The Strategic Position Outline
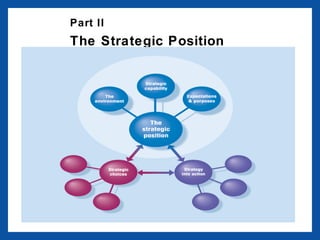
- 1. Part II The Strategic Position
- 3. The Environment – Outline • Macroenvironment – PESTEL • Scenarios • Sources of competition – 5-forces • Understanding competition – Strategic group analysis – Market segments – Critical success factors • Strategic gaps – Opportunities – Threats
- 4. Layers of the business environment Exhibit 2.1
- 6. Macroenvironment – PESTEL (1) Exhibit 2.2
- 7. Macroenvironment – PESTEL (2) Political Economic • Government stability • Business cycles • Taxation policy • GNP trends • Foreign trade • Interest rates regulations • Money supply • Social welfare • Inflation policies • Unemployment • Disposable income
- 8. Macroenvironment – PESTEL (3) Sociocultural Technological • Population • Government spending on demographics research • Income distribution • Government and industry • Social mobility focus on technological • Lifestyle changes effort • Attitudes to work and • New discoveries / leisure developments • Consumerism • Speed of technology • Levels of education transfer • Rates of obsolescence
- 9. Macroenvironment – PESTEL (4) Environmental Legal • Environmental • Competition law protection laws • Employment law • Waste disposal • Health and safety • Energy consumption • Product safety
- 10. Key Drivers of Change • Market Globalisation • Cost Globalisation • Globalisation of Government Policies • Globalisation of Competition
- 12. Porter’s Diamond • Determines the competitive advantage of nations. • Four main determinants of national advantage: 1. Factor Conditions 2. Demand Conditions 3. Related and Supporting industries 4. Firm Strategy, Structure and Rivalry
- 13. Porter’s Diamond The Determinants of National Advantage
- 14. Scenarios • Detailed and plausible views of future development of environment, based on groupings of key environmental influences and drivers of change about which there is a high level of uncertainty • Different views of possible futures • Long term view of strategy
- 15. Industries and Sectors Industry – a group of firms producing the same Industry – a group of firms producing the same principal product, e.g. mobile phones principal product, e.g. mobile phones Sector – a group of organisations providing the Sector – a group of organisations providing the same kinds of services, e.g. healthcare same kinds of services, e.g. healthcare Competitive forces in the industry: – Determine attractiveness of industry – Affect the way individual companies compete – Influence decisions on product/market strategy
- 16. Changing Boundaries of Industry • Convergence – Previously separate industries begin to overlap in activities, technologies, products and customers – Supply-led, e.g. • bundling and unbundling of sectors in public services – Various ministries – Communication and IT – Demand-led, e.g. • Substitution of one product by another (TVs and PCs) • Customers want bundling of complementary products – Package Holiday • Creates new market segments
- 17. The Five Forces Framework
- 18. Five Forces Analysis (1) The threat of entry ... Is dependent on barriers to entry such as: • Economies of scale • Capital requirements of entry • Access to supply or distribution channels • Customer or supplier loyalty • Expected retaliation • Legislation or government action • Differentiation
- 19. Five Forces Analysis (2) Threat of substitutes Reduction in demand for products as customers switch to alternatives: • Product for product substitution – e.g. email for post • Substitution of need – e.g. reliable and cheap appliances reduce need for maintenance services • Generic substitution – competition for household income, e.g. cars versus holidays – doing without
- 20. Five Forces Analysis (3) Buyer power is likely to be high where there is / are: • a concentration of buyers • many small operators in the supplying industry • alternative sources of supply • low switching costs • components/materials that are a high percentage of cost to the buyer leading to “shopping around” • a threat of backward integration
- 21. Five Forces Analysis (4) Supplier power is likely to be high where there is / are: • a concentration of suppliers • customers that are fragmented and bargaining power low • high switching costs • powerful supplier brand • possible integration forward by the supplier
- 22. Five Forces Analysis (5) Competitive Rivalry is likely to be high when: • competitors are in balance • there is slow market growth (product life cycle) • there are high fixed costs in an industry • there are high exit barriers • markets are undifferentiated Competitive rivals are organisations with similar products Competitive rivals are organisations with similar products and services aimed at the same customer group = direct and services aimed at the same customer group = direct competitors competitors
- 23. Key Aspects of 5-Forces Analysis • Use at level of strategic business units (SBU) • Define the industry/market/sector • Don’t just list the forces: derive implications for industry/organisation • Establish interconnections between the five forces
- 24. Limitations • The model was designed for analyzing individual business strategies. It does not cope with synergies and interdependencies within the portfolio of large corporations. • From a more theoretical perspective, the model does not address the possibility that an industry could be attractive because certain companies are in it. • Some people claim that environments which are characterized by rapid, systemic and radical change require more flexible, dynamic or emergent approaches to strategy formulation. • Sometimes it may be possible to create completely new markets instead of selecting from existing ones.
- 27. Dynamics of Competition (1) • Process of competition over time • Erosion of competitive advantage – Changes in five forces – Competitors overcoming adverse forces • Multipoint moves and counter moves • Speed of Cycles of competitive response – Slow: long periods of established pattern of competition – Fast: hypercompetition, constant disequilibrium and change
- 28. Dynamics of Competition (2) • Implications of speed of competitive cycle: – Slow-moving - build and sustain competitive advantages which are difficult to imitate – Fast-moving - advantage is temporary, disrupt status quo, sequence of short-lived moves
- 31. Strategic Groups • Strategic groups are organisations within an industry with similar strategic characteristics, following similar strategies or competing on similar bases.
- 32. Characteristics for identifying strategic groups
- 33. Uses of Strategic Group Analysis • To understand who are the most direct competitors of an organisation • To establish the different bases of competitive rivalry within and between the strategic groups • To assess if an organisation could move from one group to another – Depends on barriers to entry • To identify opportunities and threats – Changes in the macro-environment may create strategic space
- 34. Market Segments A market segment is a group of customers who A market segment is a group of customers who have similar needs that are different from have similar needs that are different from customer needs in other parts of the market customer needs in other parts of the market • The strategic customer – The person(s) to whom strategy is primarily addressed because they have the most influence • What customers value – critical success factors – Those product features particularly valued by a group of customers and where the organisation must excel to outperform competition
- 35. Some Bases of Market Segmentation Exhibit 2.9
- 36. A Strategy Canvas Perceived value in the electrical engineering industry Exhibit 2.10
- 38. Strategic Gaps • Strategic Gaps are opportunities in business environment not being fully exploited by the competition: • Opportunities in: 1. Substitute industries 2. Other strategic groups or strategic spaces 3. The chain of buyers 4. Complementary products and services 5. New market segment 6. Markets developing over time (Kim & Mauborgne 1999)
- 39. SWOT • A SWOT analysis summarises the key issues from the business environment and the strategic capability of an organisation that are most likely to impact on strategy development.
- 40. Environment – Key Points (1) • PESTEL identifies key drivers of change • Scenarios analyse future implications of uncertain environmental forces • 5 forces framework identifies sources of competition in an industry • Competition is dynamic
- 41. Environment – Key Points (2) • Within an industry there are strategic groups competing on similar bases • Market segments help to understand differences between customers • Critical success factors are those features particularly valued by customers • Environmental analysis identifies opportunities and threats
Hinweis der Redaktion
- Very difficult to edit this picture. Idea would be to animate the slide (see slide show), first to show the basic ovals, then bring in the annotation. These lecture notes serve as revision sheets for students so it’s good to include some of the detail.
- 3
- 6
- 4
- 4
- 4
- Kevan – I am missing some key points in the text. It is absolutely critical that students define the industry they are analysing. And that they rate the forces and derive the implications of that for the industry/organisation. Also emphasise that this is industry analysis, not analysing the individual organisation.
- Editable version
- This is a very narrow definition of critical success factors. The critical success factors for an oil company are, for example, ability to negotiate with governments, access to large amounts of capital etc. Nothing to do with customers.
