Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Respiratory System - Human Anatomy and Physiology bPharm

Respiratory System - Human Anatomy and Physiology bPharm
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (20)
Similar to Pathway of blood
Similar to Pathway of blood (20)
A red blood cell enters the right atrium from the superior vena cava..pdf

A red blood cell enters the right atrium from the superior vena cava..pdf
Describe the pathway of blood as it flows from the Right atrium to t.pdf

Describe the pathway of blood as it flows from the Right atrium to t.pdf
More from Michael Wrock
More from Michael Wrock (20)
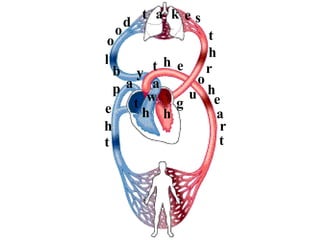
Pathway of blood
- 1. t h e p a t h w a y b l o o d t a k e s t h r o u g h t h e h e a r t
- 2. t h e p a t h w a y b l o o d t a k e s t h r o u g h t h e h e a r t
- 3. t h e p a t h w a y b l o o d t a k e s t h r o u g h t h e h e a r t
- 4. t h e p a t h w a y b l o o d t a k e s t h r o u g h t h e h e a r t
- 5. A Quick Look at the Anatomy of the Heart
- 6. An Overview of Today:
- 7. Deoxygenated (“ blue ”) (1) blood returns to the right atrium ( 2) via three major blood vessels. These are the: 1. Superior Vena Cava (3 ) – returns venous blood to the heart from the “upper” body 2. Inferior Vena Cava (4 ) – returns venous blood to the heart from the “lower” body 3. Coronary Sinus (5 ) – returns venous blood to the heart from the heart. 3 4 (opening of coronary sinus) 5 2
- 8. Deoxygenated blood then passes from the right atrium through the “three-flapped” atrioventricular or tricuspid valve (6) and into the right ventricle (7) . S.V.C. I.V.C. C.S. R.A. 6 7
- 9. The right ventricle contracts vigorously to pump the deoxygenated blood out through the pulmonary semilunar valve (8) and into a large artery called the pulmonary trunk (9) . T.V. R.V. 8 9
- 10. The pulmonary trunk immediately branches to form the left and right pulmonary arteries (10) . These arteries carry the deoxygenated blood away from the heart and to the alveoli of the lungs (11) . P.T. P.S.V from heart to heart 11 (alveolus) 10 10
- 11. ox. blood Deox. blood from heart to heart 12 In the capillary network (12) of the lungs the deoxygenated blood exchanges (13) its load of carbon dioxide (14) for a fresh supply of oxygen (15) . The blood then is termed oxygenated (“ red ”) (16) blood.
- 12. As the oxygenated blood exits the capillary network of the lungs, it enters the left & right pulmonary veins (17) which carry the oxygenated blood away from the lungs and back to the left atrium (18) of the heart. S.V.C. I.V.C. R.A. C.S. T.V. R.V. P.S.V P.T. 17 17 18
- 13. Oxygenated blood then passes from the left atrium through the “two-flapped” atrioventricular or bicuspid valve (19) , also called the mitral valve (20) , and into the left ventricle (21) . R.P.A. L.P.A. 19, 20 21
- 14. The left ventricle, which is the most muscularly walled chamber of the heart, vigorously contracts in a “twisting” motion to force the oxygenated blood through the aortic semilunar valve (22) and into the largest artery of the body, the ascending aorta (23) . R.P.V. L.A. L.P.V. B.V. 22 23
- 15. From the aorta the oxygenated blood is delivered to all areas of the “ body ” (24) (the exception being the lungs, of course).