URINARY SYSTEM DRUGS.docx
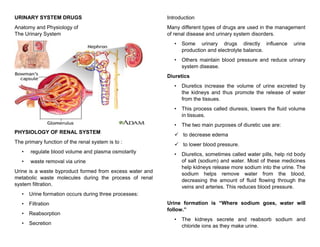
- 1. URINARY SYSTEM DRUGS Anatomy and Physiology of The Urinary System PHYSIOLOGY OF RENAL SYSTEM The primary function of the renal system is to : • regulate blood volume and plasma osmolarity • waste removal via urine Urine is a waste byproduct formed from excess water and metabolic waste molecules during the process of renal system filtration. • Urine formation occurs during three processes: • Filtration • Reabsorption • Secretion Introduction Many different types of drugs are used in the management of renal disease and urinary system disorders. • Some urinary drugs directly influence urine production and electrolyte balance. • Others maintain blood pressure and reduce urinary system disease. Diuretics • Diuretics increase the volume of urine excreted by the kidneys and thus promote the release of water from the tissues. • This process called diuresis, lowers the fluid volume in tissues. • The two main purposes of diuretic use are: to decrease edema to lower blood pressure. • Diuretics, sometimes called water pills, help rid body of salt (sodium) and water. Most of these medicines help kidneys release more sodium into the urine. The sodium helps remove water from the blood, decreasing the amount of fluid flowing through the veins and arteries. This reduces blood pressure. Urine formation is “Where sodium goes, water will follow.” • The kidneys secrete and reabsorb sodium and chloride ions as they make urine.
- 2. • Diuretics block the reabsorption of these ions, so the sodium has nowhere to go but out of the kidneys and into the urinary bladder. • Water then follows the sodium out of the kidneys and into the urinary bladder, and diuresis occurs. The Classes of Diuretics • Thiazides • Loop agent • Potassium-sparing diuretics, • Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors • Osmotics agent • Aldosterone antagonist • ADH antagonist Thiazides • Thiazides are diuretics that act directly on the distal convoluted tubules to block sodium reabsorption and promote chloride ion excretion. • Thiazides most often manage edema associated with congestive heart failure. • Oral administration of thiazides produces diuresis in all patients , with few documented side effects. This effect remains even with prolonged use, but long-term thiazide use does cause: • excessive potassium secretion • leading to hypokalemia (potassium deficiency) • cardiac dysfunction. To prevent hypokalemia suggest that potassium-rich diets or • potassium supplements accompany thiazide diuretics.
- 3. Loop diuretics • The loop of Henle, a U-shaped renal tubule, is the sodium-reabsorbing site that lends its name to this type of diuretic. • Loop diuretics influence the reabsorption action at the loop of Henle. Furosemide (Lasix, Disal, Diuride) and ethacrynic acid (Edecrin), two loop diuretics, are potent and effective drugs that block absorption of the following ions: • chloride, potassium, calcium, hydrogen, magnesium, and bicarbonate. The result of blocking reabsorption of all of these electrolytes is tremendous diuresis. The main side effects • Electrolyte imbalances, especially hypokalemia, which can lead to cardiac arrhythmias. • Parenteral administration produces diuresis immediately on a fully functional kidney. Potassium-Sparing Diuretics Drugs in this group are used as mild diuretics or in combination with other drugs. • Potassium-sparing diuretics are weaker diuretics than thiazides or loop • diuretics. • Potassium-sparing diuretics act on the distal convoluted tubules to promote sodium and water excretion and potassium retention. Mechanism of action : • Interfering the sodium-potassium pump that is controlled by aldosterone (a mineralocorticoid produced by the adrenal cortex that affects sodium and potassium levels). • Potassium is reabsorbed, and sodium is excreted. DRUGS In this category include spironolactone (Aldactone), • triamterene (Dyazide), and amiloride (Midamor). The main side effect of these drugs is hyperkalemia. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors • Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, such as acetazolamide (Diamox) and dichlorphenamide (Daranide), Mechanism of action : block the action of the enzyme “carbonic anhydrase.” This enzyme is used by the body to maintain acid- base balance (mainly between hydrogen and bicarbonate ions). Inhibition of this enzyme causes increased sodium, potassium, and bicarbonate excretion. The main side effect With prolonged use of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors can develop metabolic acidosis. Indication : mainly used to decrease intraocular pressure with open-angle glaucoma
- 4. Osmotic Diuretics • Mechanism of action : Osmotic diuretics increase the osmolality (concentration) of the filtrate in the renal tubules. This results in excretion of sodium, chloride, potassium, and water. Indication : use to prevent kidney failure, to decrease intracranial pressure, and to decrease intraocular pressure (i.e., glaucoma). Mannitol (Osmitrol and generic) and glycerin (Osmoglyn) are examples of osmotic diuretics. • Side effects are uncommon with osmotic diuretics, but can include fluid and electrolyte imbalance and vomiting. Nursing responsibilities • Administer drug with food or milk if GI upset is a problem to buffer drug effect on the stomach lining. • Administer intravenous diuretics slowly to prevent severe changes in fluid and electrolytes. • Administer oral form early in the day to prevent increased urination during sleep hours. • Monitor patient response to drugs through vital signs, weight, serum electrolytes and hydration to evaluate effectiveness of drug therapy. • Assess skin condition to determine presence of fluid volume deficit or retention. • Provide comfort measures (e.g. skin care, nutrition referral, etc.) to help patient tolerate drug effects. • Provide safety measures (e.g. adequate lighting, raised side rails, etc.) to prevent injuries. • Educate client on drug therapy to promote compliance. BLOOD PRESSURE LOWERING Drugs used to decrease hypertension, called antihypertensives The primary factor in hypertension is increased resistance to blood flow, resulting from the narrowing of peripheral blood vessels. If left untreated, elevated blood pressure are at risk for developing cardiac and renal dysfunction. Some drugs that affect blood pressure include the following : • Diuretics • Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACE Inhibitors) • Calcium Channel Blockers • Direct-Acting Arteriole Vasodilators • Beta-Adrenergic Antagonists • Alpha-Adrenergic Antagonists
- 5. Diuretics • Diuretics have an antihypertensive effect by promoting sodium and water loss, which causes a decrease in fluid volume and blood pressure. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACE Inhibitors) The kidneys regulate blood pressure via the renin- angiotensin system. Renin, an enzyme released by the kidneys, stimulates the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II (a potent vasoconstrictor). Angiotensin II causes the release of aldosterone (a mineralocorticoid from the adrenal cortex that promotes retention of sodium and water). Retention of sodium and water increases fluid volume, which elevates blood pressure. Mechanism of Action • ACE inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, which decreases aldosterone. Clinically, ACE inhibitors are used to treat hypertension. DRUGS : enalapril (Enacard, Vasitec), captopril (Capoten), lisinopril (Zestril), and benazepril (Lotensin) Calcium Channel Blockers Mechanism of Action : Calcium channel blockers block the influx of calcium ions into the myocardial cells Resulting in an inhibition of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle contractility. This decreased resistance to blood flow reduces blood pressure, thus affecting glomerular filtration. Side effects include hypotension and edema. Examples include diltiazem (Cardizem), verapamil (Isoptin), and nifedipine Procardia) Direct-Acting Arteriole Vasodilators Mechanism of Action : Direct-acting arteriole vasodilators relax smooth muscles of the blood vessels, mainly arteries, causing vasodilation.
- 6. The main side effect of this drug group is edema due to sodium and water retention. Examples include hydralazine (Apresoline) and minoxidil (Loniten). Beta-Adrenergic Antagonists Beta-adrenergic antagonists, also known as beta blockers, can affect the heart and bronchi. Beta-1 blockers work on the heart Beta-2 blockers work on the bronchial receptors. Mechanism of Action : Nonselective beta blockers will inhibit the activity of beta-1 and beta-2 receptors, resulting in bradycardia and bronchoconstriction. Side effects include decreased blood pressure, decreased cardiac output, and bronchospasm. An example of a nonselective beta blocker is propranolol (Inderal®). Nursing responsibilities • Educate patient on importance of healthy lifestyle choices which include regular exercise, weight loss, smoking cessation, and low-sodium diet to maximize the effect of antihypertensive therapy. • Monitor blood pressure and heart rate and rhythm closely to evaluate for effectiveness and ensure quick response if blood pressure falls rapidly or too much. • Provide comfort measures for the patient to tolerate side effects (e.g. small frequent meals for nausea, limiting noise and controlling room light and temperature to prevent aggravation of stress which can increase demand to the heart, etc.) • Monitor patient for any manifestations that could decrease fluid volume inside the body (e.g. vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, etc.) to detect and treat excessive hypotension. • Educate patient and family members about drug’s effect to the body and manifestations that would need reporting to enhance patient knowledge on drug therapy and promote adherence. • Emphasize to the client the importance of strict adherence to drug therapy to ensure maximum therapeutic effects. Urolithiasis • Urolithiasis—the formation of stones (calculi) in the kidney, bladder, and/or urethra—is increasingly common, with a rate of approximately 12% worldwide, and it is associated with an enhanced risk of end-stage renal disease. The most common form of kidney stone is calcium oxalate (CaOx) on the renal papillary surface. UROLITH TREATMENT Uroliths (also known as urinary calculi) are abnormal mineral masses in the urinary system. Uroliths are composed of a large amount of crystalline material (organic and inorganic crystalloids) and a small amount of organic matrix (typically mucoid material).
- 7. Overview The development of urolith formation is not fully understood, but dietary factors are known to be important in some cases. Uroliths in the urinary bladder cause hematuria (blood in the urine) and dysuria. Uroliths that lodge in the urethra may cause obstruction, which is a major concern because of the narrow diameter of the urethra. Treatment Antibiotic therapy (if warranted) Medical dissolution of the uroliths Surgical removal of the uroliths. Medical dissolution of uroliths • Dissolution therapy aims to dissolve stones through administration of oral agents to by direct chemolysis through renal irrigation. Uroliths that form in alkaline (basic) urine (struvite uroliths) Place in urine-acidifying diet that dissolves uroliths Prescribed urinary acidifiers such as methionine (Methio-tabs, Methigel) and ammonium chloride (Uroeze). Once the uroliths are dissolved or removed, s are then maintained on diets that produce acid urine. Uroliths that form in acid urine (calcium oxalate, cystine, and ammonium urate uroliths) Place in urine-alkalinizing diets Urinary alkalinizers such as potassium citrate (Urocit-K) and sodium bicarbonate (generic). Patient with renal disease should not be given acidifying diets or prescribed urinary-acidifying drugs. Some uroliths, such as ammonium urate uroliths, also indicate the need for a low-protein, low-purine, low oxalate diet to prevent recurrence. Patient with ammonium urate uroliths are also often prescribed xanthine oxidase inhibitors. • This group of drugs decreases the production of uric acid.
- 8. • Decreasing uric acid production helps prevent the formation of ammonium urate uroliths. • Allopurinol (Zyloprim, Lopurin) is an example of a xanthine oxidase inhibitor. Side effects of allopurinol use are rare. URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the loss of voluntary control of micturition (a two stage process involving the passive storage of urine and the active voiding of urine). Urinary incontinence can be divided into two main categories: 1. Disorders due to neurologic disorders 2. Nonneurologic disorders. Neurologically Caused Incontinence Cholinergic agonists (parasympathomimetic agents) are used to treat patients with ―spinal cord bladders‖—that is, damage to the nerves that control relaxation of the urinary bladder outflow sphincters. This nerve damage results in the retention of urine. Mechanism of Action : The cholinergic agonist binds to the receptors on smooth muscles, allowing sodium and calcium to enter the cells. Pharmacokenitics • Cholinergic agonists promote voiding of urine from the urinary bladder. • These drugs simulate the action of acetylcholine by direct stimulation of cholinergic receptors. • This influx of sodium and calcium in turn allows muscle contraction. • Tone of the detrusor muscle of the urinary bladder is increased, which may increase detrusor muscle contractions. Drugs An example of a cholinergic agonist is bethanechol (Urecholine, Duvoid, Urabeth). Side effects include: GI signs such as vomiting and diarrhea. Neurologically Caused Incontinence Anticholinergics (parasympatholytic drugs) are used to treat urinary incontinence by promoting urine retention in the urinary bladder. Mechanism of Action : blocking the binding of acetylcholine to its receptor sites and thereby causing muscle relaxation. Anticholinergics. These medications can calm an overactive bladder and may be helpful for urge incontinence. Examples include oxybutynin (Ditropan XL), tolterodine (Detrol), darifenacin (Enablex),
- 9. fesoterodine (Toviaz), solifenacin (Vesicare) and trospium chloride. Mirabegron (Myrbetriq). • Mirabegron (Myrbetriq). Used to treat urge incontinence, this medication relaxes the bladder muscle and can increase the amount of urine your bladder can hold. It may also increase the amount you are able to urinate at one time, helping to empty your bladder more completely. Alpha blockers. • Alpha blockers. In men who have urge incontinence or overflow incontinence, these medications relax bladder neck muscles and muscle fibers in the prostate and make it easier to empty the bladder. Examples include tamsulosin (Flomax), alfuzosin (Uroxatral), silodosin (Rapaflo), and doxazosin (Cardura). Topical estrogen • Topical estrogen. Applying low-dose, topical estrogen in the form of a vaginal cream, ring or patch may help tone and rejuvenate tissues in the urethra and vaginal areas. Neurologically Caused Incontinence • Adrenergic antagonists are divided into alpha and beta categories. • Indication : Beta-adrenergic antagonists, used in the treatment of hypertension. • Alpha-adrenergic antagonists are used to decrease the tone of internal urethral sphincters; they are useful in the treatment of decreased urinary tone due to overdistention of the urinary bladder. Mechanism of Action • Mechanism of Action : Alpha-adrenergic antagonists work by blocking circulating epinephrine or norepinephrine from binding to their receptors. These drugs are also used to decrease blood pressure. Examples of alpha-adrenergic antagonists include phenoxybenzamine • (Dibenzyline), prazosin (Minipress), and nicergoline (Sermion). The main side effect of these drugs is weakness due to decreased blood pressure.