17-INCIDENT INVESTIGATION
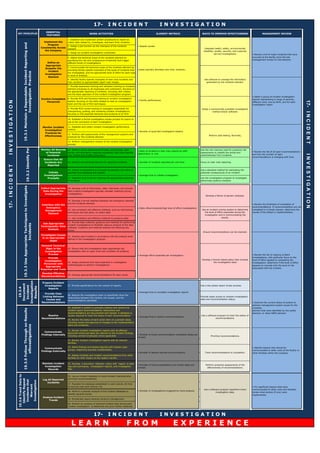
- 1. KEY PRINCIPLES ESSENTIAL FEATURES WORK ACTIVITIES ELEMENT METRICS WAYS TO IMPROVE EFFECTIVENESS MANAGEMENT REVIEW 1. Establish and implement written procedures to report on, collect data related to, investigate, and learn from incidents 2. Assign a job function as the champion of the incidents element 3. Assign an incident investigation coordinator 4. Define the technical scope of the incidents element by specifying the risk and consequence thresholds that trigger different levels of investigations. 5. Communicate the technical scope of the incidents element by providing facility-specific examples of the types of incidents that are investigated, and the appropriate level of effort for each type or level of analysis. 6. Identify facility-specific examples of near miss incidents and train workers to appropriately report near misses. 7. Provide awareness training and refresher training on incidents element processes to all employees and contractors, focusing on the appropriate reporting of incidents, including near misses, and the basic approach of the incident investigation program. 8. Provide RCA and forensics training to incident investigation leaders, focusing on the skills needed to lead an investigation team and the use of RCA techniques. 9. Provide RCA review training to managers responsible for championing, guiding, and reviewing incident investigations, focusing on the essential elements and products of an RCA 10. Establish a formal investigation review process for teams to use at the conclusion of each investigation. 11. Establish and collect incident investigation performance metrics. 12. Perform self-assessments of the management systems and practices for the incidents element. 13. Perform management reviews of the incident investigation process. Monitor All Sources of Potential Incidents 14. Perform active assessments of data, such as logs, data trends, and emergency response actuations, that could identify near misses and incident precursors. • Ratio of accident to near miss reports by shift, department, or unit Use the risk matrices used for proactive risk assessments to classify the actual and potentiallosses from incidents. Ensure that All Incidents Are Reported 15. Identify and eliminate barriers for reporting incidents. • Number of incidents reported per unit time. Focus on near miss reporting. 16. Initiate investigations as promptly as possible, but within a specified time following the incident. Use a standard method for estimating the potential consequences of an incident. 17. Establish time limits for notifying the appropriate personnel of incidents. Use the investigation program to investigate abnormally positive incidents Collect Appropriate Data During the Investigation 18. Develop a list of information, data, interviews, and records that incident investigators typically consider collecting during investigations. 19. Develop a formal interface between the emergency element and the incidents element. 20. Use consistent and effective methods, such as interviewing techniques and test plans, to collect data. 21. Use consistent and effective methods to preserve data. Use Appropriate Techniquesfor Data Analysis 22. Provide data collection guidance and methods for performing incident investigations to facilitate rigorous analysis of the data collected. Guidance and methods address the following key issues: Investigate Causes to an Appropriate Depth 23. Analyze each incident in accordance with the analysis level defined in the investigation program. Demand Technical Rigor in the Investigation Process 24. Ensure that the investigation team approaches the investigation with an open mind and considers all evidence. Provide Investigation Personnel with Appropriate Expertise and Tools 25. Assign personnel who have expertise in investigation methodologies to perform investigations. Develop Effective Recommendations 26. Develop appropriate recommendations for each cause. Prepare Incident Investigation Reports 27. Provide specifications for the content of reports. Use a two-phase report review process. Provide Clear Linking Between Causes and Recommendations 28. Require the investigation team to specifically show the relationship between the incident, the causes, and the recommendations identified. Provide ready access to incident investigation data and recommendation status. 29. Establish a system to promptly address and resolve the incident report recommendations. Resolutions and recommendations are documented and tracked. A database is usually required to track the status of each recommendation. 30. Review the status of each action item on a periodic basis, including review and approval of changes to the implementation plans and schedules. Communicate Findings lnternally 31. Review incident investigation reports with all affected personnel whose job tasks are relevant to the incident findings, including contract employees where applicable. 32. Review incident investigation reports with all relevant facilities. 33. Share findings and lessons learned with industry peer groups, respecting business confidentiality. 34. Assess incidents and incident recommendations from other facilities for their impact on the reader's facility. Maintain lncident lnvestigation Records 35. Develop a document retention policy with regard to data logs and summaries, investigation reports, and investigation files. • Number of times presentations and review dates are revised. Perform proactive assessments of the effectiveness of recommendations. 36. Use an incident database to trend incident characteristics and track recommendations. 37. Populate the database established in work activity 36 from all sources (see work activity 14). 38. Perform a periodic analysis of the incident database to identify adverse trends. 39. Periodically report adverse trends to management. 40. Perform an analysis of historical incident data during each incident investigation to determine any prior similar instances. Perform pilot testing. Normally, Adopt a commercially available investigation method and/or software. Use software to manage the information generated by the incidents element. Integrate health, safety, environmental, reliability, quality, security, and customer service investigations. Initiate Investigations Promptly • Average time to initiate investigation. 17- I N C I D E N T I N V E S T I G A T I O N 17-INCIDENTINVESTIGATION 17-INCIDENTINVESTIGATION 19.3.1MaintainaDependableIncidentReportingand InvestigationPractice 19.3.2IdentifyPotentialIncidentsforInvestigation Develop a formal restart policy that involves the investigation team Ensure recommendations can be resolved. Use an incident scoring system to determine the level of effort expended during the investigation and in communicating the results. Develop a library of generic analyses. • Average time to complete investigation reports • Examine the current status of actions to address management system issues for the incidents element that were identified by the audits element, or other RBPS element. L E A R N F R O M E X P E R I E N C E 19.3.5FollowThroughonResults oflnvestigations 19.3.6TrendDatato IdentifyRepeat Incidentsthat Warrant Investigation Interface with the Emergency Management Element • Average effort expended per investigation. 19.3.3UseAppropriateTechniquestoInvestigate Incidents 19.3.4 Document Incident Investigation Results 17- I N C I D E N T I N V E S T I G A T I O N lmplement the Program Consistently Across the Company Define an Appropriate Scopefor the lncident lnvestigation Element Involve Competent Personnel Monitor Incident Investigation Practices for Effectiveness • Number of quali.fied investigation leaders. • Facility performance. Losses typically decrease over time. However, • Repeat causes. Analyze lncident Trends • Number of investigations triggered by trend analysis. Use a software program toperform trend investigation data. • For significant lessons that were communicated to other units and facilities, review what actions (if any) were implemented. • Identify lessons that should be communicated to other units at the facility or other facilities within the company. Resolve Recommendations Communicate Findings Externally • Number of lessons learned communications. • Average time to resolve recommendations. • Number of times recommendation completion dates are revised. • Review the list of ongoing incident investigations, with particular focus on the level of effort applied to completing the investigation; determine if the level of effort appears to coincide with the level of risk associated with the incident. • Review the timeliness of completion of recommendations. If recommendations are not completed in a timely manner, determine the causes of the delays in implementation. • Review the list of all open recommendations and how the number of open recommendations is changing with time. • Select a group of incident investigation reports representing a range of severity, different units, and so forth, and for each investigation report • Review a list of major incidents that have occurred at the facility since the last management review for this element. Log All Reported Incidents Use a software program to track the status of recommendations. Prioritize recommendations. Track recommendations to completion. • Ratio oflow!moderate!high level of effort investigations
- 2. KEY PRINCIPLES ESSENTIAL FEATURES WORK ACTIVITIES ELEMENT METRICS WAYS TO IMPROVE EFFECTIVENESS MANAGEMENT REVIEW 1. Establish and implement procedures to develop and maintain process safety management perfor- mance and efficiency metrics. • The use of metrics for each operating area. 2. Assign an owner of the metrics system to monitor the program's effectiveness on a routine basis. Determine Triggersfor Metrics Collection and Reporting 3. Determine when metrics data are gathered. 4. Determine the facility areas in which the metrics element should be applied. 5. Determine the RBPS elements for which metrics would be useful. 6. Determine whether performance indicators, efficiency indicators, or both are desired. 7. Define the metrics roles and responsibilities for various groups of personnel. 8. Provide training on the metrics system. 9. Provide detailed training to those who are assigned specific roles within the metrics system. 10. Maintain records of metrics system data. 11. Establish and collect metrics data on the metrics element. 12. Provide input to interna! audits of metrics practices. 13. Develop appropriate metrics for each selected RBPS element. • Number of metricsfor which data are collected. 14. Ensure that an appropriate means exists for collecting data on selected RBPS elements. • The refresh ratefor metrics. Collect and Refresh Metrics 15. Collect and refresh metrics data at appropriate intervals. • Staff-hours required to develop metries. 16. Summarize metrics data in a useful format. 17. Communicate metrics data. 18. Establish action limits for the metrics. • Percentage of management personnel that use metrics for decision making. • Percentage of employees who have seen metrics. 19. Create a communication process for the RBPS health status and for potential corrective actions/ adjustments to the RBPS elements. • Frequency of metrics use in management review meetings. • The number of problems avoided/ discovered through the use of metrics. Establish Consistent Implementation Ensure that the Scope of Metrics Is Appropriate lnvolve Competent Personnel 18- M E A S U R E M E N T A N D M E T R I C S 18-MEASUREMENTANDMETRICS 18-MEASUREMENTANDMETRICS 20.3.1MaintainaDependablePractice20.3.2ConductMetricsAcquisition • Evidence that metrics use has caused improvement. Changes 18- M E A S U R E M E N T A N D M E T R I C S L E A R N F R O M E X P E R I E N C E • Resource utilization on the collection and refreshing of metrics. Use Metrics to lmprove RBPS Elements Use existing RBPS element software and databases to gather RBPS metrics 20.3.3Use MetricstoMake Corrective Action Decisions • Number of RBPS elements for which metrics are maintained. Use existing data collection systems to gather RBPS metrics. lmplement Appropriate Element Metrics Summarize and Communicate Metrics in a Useful Format • The number of metrics communications tools developed Coordinate data collection with the facility reliability effort as much as possible Keep Metrics Practices Effective • Results of audits or management reviews indicating that metrics are in consistent use. • The number of audit findings dealing with the metrics element • Number of people trained on metrics element. • Employee opinions about the use of key process safety performance metrics. Are workers aware of the metrics, or know where to find information about them? • Employee opinions on the effectiveness of new employee and contractor training on metrics. • Any incidents or trends that found metrics failure to be a root cause or contributing factor. • Status of corrective actions and whether they are overdue. • Any recent audit findings that addressed the metrics element. • Frequency of metrics updates. • Data collection methods.
- 3. KEY PRINCIPLES ESSENTIAL FEATURES WORK ACTIVITIES ELEMENT METRICS WAYS TO IMPROVE EFFECTIVENESS MANAGEMENT REVIEW 1. Develop an audits program that addresses issues such as: the scope of application, scheduling, team staffing, recommendation resolution, and documentation of audits. 2. Establish an audits element owner. 3. Define roles and responsibilities for the audits element. 4. Develop audit protocols. 5. Define the skills needed for the audit team members. 6. Provide the required training to the audit team members. 7. Ensure appropriate objectivity for audit teams. 8. Establish baseline schedules for audits. 9. Identify triggers for additional audits. Prepare for the Audit 10. Review audit protocols. Determine the Audit Scope and Schedule 11. Confirm the audit schedule and define the scope. Assemble the Team 12. Select team members, assign RBPS management system elements to the respective team mem- bers, and confirm their availability. Assign Responsibilities 13. Assign audit responsibilities to audit team members based on expertise, experience, and interest. Gather Advanced Information 14. Assemble and distribute to the team members information that will assist in their advance preparation for the audit. Plan Onsite Activities 15. Plan audit activities and prepare the onsite agenda. 16. Conduct the audit kick-off meeting. 17. Gather audit data though records sampling and reviews, observations, and interviews. 18. Assess RBPS implementation strengths, weaknesses, and gaps relative to established require- ments. 19. Report preliminary audit observations and findings in periodic meetings during the audit. 20. Conduct an audit close-out meeting. 21. Prepare a draft report and forward it to the appropriate facility personnel for review. 22. Issue the final report and forward it to the appropriate facility personnel. 23. Develop an action plan to address report findings; assign responsibilities and establish deadlines. 24. Follow up to resolve, and document resolution of, audit recommendations. 25. Maintain required documentation of the audit, including resolution of recommendations 26. Monitor RBPS performance over time. 27. Identify continuing RBPS management system or performance weaknesses. 28. Implement RBPS management system enhancements to address weaknesses. 29. Identify RBPS management system strengths. 30. Disseminate information on RBPS management system best practices to other facilities. • Percentage of recommendations that are rejected by thefacility management. Avoid making audits a competition. Make appropriate use of written audit protocols to help ensure comprehensive audits. Standardize audit procedures. 21.3.3UseAuditsto EnhanceRBPS Effectiveness Ensure that resources to support the audits program are properly budgeted Provide for a high level review of audit results. Prioritize follow-up activities. 19- A U D I T I N G 19-AUDITING 19-AUDITING 21.3.1Maintaina DependablePractice 21.3.2ConductElementWorkActivities • Percentage of near miss and incident investigations identifying RBPS management system weaknesses that were not detected by prior audits Pay careful attention to audit logistics. Give proper consideration to audit team composition. 19- A U D I T I N G L E A R N F R O M E X P E R I E N C E Monitor RBPS Maturation over Timefor Each Facility Share Best Practices • Percentage of auditfindings that are repeat findings. A • Trends in the number or significance of findings over a series of audits of the same facility. • Confirm that recommendation action items are closed out only upon the implementation of the action explicitly recommended. Document the Audit Properly train audit team members. Conduct the Audit Be discriminating in the scheduling of audits. Ensure Consistent Implementation Involve Competent Personnel Identify When Audits Are Needed • Number of previous audits conducted by each audit team member. • Percentage of audits havingfew significantfindings. • Percentage of audits completed according to schedule. • Evaluate whether the scope of the audit program covers every relevant facility and activity, consistent with the organization's scope of application for the RBPS management system • Evaluate whether the established frequencies for the audit(s) reflect (1)the perceived risk associated with the activities and facilities being audited and (2) past audit results and incident histories. • Determine whether audits are conducted according to schedule. • Evaluate whether the audit team staffing is appropriate. • Review the audit report(s) and determine if the documentation is sufficient to establish a basis for evaluating the quality of the audit. Address Audit Findings and Recommendations • Interval between completion of onsite work and completion of the audit report. • Number of person-days required to complete an audit. • Number or percentage of unresolved audit recommendations. • Average and maximum number of days overdue for open recommendations. • Evaluate whether the action items proposed to address the audit findings are appropriate to correct the deficiencies detailed by the report findings or recommendations. • Determine whether responsibilities for the resolution of audit recommendations are clearly as- signed and deadlines established. • Determine whether recommendation action item deadlines are consistently met. If not, what is done in lieu of the required activity? Ensure that an adequate amount of representative data is reviewed. Establish an integrated corrective action tracking system Make maximum use of computer databases when performing records reviews.
- 4. KEY PRINCIPLES ESSENTIAL FEATURES WORK ACTIVITIES ELEMENT METRICS WAYS TO IMPROVE EFFECTIVENESS MANAGEMENT REVIEW 1. Develop a written policy for managing the management review element. 2. Include specific roles and responsibilities in the management system governing the management review element. 3. Develop management review protocols. 4. Establish baseline schedules for reviews. Validate Program Effectiveness 5. Identify measures by which the effectiveness of management reviews will be judged. Prepare for the Review Work activities 6 through 9 address this essential feature. Determine the Review Scope 6. Establish the scope of the review. Schedule the Review 7. Confirm the review schedule. Gather Information 8. Gather information necessary for the review. 10. Conduct the review meeting. 11. Assess RBPS implementation strengths, weaknesses, and gaps relative to established require- ments. Document the Review 12. Document the review and forward it to the appropriate facility personnel. 13. Develop an action plan to address review findings; assign responsibilities and establish deadlines. 14. Followup to resolve review recommendations, and document resolution. 15. Identify relevant metric(s) for each RBPS element. • The type and number of findings in audits. 16. Trend RBPS performance over time. 17. Identify continuing RBPS management system or performance weaknesses. 18. Implement management system enhancements to address weaknesses. Conduct Field lnspections 19. Periodically spot check work practices in the field to verify that they are consistent with RBPS element requirements. 22.3.3Monitor Organizational Performance Establish Standards for Performance • The number of repeatfindings in reviews. • Changes in performance goals Define Roles and Responsibilities 20- M A N A G E M E N T R E V I E W A N D C O N T I N U O U S I M P R O V E M E N T MANAGEMENTREVIEWANDCONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT 20-MANAGEMENTREVIEWANDCONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT 22.3.1Maintain aDependable Practice 22.3.2ConductReviewActivities Prepare a Presentation Address Review Findings/Recommen dations • The time required to resolve deficiencies identified by management reviews. • The number of deficiencies identified by management reviews. • Number of management reviews per time period. Establish an integrated corrective action tracking system. Provide workers with advance notice of special areas of inquiry. Lookfor trends across different elements Make appropriate use of written protocols to help ensure comprehensive reviews. M A N A G E M E N T R E V I E W A N D C O N T I N U O U S I M P R O V E M E N T L E A R N F R O M E X P E R I E N C E Strive to Continuously Improve • Percentage of reviews delegated to subordinates. • The number of incidents attributed to RBPS element failures Provide an anonymous employee-reporting program. Avoid making reviews a competition. The overall design and conduct of management reviews has been described in this chapter. Like all other elements, the management review element should be subject to review periodically to ensure that the program is working properly. However, rather than have the management reviewers attempt to review themselves, this review can best be conducted as part of the periodic external audit program. Any weaknesses revealed should be resolved as an audit finding.
