Toxicokinetics toxicology pre-clinical pharmacology
- 1. TOXICOKINETICS Mr Dilip N Kawane M Pharm (Pharmacology)
- 2. Toxicokinetics(TK) is defined by the ICH as ‘the generation of pharmacokinetic data, either as an integral component in the conduct of non-clinical toxicity studies or in specially designed supportive studies, to assess systemic exposure. While developing a molecule as a therapeutic agent researchers consider not only benefit but also risk associated with it. Hence toxicological evaluation got more importance in drug development stages especially in preclinical stage. Theoretical approach development of pharmacokinetic models that predict drug disposition after drug administration. (Mathematics and computer Techniques are heavily utilized). Experimental approach development of biologic sampling techniques, analytical methods for the measurement of drugs and metabolites, procedures that facilitate data collection and manipulation. The study of Toxicokinetics
- 3. Toxicokinetics (TK) is generation of kinetic data for systemic exposure and toxicity assessment of the drug. These studies help us to estimate the observed toxicity to that dose. TK evaluation is very important in drug development phase in both regulatory and scientific perspective. There are several guidelines to conduct TK study in animals recommended by regulatory bodies (OECD). Toxicokinetics evaluation is useful in Selection of dose Dosing form Alternative dosing route Evaluation of toxicological mechanism Reduces the animal number Also used for the setting safe dose level in clinical phases
- 4. On the other hand, TK data are practically used for the purpose of drug discovery such as lead-optimization and candidate-selection. The primary objective of the toxicokinetics studies is, • To describe the systemic exposure achieved in animals and its relationship to dose level and the time course of the toxicity study . • Exposure data in animals should be evaluated before human clinical trials. • Choice of species and treatment regimen used in non clinical studies . • Information on systemic exposure of animals during repeated-dose toxicity studies is essential for the interpretation of study results, to the design of subsequent studies and to the human safety assessment.
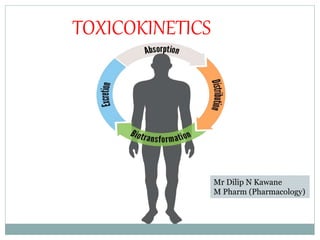
- 5. A.Toxicokinetics i) Absorption • Transfer of chemicals from the gut lumen, lungs, or skin into the general circulation involves movement across cell membranes, and simple passive diffusion of the unionized molecule, down a concentration gradient is the most important mechanism. Absorption is the process by which the chemical enters the body. It depends on the route of administration. • Oral route – the GIT is the most important route of absorption, as most acute poisonings involve ingestions. • Dermal route – lipid solubility of a substance is an important factor affecting the degree of absorption through the skin.
- 6. • Inhalational route – toxic fumes, particulate and noxious gases may be absorbed through the lungs. Bioavailability • is the fraction of unchanged drug reaching the systemic circulation following of non-vascular administration. Therefore, a portion of the chemical fails to reach the systemic circulation in original form after oral administration. Extent of absorption • It is often useful to determine how much of the toxicant actually penetrates the membrane barriers (e.g skin or GIT) and gets into the blood stream. • The area under the curve (AUC) of the concentration- time profiles for oral or dermal routes is compared with the AUC for IV ROA.
- 7. ii) Distribution • Distribution-is defined as the apparent volume into which a substance is distributed. Volume of distribution (Vd) is calculated from the dose taken and the resulting plasma concentration: Vd = dose /plasma concentration • The importance of volume of distribution in toxicology is, - Predicting peak blood concentration of the chemical taken - Calculating the amount of substance in the body to verify the quantity ingested - Deciding whether to apply systemic toxin elimination technique.
- 8. • Factors determining the rate of distribution of chemicals in the body are I. Protein binding – chemicals highly bound to protein have small volume of distribution II. Plasma concentration – when the volume of distribution of chemicals is small, most of the chemical remains in the plasma III. Physiological barriers – chemicals will not uniformly distributed to the body due to specialized barriers e.g blood brain barrier.
- 9. iii) Biotransformation (metabolism) • Biotransformation is the biochemical transformation of a chemical. • It is a process by which the body transforms a chemical and makes it more water soluble so the chemical can be eliminated more rapidly via the kidney into the urine. • Biotransformation can produce metabolites that are pharmacologically active and toxic. E.g. parathion→ parathoxon (toxic metabolite). Liver is the major site of biotransformation for many chemicals & other organs that are involved are lungs, kidneys, skin &so on. Interactions during biotransformation include
- 10. • There are two phases of biotransformation • Phase I – the drug is converted into more polar compound e.g oxidation, reduction, &hydrolysis • Phase II (conjugation) – a drug or its metabolite is conjugated with an endogenous substance e.g glucuronide conjugate • Enzyme inhibition- by this the biotransformation of drugs is delayed & is a cause of increased toxicity • Enzyme induction- by this the biotransformation of drugs is accelerated & is a cause of therapeutic failure.
- 11. • First – pass effect – is the biotransformation of some chemicals by the liver during the initial pass from the portal circulation after oral administration. • Half life (t ½) –is the time required to reduce the blood concentration of the chemical to half.
- 12. IV) Excretion - Excretion is the final means of chemical elimination, either as metabolites or unchanged parent chemical. - Excretion through the lungs is the major route for gaseous substances; and in the case of non-volatile water – soluble drugs, the kidneys are the most important routes of excretion. - Additional routes include sweat, saliva, tears, nasal secretions, milk, bile and feces - Excretion is a major determinant of the potential toxicity of a foreign chemical, rapid excretion → less toxicity
- 13. • The kidney is a major route of excretion and it functions to excrete body wastes and toxic chemicals. • Many chemicals have to be biotransformed to more water- soluble products before they can be excreted in the urine. • Kidney damage (chemicals, infections, age)→ reduced excretion-----------toxicity.
- 14. • Clearance – elimination of chemicals from the body may be described by the term clearance (CL). It is a quantitative measure of the volume of blood cleared of drug per unit time,usually expressed in milliliter per 4 minute. • Clearance is calculated as follows CL = 0.7 (VD)/ (t1/2) = ml/min Where the VD is expressed in milliliter per kilogram & the half-life is expressed in minutes or hours. Repeated exposure--- -------- accumulation (increased toxicity) (Kidney damage, liver damage, infants, elderly)
- 15. • Certain points regarding the toxicokinetics of toxic agents; Drug absorption after a toxic ingestion may be delayed and prolonged; The half-life and total body clearance are often lengthened; Liver-metabolizing enzymes may become saturated, slowing hepatic elimination; Chemicals with large volumes of distribution are often highly tissue-bound and measures to enhance their elimination are not effective; Poor perfusion of the liver and kidneys secondary to the toxic effects of the substance may slow clearance.
- 16. IMPORTANCE OF TOXICOKINETICS: Toxicokinetics evaluation is important in drug development stages. TK data is important to know the toxic response(s) to that of drug exposure obtained in drug development stages (preclinical). To set safe dose for clinical use of new drugs. Useful in the understanding of differences in responses or sensitivity between individual animals, genders, species or life stages, and supporting the extrapolation of findings in experimental animals to humans.
- 17. Kinetic data can also support mode-of action analysis and extrapolation across exposure routes. Now a day toxicokinetics used in other areas also with other areas of pharmacokinetics. Measuring drug levels in non plasma samples (tissues, urine and bile). It helps in optimizing the dosage regimen for individual patients. It helps in explaining the drug interactions. It helps in determining the influence of altered physiology on drug ADME.
- 18. Importance of toxicokinetics Drug Development Formulation Development Deciding Dosage Regimen Designing Rational Dose, Frequency and Duration Rational Drug Design (QSPKR) Clinical Pharmacy ADME study, Bioavailability and Bioequivalence studies In Vitro –In Vivo correlation studies Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics Relationship
- 19. Importance of saturation kinetics Drugs that demonstrate saturation kinetics usually show the following characteristics: 1. Elimination of drug does not follow simple first-order kinetics that is, elimination kinetics are nonlinear. 2. The elimination half-life changes as dose is increased. Usually, the elimination half-life increases with increased dose due to saturation of an enzyme system. 3. The area under the curve (AUC) is not proportional to the amount of bioavailable drug. 4. The saturation of capacity-limited processes may be affected by other drugs that require the same enzyme or carrier-mediated system (ie,competition effects). 5. The composition and/or ratio of the metabolites of a drug may be affected by a change in the dose.
- 20. ALTERNATIVE METHOD TO ANIMAL TOXICITY TESTING Alternative test methods are test methods that reduce, refine and replace animal use. Reduction, refinement, and replacement are commonly referred to as “the 3Rs (4Rs includes Rehabilitation) of alternatives”. The concept of 3Rs was first proposed by William Russell and Rex Burch in the “Principles of Humane Experimental Technique”.
- 21. Alternatives to animal testing are the development and implementation of test methods that avoid the use of live animals. Human biochemistry, physiology, pharmacology, and endocrinology and toxicology has been derived from animal models. 10 to 100 millions of animals are using for experimentation in a year Animals used experimentation distributed among zebra-fish to Primates Vast majority of animals are sacrificed at end of research programme
- 22. 1R= Replacement of test animals 2R=Refinement ( better tests) 3R=Reduction ( decrease of the number of animals) 4R=Responsibility ( tests scientifically acceptable)
- 23. a. Using of living system In vitro Techniques Invertebrates Animals Micro-organisms b. Using Non-living systems Chemical Technique Physical/Mechanical Systems c. Use of computer simulation These principles are now followed in many testing establishments worldwide. A. Replacement Refers to the preferred use of non-animal methods over animal methods whenever it is possible to achieve the same scientific aim.
- 24. B. Reduction Refers to methods that enable researchers to obtain comparable levels of information from fewer animals, or to obtain more information from the same number of animals. A. Animal Sharing B. Improved Statistical C. Phylogenetic Reduction D. Better Quality Animal E. Post-Marketing Surveillance F. Autopsies and Biopsies G. Epidemiological Studies
- 25. C. Refinement refers to methods that alleviate or minimize potential pain, suffering, or distress, and enhance animal welfare for the animals used. a) Decreased Invasiveness b) Improved Instrumentation c) Improved Control Pain d) Improved Control of techniques
- 26. Globalization of R- concept Dr. David B. Morton, expanded this concept to the Fifteen R's :- 1. Reduce the number used. 2. Refine end points and procedures. 3. Replace with in vitro, ex vitro methods when possible. 4. Respect all animals regardless of species. 5. Recognize any adverse effects. 6. Relieve pain with analgesics, distress with anxiolytics. 7. Refuse to carry out some procedures if concerned. 8. Reconsider protocol if unsure. 9. Read about the science and the ethical issues. 10.Reflect on the work you have carried out. 11.Reason out why you are doing the research 12.Record all your observations carefully. 13.Reward rather than cause harm and for happiness. 14.Reappraise techniques for efficacy. 15.Resolve to learn new techniques.
- 27. ACCORDING TO OECD 1. Complete replacement of the animal experiment • TG 428 Skin absorption: in vitro method • TG 430 In vitro skin corrosion: transcutaneous electrical resistance (TER) • TG 431 In vitro skin corrosion: human skin model test • TG 432 In vitro 3T3 NRU photo toxicity test • TG 437 Bovine corneal opacity and permeability test method for identifying ocular corrosives and severe irritants • TG 438 Isolated chicken eye test method for identifying ocular corrosives and severe irritants • TG 439 In vitro skin irritation: reconstructed human epidermis (RhE) test method
- 28. 2. Reduction in the number of animals and stress of the laboratory animals • TG 420 Acute oral toxicity—fixed dose procedure • TG 423 Acute oral toxicity—acute toxic class method • TG 425 Acute oral toxicity—up-and-down procedure • TG 429 Skin sensitization—local lymph node assay • TG 436 Acute inhalation toxicity—acute toxic class method
- 29. Animal Models • Animal Testing alternative (s) • In vitro (method, model, technique) • Non-animal alternative (s) Cell Culture Tissue Culture Organ Culture • Single-cell Organisms Invertebrates • Fish • Simulator (s) • Mannequin (s) • Mathematical Model (s) • Computer-interfaced Interactive Digital Image Libraries Virtual Surgery Virtual Reality • Computer simulation (s) Computer program (s) Computer Software Computer Aided Instruction • Physiological Simulation (s) Videodisc (s) Video display ALTERNATIVE METHOD TO ANIMAL TOXICITY TESTING
- 30. The use of animals can be further subdivided according to the degree of suffering •Minor animal suffering: Observing animals in behavioural studies, single blood sampling, immunization without adjutants, etc. •Moderate animal suffering: Repeated blood sampling, recovery from general anaesthesia, etc. • Severe animal suffering: LD50% test, starvation vaccine potency tests, etc.
- 31. 1. Cell culture and tissue engineering I. Skin corrosion and skin irritation II. Skin absorption III.Phototoxicity 2. Human-based I. Skin irritation II. Pyrogenicity III.Modular immune in vitro construct 3. Computer simulation 4. Medical imaging 5. Microfluidic Chip 5. Fungal model for mammalian drug metabolism 6. Future alternatives I. Organs on a chip II. Human toxome
- 32. TISSUE CULTURE • In vitro cultivation of organs, tissues & cells at defined temperature using an incubator & supplemented with a medium containing cell nutrients & growth factors is collectively known as tissue culture • Different types of cell grown in culture includes connective tissue elements such as fibroblasts, skeletal tissue, cardiac, epithelial tissue (liver, breast, skin, kidney) and many different types of tumor cells. Common cell lines Human cell lines • -MCF-7 breast cancer • HL 60 Leukemia • HEK-293 Human embryonic kidney • HeLa Henrietta lacks
- 33. Primate cell lines • Vero African green monkey kidney epithelial cells • Cos-7 African green monkey kidney cells • And others such as CHO from hamster, sf9 & sf21 from insect cells • Skin irritation & skin corrosion refers to localized topical exposure of the skin to a substance • EpiDerm , Mattek , EpiSkin and Skin Ethic RHE are derived from human skin cells which cultured to Produce human skin model • In 2010 august OECD published test guidelines 439 : for irritant chemicals
- 34. Skin absorption test The test substance is applied to the surface of an excised skin sample in a diffusion cell. Skin from human or animal sources can be used. Although viable skin is preferred, non-viable skin can also be used. Phototoxicity Phototoxicity is a rash, swelling or inflammation, like a severe sunburn. the 3T3 Neutral Red Uptake (NRU) Phototoxicity Test,. HeLa cells An immortal cell line used in oncological research derived from cervical cancer cells
- 35. ENDOTHELIAL CELLS : study of natural anticoagulation novel in vitro EC culture system allows for the screening of endothelial protectants effect of substances this model also mimic xenotransplantation. Simulation of stroke related Damage in cultured human nerve cells • 2 types of cells : Ntera2 and NT2 • focuses on neuronal cell biology , suitable for screening neuroprotective drugs • It has potential to replace lab.animal in basic stroke research Permanent fish cell culture as imp tool in ecotoxicology PLHC-1 and RTG-2 cell culture for ecotoxicological tests , screening
- 36. parasite cyst in cultured cells : N.caninum oocyst which enables generate all stages of this parasite Render animal model reductant Aggregating brain cell cultures : these are 3 dimensional primary cell culture ,study of neuro- degenerative drugs Study of angiogenesis : heart of rat n mouse . For screening , Mouse kupffer call line : to study diseased condition with microbes, liver transplantation , tumours , drug delivery
- 37. II. In-silico methods in Drug Discovery A. Molecular docking B. Virtual High through put screening. C. QSAR (Quantitative structure-activity relationship) D. Pharmacophore mapping A. Molecular Docking RL • Docking is the computational determination of binding affinity between molecules (protein structure and ligand). • Given a protein and a ligand find out the binding free energy of the complex formed by docking them.
- 38. B. Virtual High through put screening. 1. Receptor based methods-make use of the structure of the target protein. 2. Ligand based methods-based on the known inhibitors 1. Receptor based methods •Uses the 3D structure of the target receptor to search for the potential candidate compounds that can modulate the target function. •These involve molecular docking of each compound in the chemical database into the binding site of the target and predicting the electrostatic fit between them. •The compounds are ranked using an appropriate scoring function such that the scores correlate with the binding affinity. •Receptor based method has been successfully applied in many targets
- 39. 2. Ligand based strategy • In the absence of the structural information of the target, ligand based method make use of the information provided by known inhibitors for the target receptor. • Structures similar to the known inhibitors are identified from chemical databases by variety of methods, • Some of the methods widely used are similarity and substructure searching, pharmacophore matching or 3D shape matching. • Numerous successful applications of ligand based methods
- 40. C. QSAR • QSAR is statistical approach that attempts to relate physical and chemical properties of molecules to their biological activities. • Various descriptors like molecular weight, number of rotatable bonds LogP etc. are commonly used. • Many QSAR approaches are in practice based on the data dimensions. • It ranges from 1D QSAR to 6D QSAR
- 41. D. Pharmacophore mapping • It is a 3D description of a pharmacophore, developed by specifying the nature of the key pharmacophoric features and the 3D distance map among all the key features. • A Pharmacophore map can be generated by superposition of active compounds to identify their common features. • Based on the pharmacophore map either de novodesign or 3D database searching can be carried out.
