Japan: History, Government, Economy and People
- 1. JAPAN
- 3. Tokyo
- 4. The Japanese desire for power
- 22. Economy
- 23. Labor
- 24. Interest Rates
- 32. Contract’s
- 34. Credit
- 35. Disclosure Index
- 36. CDI Commitment to Development
- 39. TRADE
Hinweis der Redaktion
- The Japanese people are the ethnic group that are identified as Japanese by culture and/or ancestry. The term is often used more broadly to refer to all people having Japanese nationality. Worldwide, approximately 130 million people are of Japanese descent. Of these, approximately 127 million are residents of Japan. Japanese culture has evolved greatly over the years, from the country's original Jomon Culture to its contemporary hybrid culture, which combines influences from Asia, Europe, and the Americas. It has likewise influenced the aesthetics of other countries, in areas ranging from impressionistic paintings to comic books and video games.
- Tokyo ( literally "Eastern capital") is the de facto capital of Japan [1] , and most popular city in the country. Tokyo is the seat of the Japanese government and the Imperial Palace, the home of the Japanese Imperial Family. With a population of over 35 million people in the Greater Tokyo Area[2]. It has the largest metropolitan GPD in the world for a city, and for a decade has held the title of the world's most expensive city. (1)(2)Encylopedia Britannica
- In the 1700’s 1800’s and until its defeat in the aftermath of the Second World War Japan had made numerous efforts to establish itself as a world force thru aggression. Over the course of a few hundred years Japanese forces had invaded and occupied Korea, China, Vietnam and other sovereign nations as it endeavored to establish its position as a power broker in the international community. With its defeat, at the end of WWII, there were a number of consequences. The surrender of Japanese forces brought with it a promise by the Japanese monarchy not to rebuild either its army or navy. Resultantly Japan had to face the world scene and move forward without its traditional military capability. How would this impact its ability to find a meaningful place on the world stage? Recognizing that there were no substantial natural resources indigenous to Japan that would allow it to have value at the world table the Japanese society looked inward and found that thru its intellect and ingenuity it could establish itself as a world power once again Starting in the 1950’s Japan developed and eventually became world market leaders in a number of industries including, electronics, automotive and finance. When you think of SONY, Panasonic, Kenwood etc. one will observe the instinct to stay ahead of the curve in developing consumer products and creating devices (chips, etc.) that transformed the entertainment and communications industries. Japan stands now on the threshold of becoming the entity with the #1 market share in automobile sales. From a financial perspective the Japanese have used its currency to create value that previously did not exist and develop financial mechanisms carry trade, etc.) and products that facilitate ways to effect transactions. In addition the financial where withal has allowed Japan to invest and become one of the largest holders of valuable real estate in the world (Rockefeller Center, other properties in New York City.)
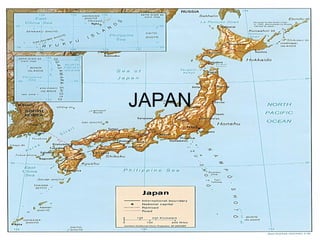
- Japan consists of over 3,000 islands stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk south all the way to Taiwan. These islands, located in the Pacific Ocean are mountainous, and many are volcanic. Japan boasts that it has the second-largest economy in the world and is a world leader in industry. It is a unitary constitutional monarchy with an emperor and an elected parliament, (it is one of the oldest legislatures in Asia.) Despite its rugged terrain, it is one of the most populous and most densely populated countries in the world. Tokyo is the largest metropolitan area in the world with over thirty million residents. From the 12th century to the mid-1800s, Japan was a feudal country led by clans of warriors. After the Meiji Restoration of 1868, Japan adopted many European and American customs and institutions. It has also adopted many Chinese customs throughout the year. Its culture today is a mixture of these influences along with traditional Japanese culture. Japan's name in the kanji character writing system is translated as "Land of the Rising Sun", and comes from the country's location, off the eastern coast of Asia.
- Parties in the Government: (DJP) Democratic Party of Japan, (JCP) Japan Communist Party, Komeioto, Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), Social Democratic Party (SDP).
- The currency of Japan, the yen is established on a floating economy of about 119.81 ¥ per us $1.00. The Yen was established as the main currency by the New Currency Act of Meji in 1871. Originally the Yen was printed by the the central government and private mints. These mints reestablished themselves as National Banks until the Bank of Japan was established in 1885.
- According to its charter the mission’s of the bank of Japan deal with issuance and management of the banknotes, implementations of monetary police, providing settlement services and ensuring the stability of the financial system, international activities, compilation of data, economic, analysis, and research activities. The Law sets the Bank's objectives "to issue banknotes and to carry out currency and monetary control" and "to ensure smooth settlement of funds among banks and other financial institutions, thereby contributing to the maintenance of an orderly financial system.“ The Law also stipulates the Bank's principle of currency and monetary control as follows: "currency and monetary control shall be aimed at, through the pursuit of price stability, contributing to the sound development of the national economy." (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/type/exp/about/expboj.htm)
- 36 00 N, 138 00 E -Japan is an “archipelago”, (group or chain of islands) it is a group located off of the east coast of Asia. It is separated from the coast by the Sea of Japan. Its main cities are Tokyo, Yokahama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Kyoto, Kobe, Fukuoka, Kawasaki, and Hiroshima. -Japan, is a country of 4 main land masses that include Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu and Shikoku. They extend along the east coast of Asia Located in the pacific. The main island is Honshu, and the country has three other large islands—Hokkaido to the north and Shikoku and Kyushu to the south. More than 4,000 smaller islands surround the four largest. About 73 % of Japan is mountainous, and all its major cities, except the ancient capital of Kyoto, sit on the narrow coastal plains. Only an estimated 18% of Japan's territory is suitable for settlement. So Japan has large cities are big and densely populated. Tokyo, the capital, is the planet's largest urbanized area at 12 million people. However, Tokyo has a worrisome environmental history of destructive earthquakes and tsunamis (seismic sea waves). A major earthquake in 1923 killed an estimated 143,000 people.
- Agriculture makes up only about 2% of the GNP. Most important agricultural product is rice. Resources of raw materials are very limited and the mining industry rather small.
- The electronics industry is one of Japans largest industries. Japan is the world’s second largest producer and third largest market for electronic equipment and components, accounting for 15% and 12% of the worldwide total, respectively in 2005. Consumer electronics, once the mainstay of the Japanese electronics industry, continues to lose share as Japanese manufacturers shift production to low cost countries in the Far East . In 1985 consumer products accounted for 23% of total output but this had fallen to 10% in 2004. The sector, however, has benefited from the move to digital products. Today components and computing account for the largest share of production accounting for 45% and 18% of output, respectively.
- Japans population growth rate is 0.02%, with a birth rate of 9.37 births per 1,000, which keeps the population pretty even with 9.16 deaths per 1,000. Japanese cities are noted for their high population densities, due to its inaccessible mountainesque terrain. With over 30 million residents, the Greater Tokyo Area is the largest metropolitan area in the world.
- The way that one conducts themselves in a business environment is is just as important if not more important, as the quality of the business they themselves represent. It is custom when formally meeting an individual, to greet a person and present their “meishi.” it is proper to do so when you bow, holding the card on its for corners and stating your name, position and the company that you work for, it is important to recognize and acknowledge the position that one has. Then you place the card in front of you (if you are sitting) or in your wallet. Never put it in your pocket or fold it and put it away. To do so is to show disrespect. Avoid expressing yourself too directly. It is rude to express opposing opinions. That is why it is difficult to debate for the Japanese, there is your Honne and your Tatemae, your personal opinion and your public one. In public it is customary to go along with the group consensus. Avoid interrupting people when they are speaking or thinking about an answer. Japanese do not mind short periods of silence in the middle of a discussion. Avoid staring someone directly in the eyes. When sitting down to a business meeting with your Asian counterparts, the seating arrangement will be determined by the status of the participants. Do not just sit anywhere; as the guest, you will be directed to the appropriate seat. As a general rule, the highest ranking person from the host side will sit at the head of the table. Then, other people will take their seats starting from the seats closest to him and working to the other end of the table. Those of higher status sit closest to the boss. You should stand at your seat and wait for the top guy to tell you to be seated. Then, when the meeting is finished, wait until he has stood up before standing up yourself. Non-alcoholic drinks will probably be served at the beginning of the meeting and they will be distributed in the order of descending importance of recipients. You should wait for the highest ranking person their to take a sip before you take your own. Gifts are always appreciated. You may want to take notes during the meeting. Taking notes shows that you are interested and your host will appreciate it . But, you should make certain never to write anyone's name in red ink (even your own) and so carry a black or blue pen. It is important to know small customs so that you do not seem rude or disrespectful. It is also important because it can determine whether your business goes well or not.
- Bowing is a very important custom in Japan. There is not really a great deal of physical contact. In Japan, Japanese people bow all the time. Most commonly, they greet each other by bowing instead of handshaking. It is impolite not to return a bow to whoever bowed to you. Japanese people tend to become uncomfortable with any physical forms of contact. At times they have become used to shaking hands with westerners. Bowing has many functions in one. It expresses the feeling of respect, thanking, apologizing, greeting, and so on. It's a convenient and important custom for you to learn. You can bow, when you say, "Thank you", "Sorry", "Hello", "Good bye", "Congratulations", "Excuse me", "Good night", "Good Morning", and more!! Bowing seems easy, but there are different ways of bowing. It depends on the social status or age of the person you bow to. If the person is higher status or older than you are, you should bow longer and deeper. It is polite to bow, bending from your waist. Men usually keep their hands in their sides, and women usually put their hands together on their thighs with their fingers touching. If it is a casual situation, you can bow like nodding. The most frequent bow is a bow of about 15 degrees. You might feel strange to do it, but try to bow in Japan. You will be considered very polite.
- -Casual American-style attire is still uncommon in the Japanese business place. You should dress appropriately for the occasion when meeting your counterparts on business. -The Japanese are very conservative in their style of dress. It is common to wear a dark colored suit with a tie. Women on the other hand wear pants suites or knee length or longer skirts. Both though should always wear clean socks with out holes, since it is customary to take off your shoes in many places, such as restaurants for it is frowned upon and considered rude to do other wise.
- It is important to know what times business's are open so that you can conduct business at proper hours.
- Succeeding in Japanese high-technology markets largely depends on having the right product at the right time. Yet for U.S. firms, gaining market share in Japan also results from traveling to Japan to establish contacts and deliver the hands-on customer service the Japanese expect. Japan's foreign direct investment abroad has boomed over the past decade as many Japanese companies have set up production facilities overseas.
- There is no National Religion in Japan but the main religions in Japan are Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, with a decent percentage also that are Christian. (1.6 million) Shinto's is one of the largest followings and the native religion of Japan.
- -Group goals are encouraged over individual -High rate of success by international standards -International education scores Japan is ranked number 5 (us is 12) Strong work ethic is instilled in students. Education is an important issue in Japanese society. These are the three ways that a child is educated in Japan: by attending a public school for a compulsory education, by attending a private school for a compulsory education, or by attending a private school that does not adhere to standards set by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). As well they have schools that some parents enroll their children in after their normal school that occur at times during the week and on Saturdays. While high school is not mandatory, more than 90% of the population attends high school. More than 2.5 million students proceed to universities and colleges. In the past, the selection process for advancing to higher education had been described as "hellish" and "war-like". But with the number of Japanese children being born declining, the tide has turned the other way. Schools are recently having to compete amongst themselves to gather students. However, many children continue to be sent to Juku (cram schools) in addition to state schools. Japan’s education system has been preparing its students to become diligent workers for a long road of business ahead.
- National holidays are recognized in Japan as they are in the US, yet Japan has their own set of Holidays. On National Holidays there is no work normally and there was a provision of the Public Holiday law when a holiday falls on a Sunday the next Monday is taken off. If there is are two holidays that have a day in-between then that day is also taken off. It is important to know what days one has off in a country so you can plan when to do business.
- The primary goals of trade unions are to defend the employment and the livelihoods of workers, and to build democracy in the workplace, community and society as a whole. The three tear structure consists of affiliated tear enterprise unions, industry trade unions, and national centers (at the top). “The enterprise-based unions utilize negotiations and labor-management consultations in the workplace to improve working conditions, to monitor corporate activities, and to provide services to their members. The industrial federations for their part are composed of enterprise-based unions in the same industry. Their member unions exchange information on common working conditions in the industry, discuss industrial policies and other problems, and strive to rectify these industry-specific problems. (http://www.jtuc-rengo.org/about/index.html) RENGO is a national center, made up of these industrial federations. From the standpoint of "defending the employment and livelihoods of all working people,” including RENGO union members, they work with the national government and employers’ organizations on issues such as labor standards, tax systems and social security, which cannot be settled at the industry or local level. (http://www.jtuc-rengo.org/about/index.html)
- Japan is the world's second largest economy after the United States. Services make up the largest part of Japan's economy. In 2000, service sector (such as trade, government, and real estate) accounted for 67 percent of Japan's GDP, while industry (mining, manufacturing, and construction) made up 32 percent, and agriculture (including forestry and fishing) contributed simply 1 percent. GDP: $4.664 Trillion Japan’s population, a little less than half that of the United States, generates a gross domestic product (GDP) that is about half as large as U.S. GDP. GDP per person is very high, and Japan’s consumers are quite wealthy by world standards. When Japan’s higher living costs are taken into account, income per person is about 80 percent of the U.S. level. (http://www.mapsofworld.com/country-profile/japan1.html) Sources for image: World Bank and ERS
- There are differences between the Japanese and U.S. societies. Japan has a shrinking labor force. Its population is getting older because the birth rate is very low. Strict policies deter immigration. Japanese statistics indicate that population growth turned negative in 2005, and population is projected to continue to shrink. Women’s labor force participation has been growing, but remains lower than in the United States. In general, Japan’s workers are working shorter hours than in the past. The scarcity of labor makes production in Japan expensive, and has forced Japan’s firms to investigate strategies that use less Japanese labor, including further automation and moving production to other countries.
- Japan's monetary policy of zero interest rates was introduced in March 2001 in an attempt to revive the economy, which had been in long-term recession since the early 1990s. Japan's consumers are again getting a taste for spending One of the main problems was deflation - falling prices - which meant that consumers and businesses were reluctant to spend or invest because any purchase was likely to be cheaper in the future. The zero interest rate was designed to make it cheaper for consumers and companies to borrow money for spending, and less attractive for them to save.
- From its beginnings, nearly all of the Japanese automakers were associated with zaibatsu, or later keiretsu - Japanese business conglomerates. In the post-war period, these large companies had close ties with the government, who urged them to absorb all of the smaller carmakers into large brands that could be marketed internationally. Nissan (Datsun at the time) was a prime example, taking control of Prince and many other smaller companies to form a large brand. Mitsubishi Motors was a part of a large keiretsu as well. However, one of the lone exceptions of the time was Honda. The company was formed as a tiny firm, and had (and still has) experienced no major takeovers or mergers. During the massive expansion of many Japanese companies after WWII, many of the automakers sought to expand into other markets, mainly the US. In 1957, the first Japanese car to be imported to the United States was the Toyota Crown, followed by the 1958 Datsun 1000. -During the 1960s, Japanese automakers launched a number of new key cars in their domestic market. These small automobiles had much smaller engines (from 360cc to 600cc) to keep costs, and taxes much lower than larger cars. Which made it possible for the average person in Japan to afford an automobile, which boosted sales dramatically and jumpstarted the auto industry toward becoming what it is today. Japan entered the automobile market in the US in the 1970’s by the 1980s, the Japanese manufacturers were gaining a major standing in the US and world markets. With Japanese manufacturers producing very affordable, reliable, and popular cars throughout the late 1990s, Japan had become the largest car producing nation in the world by the year 2000. However, its market share has decreased slightly in recent years, mainly due to new competition from China and India and a shift in the focus of Japanese government policies. Industry speculators have predicted, however, that by 2007 or 2008, Toyota will become the largest automaker in the world, surpassing American GM by producing upwards of 9.4 million vehicles. (Harper)
- machinery and equipment, fuels, foodstuffs, chemicals, textiles, raw materials
- The Japanese industry of Steel and Iron production is one that is innovative. The Japanese purchase iron ore in the United States, ship it across the US to be processed in Japan and then ships it back the United States. and are still able to sell its products at a competitive price.
- Westerners often begin by asking for more than what they want and make concessions. The Japanese prefer to use trial balloons and indirect suggestions in private. The typical Japanese negotiating method stresses intuitive understanding of the opposing side and behavior analysis through non-verbal signals. (The Japanese Negotiator: Subtlety and Strategy Beyond Western Logic) This frequently leads to such tactics as non-negotiable demands (stall), time indifference (stall), ambiguous response (stall), and an overall pattern of being receptive and quiet during negotiations. Western methods — especially American — are defensive overall, and are usually earnest, direct, aggressive, demanding, logical, forcefully argumentative, tactical and combative (power drive all the way as taught in Debating I). (How To Japanese, CD ROM) http://home.inter.net/glaabs/index.html
- Japan Credit Bureau, usually abbreviated as JCB, is a credit card company based in Tokyo, Japan. Its English name is JCB Co., Ltd. Founded in 1961, JCB established dominance over the Japanese credit card market when it purchased Osaka Credit Bureau in 1968. JCB cards are now accepted by 11 million merchants in 189 countries, and are commonly accepted at hotels and upscale shopping outlets in major cities around the world. JCB also operates a network of membership lounges targeting Japanese, Chinese, and Korean travelers in Europe, Asia, and North America. In the United States, JCB is accepted primarily at businesses concerned with travel and hospitality (such as airlines, car rental companies, and hotels), but increasingly also at businesses such as department stores, gas stations, and Japanese specialty retailers such as Mitsuwa and Marukai. JCB accounts in the US are issued by JCBUSA. Additionally, on August 23, 2006, JCB announced an alliance with the Discover Network. The two companies have signed a long-term agreement that will lead to acceptance of Discover Network brand cards at JCB point-of-sale terminals in Japan and of JCB cards on the PULSE network in the U.S. This partnership is expected to be fully operational by 2008
- Japan ranks 21st overall in 2006. Japan’s barriers to exports from developing countries are the highest in the CDI (driven mainly by rice tariffs) and its foreign aid is the smallest as a share of income. Japan also has a poor environmental record from the perspective of poor countries and admits very few immigrants. Japan’s strongest contributions to development come through government support for research and development and through policies that promote investment in poor countries. ( www.cgdev.org/.../_active/cdi/_country/japan/ )
- -www.cgdev.org -www.Google.com -www.CiaFactbook.com -www.YahooFinance.com -www.Yahoo.com -Kiss, Bow, Shake Hands -Japanese Society and Culture in Perspective An introduction by Hans Brinckmann -http://www.jref.com/culture/japanese_manners_etiquette.shtml