Agitation Sleep disturbance Fatigue Lethargy Depression Somatic changes : Breast tenderness or swelling Abdominal tenderness or bloating Joint pain Headache Edema Diarrhea or constipation Patient may also experience exacerbations of skin problems such as; ache - respiratory problems such as asthma, and neurologic problems such as seizures. Treatment: Treated symptomatically: treatment may include; Antidepressants, NSAID's (nonsteroidal anti- inflammatory drugs), Vitamins Tranquilizers Sedatives Progestins Treatment may require; a diet that is low in simple sugars, caffeine, and salt, with adequate amounts of protein, high amounts of complex carbohydrates, and possibly, vitamin supplements formulated for PMS There is also a self - help groups that exist for women with PMS check in your local area. MENOPAUSE: The mechanisms of menstruation cease to function. Menopause results from a complex, long term syndrome of physiologic changes, the climacteric-cause by declining ovarian function. Cause: Physiologic menopause, the normal decline in ovarian function caused by aging, begins in most women between ages 40 and 50 and results in infrequent ovulation, decreased menstruation, and eventually, cessation of menstruation ( usually ages 45 - 55)
- 6. Medical and Surgical Nursing Lecture Notes on Female Reproductive System System Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R Abejo R.N, MAN Medical and Surgical Nursing Abejo6 Pathologic menopause (premature menopause), the gradual or abrupt cessation of menstruation before age 40, cause unknown, however certain disorders, especially severe infections and reproductive tract tumors, may cause pathologic menopause by seriously impairing ovarian function. Other factors that may incur pathologic menopause include malnutrition, debilitation, extreme emotional stress, excessive radiation exposure, and surgical procedures that impair ovarian blood supply. Artificial menopause is the cessation of ovarian function following radiation therapy or surgical procedures. Symptoms: Declining ovarian function and decreased estrogen levels accompanying all forms of menopause produce various menstrual irregularities; Decrease in the amount and duration of menstrual flow Spotting Episodes of amenorrhea (absence or abnormal stoppage of menses) and polymenorrhea (abnormal frequent menstruation) (possible with hypermenorrhea)-excessive menstrual cycle These irregularities may last only a few months or may persist for several years before menstruation ceases permanently. Changes in the body's systems usually don't occur until after the permanent cessation of menstruation Reproductive system: changes may include; shrinkage of vulval structures and loss of subcutaneous fat, possible leading to atrophic vulvitis; atrophy of vaginal mucosa and flattening of vaginal rugae, possibly causing bleeding after coitus or douching; vaginal itching and discharge from bacterial invasion; and loss of capillaries in the atrophying vaginal wall, causing the pink, rugose lining to become smooth and white. Menopause may also produce excessive vaginal dryness and dyspareunia due to decreased lubrication from the vaginal walls, and decreased secretion from Bartholin's glands; a reduction in the size of the ovaries and oviducts; and progressive pelvic relaxation as the supporting structures of the reproductive tract lose their tone from the absence of estrogen Urinary system: Atrophic cystitis, resulting from the effects of decreased estrogen levels on bladder mucosa and related structures, may produce pus in the urine (pyuria), painful or difficulty urinating (dysuria), and urgency, and incontinence. May have on occasion have blood in the urine (hematuria) Breasts: Menopause may cause reduced breast size Integumentary system: Estrogen deprivation may lead to loss of skin elasticity and turgor. The patient may have slight alopecia (balding), and may experience loss of pubic and axillary hair. Autonomic nervous system: Hot flashes and night sweats. Patient may experience vertigo, syncope, tachycardia, dyspnea, tinnitus, emotional disturbances such as irritability, nervousness, crying spells, and fits of anger. Patients may also experience and exacerbation of preexisting neurotic disorders such as; depression, anxiety, and compulsive, manic, or schizoid behavior Vascular and musculoskeletal systems: Menopause may also induce atherosclerosis and osteoporosis. Artificial menopause, without estrogen replacement, produces symptoms within 2 to 5 years in 96% of women. Since menstruation in both pathologic and artificial menopause often ceases abruptly, severe vasomotor and emotional disturbances may result. Menstrual bleeding after 1 year of amenorrhea may indicate organic disease Treatment: Since physiologic menopause is a normal process, it may not require intervention. Atypical or adenomatous hyperplasia requires drug therapy Cystic endometrial hyperplasia doesn't require treatment If osteoporosis occurs, calcium is given Estrogen therapy Women who take estrogen must be monitored regularly to detect possible cancer early. If the uterus remains progestin is recommended in addition to estrogen. FEMALE NFERTILITY: Infertility may be caused by any defect or malfunction of the hypothalamic - pituitary - ovarian axis, such as certain neurologic diseases. Other possible cause include: Cervical factors, such as infection and possibly cervical antibodies that immobilize sperm Psychological problems Ovarian factors Tubal and peritoneal factors, such as tubal loss or impairment secondary to ectopic pregnancy Uterine abnormalities, such as; congenitally absent, double uterus; leiomyomas or Asherman's syndrome, in which the anterior and posterior uterine walls adhere because of scar tissue formation Approximately 15% of all couples in the US cannot conceive after regular intercourse for at least 1 year without contraception. 45 to 50% of all infertility is attributed to the female. Symptoms: Diagnosis requires a complete examination and health history. Questions includes patient's reproductive and sexual function, past diseases, mental state, previous surgery, types of contraception used in the past, and family history Treatment: Intervention aims to correct the underlying abnormality or dysfunction within the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian complex. Hormone therapy may be necessary in hyperactivity ;or hypoactivity of the adrenal or thyroid gland Progesterone replacement for progesterone deficiency Anovulation requires treatment with clomiphene citrate If mucus production decreases (an adverse effect of clomiphene citrate), small doses of estrogen may be given concomitantly to improve the quality of cervical mucus Surgical restoration may correct certain anatomic causes of infertility, such as fallopian tube obstruction Artificial insemination has proven to be an effective alternative strategy for dealing with infertility problems In vitro (test tube) fertilization has also been successful
