10-cerebellum.ppt
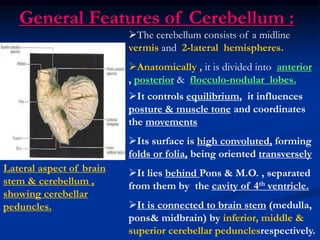
- 1. General Features of Cerebellum : Lateral aspect of brain stem & cerebellum , showing cerebellar peduncles. It controls equilibrium, it influences posture & muscle tone and coordinates the movements Its surface is high convoluted, forming folds or folia, being oriented transversely It lies behind Pons & M.O. , separated from them by the cavity of 4th ventricle. It is connected to brain stem (medulla, pons& midbrain) by inferior, middle & superior cerebellar pedunclesrespectively. The cerebellum consists of a midline vermis and 2-lateral hemispheres. Anatomically , it is divided into anterior , posterior & flocculo-nodular lobes.
- 2. External Features of Cerebellum : It has anterior notch ,which is wider and lodging the back of pons & medulla. It is separated from them by cavity of 4thventricle It has also posterior notch occupied by falx cerebelli, which separates the 2 cerebellar H. Inferior surface : rounded on each side and presents : a deep groove (vallecula) between the 2-cerebellar hemispheres,which is occupied by the inferior vermis. -Tonsil is a small part of cerebellar hemisphere that lies lateral to inferior vermis. Superior surface Inferior surface
- 3. External Features of Cerebellum : Superior surface : lies beneath tentorium cerebelli and has a raised superior vermis + a large cerebellar hemisphere on each side + primary & horizontal fissures. 1- Primary fissure V-shaped,well defined fissure, lies on superior surface and separates the small anterior lobe from the larger middle lobe (or posterior lobe). 2- Horizontal fissure lies along the sides of cerebellum, extending from anterior notch to posterior notch, separates the superior from the inferior surfaces. 3- Secondary (posterolateral) fissure lies on inferior surface and separates flocculo-nodular lobe from the ramainder of cerebellum.
- 4. Schematic drawing of cerebellum showing the relationships between the anatomical & functional divisions of cerebellum. Green =archi-cerebellum, blue=paleo-cerebellum. Pink= neo-cerebellum Functional subdivision of cerebellum : 1- Archi-cerebellum = posterior lobe (Vestibular part) : _ It is formed of the flocculo- nodular lobe + associated fastigial nuclei, lying on inf. Surface in front of postero-lateral fissure. _Embryologically, it is the oldest part of cerebellum. _It receives afferent Fs. From vestibular apparatus of internal ear Via vestibulo-cerebellar tracts. _It is concerned with equlibrium.
- 5. Connections of archicerebellum I- Archicerebellum It is concerned with equilibrium. It represents flocculo-nodular lobe. It has connections with vestibular & reticular nuclei of brain stem through the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Afferent vestibular Fs. Pass from vestibular nuclei in pons & medulla to the cortex of ipsilateral flocculo-nodular lobe. Efferent cortical (purkinje cell) Fs. Project to fastigial nucleus, which projects to vestibular nuclei & reticular formation. It affects the L.M.system bilaterally via descending vestibulo-spinal & reticulo-spinal
- 6. Schematic drawing of cerebellum showing the relationships between the anatomical & functional divisions of cerebellum. Green =archi-cerebellum, blue=paleo-cerebellum. Pink= neo-cerebellum 2- Paleo-cerebellum= (spinal part) : -_it is formed of midline vermis + surrounding paravermis + globose & emboliform nuclei. _It receives afferent proprio- ceptive impulses from Ms.& tendons Via spino-cerebellar tracts (dorsal & ventral) mainly. -it sends efferents to red nucleus of midbrain. -it is concerned with muscle tone
- 7. Connections of Paleo-cerebellum. 2-Paleo-cerebellum It is concerned with muscle tone & posture. Afferents spinal Fs. consist of dorsal & ventral spino-cerebellar tract from muscle, joint & cutaneous receptors to enter the cortex of ipsilateral vermis & para vermis Via inferior & superior cerebellar peduncles . Efferents cortical fibres pass to globose & emboliform nuclei, then Via sup. C. peduncle to contra- lateral red nucleus of midbrain to give rise descending rubro-spinal tract.
- 8. Schematic drawing of cerebellum showing the relationships between the anatomical & functional divisions of cerebellum. Green =archi-cerebellum, blue=paleo-cerebellum. Pink= neo-cerebellum 3- Neo-cerebellum= (cerebral part) : _It is the remaining largest part of cerebellum. _It includes the most 2-cerebellar hemispheres + dendate nuclei. _It receives afferent impulses from the cerebral cortex+pons Via cerebro-ponto- cerebellar pathway. -it sends efferents to V.L.nucleus of thalamus. -it controls voluntary movements (muscle coordination).
- 9. Connections of Neo-cerebellum. 3- Neo-cerebellum It is concerned with muscular coordination. It receives afferents from cerebral cortex involved in planning of movement- to pontine nuclei ,cross to opposite side Via middle Cerebellar peduncle to end in lateral parts of cerebellum (cerebro-ponto-cerebellar tract). Neo-cerebellar efferents project to dendate nucleus,which in turn projects to contra-lateral red nucleus & ventral lateral nucleus of thalamus ,then to motor cortex of frontal lobe, giving rise descending cortico-spinal & cortico- bulbar pathways. Efferents of dentate nucleus form a major part of superior C. peduncle.
- 10. Cerebellar Lesions Are usually vascular, may be traumatic or tumour. Manifestations of unilateral cerebellar lesions : 1-ipsilateral incoordination of (U.L) arm = intention tremors : it is a terminal tremors at the end of movement as in touching nose or button the shirt. 2-Or ipsilateral cerebellar ataxia affects (L.L.) leg, causing wide-based unsteady gait. Manifestations of bilateral cerebellar lesions (caused by alcoholic intoxication, hypothyrodism, cerebellar degeneration & multiple sclerosis) : 1-dysarthria : slowness & slurring of speech. 2-Incoordination of both arms.= intention tremors. 3-Cerebellar ataxia : intermittent jerky movements or staggering , wide-based, unsteady gait. 4-Nystagmus : is a very common feature of multiple sclerosis. It is due to impairment coordination of eye movements /so, incoordination of eye movements occurs and eyes exhibit a to-and-fro motion. Combination of nystagmus+ dysarthria + intension tremors constitutes Chacot’triad, which is highly diagnostic of the disease.
- 12. Internal Structure of cerebellum : Sagittal section of cerebellum. T.S.of cerebellum & brain at level of 4th V. to show cerebellar nuclei. It consists of an outer layer of grey matter (cerebellar cortex) , & inner layer of white matter containing 4-pairs of cerebellar nuclei : above roof of 4th V. from medial to lateral : 1-Fastigial nucleus. 2-Globose nucleus. 3-Emboliform nucleus. 4-Dendate nucleus. (the only one that can be seen clearly with the naked eye).
- 13. Cerebellar cortex It is highly convoluted, forming numerous transversely oriented folia. It contains nerve cells, dendrites and synaptic connections of cellular neurones. The cellular organization of the cortex consists of 3-layers : 1-Outer molecular layer. 2-Intermediate, purkinje cell layer. 3-Inner granular layer, which is dominated by granule cell. T.S of cerebellar folia showing layers of cerebellar cortex. Afferent & Efferent connecltions and their relationships to principal cells of cerebellar cortex.
- 14. Cerebellar cortex Molecular layer : contains 1-Cells : molecular cells (stellate cells) & basket cells. 2-Nerve Fibres : a- dendrites of Purkinje cells (arborisations). B-axons of granule cells. ( bifurcate to produce 2-parallel fibres , oriented along long axis of folium). C-ending of climbing fibers. Purkinje cell layer : it is formed of one layer (unicellular) of large flask- shaped purkinje cells. Their arborisations are at right angles to long axis to folium. Granular layer : it is formed of small granule cells & ending of mossy fibres.
- 15. MThere are 3-types of Nerve Fibres in white Matter : 1-Axons of purkinje cells : the only axons to leave cerebellar cortex to end in deep cerebellar nuclei specially dendate nucleus. 2-Mossy Fibres : end in the granular layer. 3-Climbing Fibres : end in the molecular layer.
- 16. Afferent Fibres to cerebellum : Mostly end in cerebellar cortex, excitatory to cortical neurones, as mossy or climbing Fs. passing through the cerebellar peduncles. The following are Afferent fibres: 1-dorsal & ventral spino-cerebellar tract. (passing via I.C.P & S.C.P) 2-vestibulo-cerebellar Fs. (via I.C.P) 3-olivo-cerebellar Fs. (via I.C.P)/ (extrapyramidal fibres), (end as climbing or mossy fibres) 4-ponto-cerebellar Fs. (via M.C.P). (In M.O)
- 17. M Efferent Fibres of the cerebellum : It sends the following fibres : 1-Cerebello-vestibular Fs. to vestibular nuclei of pons & M.O. 2-Cerebello-olivary Fs. To M.O. 3-Dendato-rubro-thalamic tract To red nucleus of midbrain & ventro- lateral nucleus of the thalamus and finally to motor cortex of frontal lobe to coordinate movement via cortico-spinal & corticobulbar tracts.
- 18. The Fourth Ventricle It is a cavity of hindbrain. Position : lies between pons & M.O. anteriorly and the cerebellum posteriorly. It is a diamond-shaped space which is lined by ependyma. Its superior angle is continuous with cerebral aqueduct of midbrain. inferior angle is continuous with centeral canal of closed M.O. Its lateral angles extend laterally to form a lateral recess on each side to open into subarachnoid space.
- 19. The Boundaries of 4th Ventricle Superiolateral boundary : -it is formed by superior cerebellar peduncle on each side. Inferiolateral boundary : -it is formed by inferior cerebellar peduncle + gracile & cuneate tubercles on each side.
- 20. The Roof of 4th Ventricle -it is a tent-shaped when seen laterally, and diamond-shaped when seen behind. -it is formed of superior & inferior medullary vela, which are thin sheets of white matter /consists of : ependyma covered by pia mater. -Sup.medullary velum connects the 2 sup.cerebellar peduncles. -Inf.medullary velum connects the 2 inf.cerebellar peduncles. -Inferior vermis of cerebellum : lies in the middle of roof of 4th ventricle.
- 21. The Roof of 4th Ventricle The lower part of roof is invaginated by tela choroidea of 4th ventricle. The tela choroidea is a double layer of pia mater which encloses the choroid plexus of 4th ventricle. The choroid plexus is a vascular capillary tuft covered by ependymal cells and secretes C.S.F. into the lumen of 4th ventricle.
- 22. The Openings of 4th Ventricle The roof contains 3 aperatures which transmit C.S.F. from ventricular lumen to subarachnoid space. Median aperature (foramen of Magendie) : lies in the median plane at lower end of inferior medullary velum, and opens into subarachnoid space at cistrna magna at cerebello-medullary angle 2 lateral openings (foramina of Luschka) : each one lies at the lateral end of lateral recess to open into subarachnoid space at cerebello-pontine angle. choroid plexus partly protrudes out through each lateral aperture.
- 23. The Floor of 4th Ventricle A diagram to show the floor & lateral boundaries of 4th ventricle. It is called rhomboid fossa. It is diamond-shaped and is divided into right & left halves by the median sulcus. It is crossed in the middle by transvere Fs. (ponto-cerebellar Fs.)called medullary stria, which divide floor of 4th ventricle into upper (pontine) & lower (medullary) part.
- 24. The Floor of 4th Ventricle A diagram to show the floor & lateral boundaries of 4th ventricle. Upper pontine part : presents on each side of median sulcus. 1-Medial eminence : a rounded elevation produced by the abducent nucleus. 2-Facial colliculus : an elevation on the top of lower part of medial eminence. It is produced by the fibres of facial nerve which surround abducent nucleus. 3-Superior fovea : a groove lateral to facial colliculus. 4-Vestibular area : lateral to superior fovea. It overlies superior, medial & lateral vestibular nuclei.
- 25. The Floor of 4th Ventricle A diagram to show the floor & lateral boundaries of 4th ventricle. Lower medullary part : presents on each side of the median sulcus. 1-Inferior fovea : inverted V-shaped groove. 2-Hypoglossal area : medial to inferior fovea. It overlies hypo-glossal nucleus. 3-Vagal area (triangle) : between limbs of inferior fovea.It overlies dorsal nucleus of vagus. 4-Vestibular area : lateral to inferior fovea. It overlies inferior vestibular nucleus.