ELECTROCHEMSTRY POWER POINT
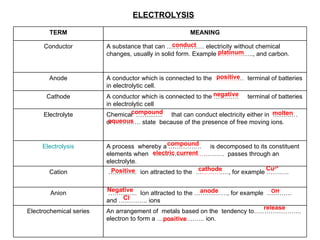
- 1. ELECTROLYSIS conduct platinum positive negative compound aqueous molten compound electric current Positive cathode Cu 2+ Negative anode Cl - release positive OH - TERM MEANING Conductor A substance that can ……………… electricity without chemical changes, usually in solid form. Example ………… ….., and carbon. Anode A conductor which is connected to the ……… … terminal of batteries in electrolytic cell. Cathode A conductor which is connected to the ………… terminal of batteries in electrolytic cell Electrolyte Chemical ……........ that can conduct electricity either in ………… or …………. state because of the presence of free moving ions. Electrolysis A process whereby a ……………. is decomposed to its constituent elements when …………… ……… ………. passes through an electrolyte. Cation ………… .. ion attracted to the … ……… …., for example ……….. Anion ………… .. Ion attracted to the ……………., for example ………… and ………….. ions Electrochemical series An arrangement of metals based on the tendency to………………….. electron to form a ………………….. ion.
- 7. Position of ion in electrochem series H + , SO 4 2- , OH - 2H + + 2e -> H 2 Bubbles are released 4OH - -> 2H 2 O + O 2 + 4e Bubbles are released Concentration H + , Cl - , OH - Position of ion in electrochem series Position of ion in electrochem series Position of ion in electrochem series Concentration Type of electrode 2H + +2e -> H 2 Bubbles are released 2H + + 2e -> H 2 Bubbles are released 2H + + 2e -> H 2 Bubbles are released 2H + + 2e -> H 2 Bubbles are released Ag + + e -> Ag Shiny grey solid deposited Ag + + e -> Ag Shiny grey solid deposited 4OH - -> 2H 2 O + O 2 + 4e Bubbles are released 4OH - -> 2H 2 O + O 2 + 4e Bubbles are released 4OH - -> 2H 2 O +O 2 + 4e Bubbles are released 2Cl - -> Cl 2 + 2e A greenish-yellow gas released 2I - -> I 2 + 2e Brown solution is formed Ag + , NO 3 - , H + , OH - Ag + , NO 3 - , H + , OH - , K + , H + , I - , OH - K + , H + , I - , OH - H + , Na +, OH - , SO 2 - Ag -> Ag + + e Silver electrode becomes thinner ELECTROLYTE ELECTRODE FACTOR THAT AFFECT ELECTROLYSIS IONS PRESENT HALF EQUATION AT THE ANODE AND OBSERVATION HALF EQUATION AT THE CATHODE & OBSERVATION Dilute sulphuric acid Carbon Concentrated hydrochloric acid Carbon Silver nitrate solution Carbon Silver nitrate solution Silver Potassium iodide solution Carbon Concentrated potassium iodide solution Carbon Sodium sulphate solution Carbon
- 11. Silver electroplating Anode is silver Ag -> Ag+ + e Silver anode becomes thinner Ag+ + e -> Ag Shiney Grey solid deposited Purification of copper Anode is impure copper Cu -> Cu 2+ + 2e Impure copper becomes thinner Cathode is pure copper Cu 2+ + 2e -> Cu Pure copper becomes thicker Extraction of Aluminium Anode is with carbon 2O 2- -> O 2 + 4e Colorless gas given off. Cathode is steel container is coated with carbon Al 3+ + 3e -> Al Grey liquid metal formed Metal Extraction Purification of metal Electroplating CATHODE/ HALF EQUATION / OBSERVATION ANODE / HALF EQUATION / OBSERVATION EXAMPLE APPLICATION
- 17. ZINC ELECTRODE : …………………… terminal because ………………………………………….. Half equation : ……………………………………………………………… Observation : ……………………………………… COPPER ELECTRODE : ……………… terminal because ………………………………………. Equation : ……………………………………………………………….. Observation : ………………………………………………………………… If the zinc metal is replaced with a magnesium metal , the voltage reading increases because magnesium is further from copper in the Electrochemical Series Negative zinc is more electropositive than copper Zn -> Zn 2+ + 2e Zinc electrode becomes thinner Positive copper is less electropositive than zinc (i)Brown solid deposited. (ii) The intensity of blue colour of copper(II) sulphate decreases. Cu 2+ + 2e -> Cu
- 18. Metal Displacement Reaction. The metal which is situated at a higher position ( higher tendency to release electron) in the electrochemical series is able to displace a metal below it from its salt solution . Copper Silver nitrate solution Grey solid Blue solution