Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Recommended
Author: Ian BennettThe Contribution of Health Literacy to Disparities in Self Related Health Sta...

The Contribution of Health Literacy to Disparities in Self Related Health Sta...Leonard Davis Institute of Health Economics
Presented on during my dietetic internship at Mount Sinai Hospital Incorporating Psychology into Dietetics Practice in the Head & Neck Cancer Po...

Incorporating Psychology into Dietetics Practice in the Head & Neck Cancer Po...Claudia Gonzalez MS, RD
More Related Content
What's hot
Author: Ian BennettThe Contribution of Health Literacy to Disparities in Self Related Health Sta...

The Contribution of Health Literacy to Disparities in Self Related Health Sta...Leonard Davis Institute of Health Economics
Presented on during my dietetic internship at Mount Sinai Hospital Incorporating Psychology into Dietetics Practice in the Head & Neck Cancer Po...

Incorporating Psychology into Dietetics Practice in the Head & Neck Cancer Po...Claudia Gonzalez MS, RD
What's hot (17)
2o C Parte 3 Primary Prevention Mental Health Programs

2o C Parte 3 Primary Prevention Mental Health Programs
The Contribution of Health Literacy to Disparities in Self Related Health Sta...

The Contribution of Health Literacy to Disparities in Self Related Health Sta...
A Population-Based Study of Body Mass Index and Physical Activity Disparitie...

A Population-Based Study of Body Mass Index and Physical Activity Disparitie...
Incorporating Psychology into Dietetics Practice in the Head & Neck Cancer Po...

Incorporating Psychology into Dietetics Practice in the Head & Neck Cancer Po...
Easing Depression May Boost Heart Health, Study Finds

Easing Depression May Boost Heart Health, Study Finds
Engagement Is Everything, How To Apply Psychology to Improve Digital Experien...

Engagement Is Everything, How To Apply Psychology to Improve Digital Experien...
Similar to PAS 17 Readines
Similar to PAS 17 Readines (20)
R E S E A R C H A R T I C L ERelationship Between Frequenc.docx

R E S E A R C H A R T I C L ERelationship Between Frequenc.docx
Child Abuse and Addiction in Obesity_ crimson Publishers

Child Abuse and Addiction in Obesity_ crimson Publishers
Risks and Strategies Associated with Psychoactive Drugs Use and Young People

Risks and Strategies Associated with Psychoactive Drugs Use and Young People
Calculation of dose in pediatrics by syeda shiza aleem

Calculation of dose in pediatrics by syeda shiza aleem
Assessment 7 Course Textbook Edberg, M. (2015). Essentials .docx

Assessment 7 Course Textbook Edberg, M. (2015). Essentials .docx
1ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY FOR SEDENTARY LIFESTYLESTHESE ARE.docx

1ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY FOR SEDENTARY LIFESTYLESTHESE ARE.docx
PAS 17 Readines
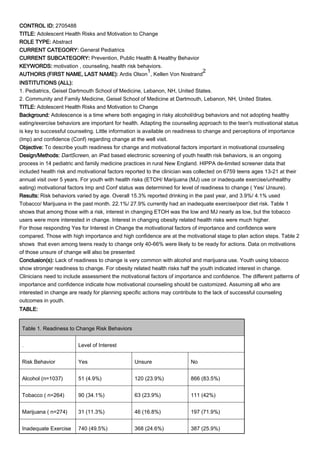
- 1. CONTROL ID: 2705488 TITLE: Adolescent Health Risks and Motivation to Change ROLE TYPE: Abstract CURRENT CATEGORY: General Pediatrics CURRENT SUBCATEGORY: Prevention, Public Health & Healthy Behavior KEYWORDS: motivation , counseling, health risk behaviors. AUTHORS (FIRST NAME, LAST NAME): Ardis Olson 1 , Kellen Von Nostrand 2 INSTITUTIONS (ALL): 1. Pediatrics, Geisel Dartmouth School of Medicine, Lebanon, NH, United States. 2. Community and Family Medicine, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Lebanon, NH, United States. TITLE: Adolescent Health Risks and Motivation to Change Background: Adolescence is a time where both engaging in risky alcohol/drug behaviors and not adopting healthy eating/exercise behaviors are important for health. Adapting the counseling approach to the teen's motivational status is key to successful counseling. Little information is available on readiness to change and perceptions of importance (Imp) and confidence (Conf) regarding change at the well visit. Objective: To describe youth readiness for change and motivational factors important in motivational counseling Design/Methods: DartScreen, an iPad based electronic screening of youth health risk behaviors, is an ongoing process in 14 pediatric and family medicine practices in rural New England. HIPPA de-limited screener data that included health risk and motivational factors reported to the clinician was collected on 6759 teens ages 13-21 at their annual visit over 5 years. For youth with health risks (ETOH/ Marijuana (MJ) use or inadequate exercise/unhealthy eating) motivational factors Imp and Conf status was determined for level of readiness to change ( Yes/ Unsure). Results: Risk behaviors varied by age. Overall 15.3% reported drinking in the past year, and 3.9%/ 4.1% used Tobacco/ Marijuana in the past month. 22.1%/ 27.9% currently had an inadequate exercise/poor diet risk. Table 1 shows that among those with a risk, interest in changing ETOH was the low and MJ nearly as low, but the tobacco users were more interested in change. Interest in changing obesity related health risks were much higher. For those responding Yes for Interest in Change the motivational factors of importance and confidence were compared. Those with high importance and high confidence are at the motivational stage to plan action steps. Table 2 shows that even among teens ready to change only 40-66% were likely to be ready for actions. Data on motivations of those unsure of change will also be presented Conclusion(s): Lack of readiness to change is very common with alcohol and marijuana use. Youth using tobacco show stronger readiness to change. For obesity related health risks half the youth indicated interest in change. Clinicians need to include assessment the motivational factors of importance and confidence. The different patterns of importance and confidence indicate how motivational counseling should be customized. Assuming all who are interested in change are ready for planning specific actions may contribute to the lack of successful counseling outcomes in youth. TABLE: Table 1. Readiness to Change Risk Behaviors . Level of Interest Risk Behavior Yes Unsure No Alcohol (n=1037) 51 (4.9%) 120 (23.9%) 866 (83.5%) Tobacco ( n=264) 90 (34.1%) 63 (23.9%) 111 (42%) Marijuana ( n=274) 31 (11.3%) 46 (16.8%) 197 (71.9%) Inadequate Exercise 740 (49.5%) 368 (24.6%) 387 (25.9%)
- 2. (n=1495) Poor Diet ( n=1888) 936 ( 49.6%) 436 (23.1%) 516 (27.3%) Table 2. Motivational Status, Importance by Confidence . Low Confidence High Confidence Alcohol Use n=50 Low Importance 10% 20% High Importance 4% 66% Tobacco Use n=90 Low Importance 15.6% 27.8% High Importance 16.7% 40% Marijuana Use n=29 Low Importance 13.7% 6.9% High Importance 17.2% 62.1% Inadequate Exerice n=738 Low Importance 21.7% 15.9% High Importance 20.6% 41.9% Poor Diet n=933 Low Importance 16.8% 14.9% High Importance 16.4% 51.9% Low Importance 1-6, High Importance 7-10 Low Confidence 1-6, High Confidence 7-10 (No Image Selected) Content Type Expertise: Clinical Care Updates, Health Services/Clinical Outcomes Research, Population Health/Global/Social determinants of Health APA SIG Comm Region: None of These Sabbath Conflict: No Conflict First Author Trainee?: No, Not a Trainee AWARDS: