French verbs 1
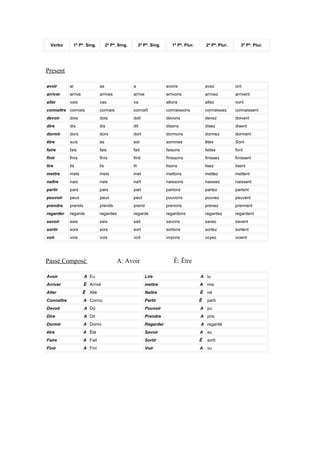
- 1. Verbo 1ª Pª. Sing. 2ª Pª. Sing. 3ª Pª. Sing. 1ª Pª. Plur. 2ª Pª. Plur. 3ª Pª. Plur. Present avoir ai as a avons avez ont arriver arrive arrives arrive arrivons arrivez arrivent aller vais vas va allons allez vont connaître connais connais connaît connaissons connaissez connaissent devoir dois dois doit devons devez doivent dire dis dis dit disons disez disent dormir dors dors dort dormons dormez dorment être suis es est sommes êtes Sont faire fais fais fait faisons faites font finir finis finis finit finissons finissez finissent lire lis lis lit lisons lisez lisent mettre mets mets met mettons mettez mettent naître nais nais naît naissons naissez naissent partir pars pars part partons partez partent pouvoir peux peux peut pouvons pouvez peuvent prendre prends prends prend prenons prenez prennent regarder regarde regardes regarde regardons regardez regardent savoir sais sais sait savons savez savent sortir sors sors sort sortons sortez sortent voir vois vois voit voyons voyez voient Passé Composé A: Avoir Ê: Être Avoir A Eu Lire A lu Arriver Ê Arrivé mettre A mis Aller Ê Allé Naître Ê né Connaître A Connu Partir Ê parti Devoir A Dû Pouvoir A pu Dire A Dit Prendre A pris Dormir A Dormi Regarder A regardé être A Été Savoir A su Faire A Fait Sortir Ê sorti Finir A Fini Voir A vu
- 2. Imparfait avoir avais avais avait avions aviez avaient arriver arrivais arrivais arrivait arrivions arriviez arrivaient aller allais allais allait allions alliez allaient connaître connaissais connaissais connaissait connaissions connaissiez connaissaient devoir devais devais devait devions deviez devaient dire disais disais disait disions disiez disaient dormir dormais dormais dormait dormions dormiez dormaient être étais étais était étions étiez étaient faire faisais faisais faisait faisions faisiez faisaient finir finissais finissais finissait finissions finissiez finissaient lire lisais lisais lisait lisions lisiez lisaient mettre mettais mettais mettait mettions mettiez mettaient naître naissais naissais naissait naissions naissiez naissaient partir partais partais partait partions partiez partaient pouvoir pouvais pouvais pouvait pouvions pouviez pouvaient prendre prenais prenais prenait prenions preniez prenaient regarder regardais regardais regardait regardions regardiez regardaient savoir savais savais savait savions saviez savaient sortir sortais sortais sortait sortions sortiez sortaient voir voyais voyais voyait voyions voyiez voyaient Le Passé - French Past Tenses Passé composé - French Compound Past Tense The most common French past tense The passé composé is the most common French past tense, often used in conjunction with the imperfect1. The passé composé can express any of the following: I. An action completed in the past As-tu étudié ce weekend ? Did you study this weekend? Ils ont déjà mangé. They have already eaten.
- 3. II. An action repeated a number of times in the past Oui, j'ai mangé cinq fois hier. Yes, I did eat five times yesterday. Nous avons visité Paris plusieurs fois. We've visited Paris several times. III. A series of actions completed in the past Quand je suis arrivé, j'ai vu les fleurs. When I arrived, I saw the flowers. Samedi, il a vu sa mère, a parlé au médicin et a trouvé un chat. Saturday he saw his mother, talked to the doctor, and found a cat. Related lesson: Repeating auxiliary verbs2 The passé composé has three possible English equivalents. For example, j'ai dansé can mean 1. I danced (simple past) 2. I have danced (present perfect) 3. I did dance (past emphatic) One of the most striking differences between French and English is in verb tenses. Learning how to use the various past tenses can be very tricky, because English has several tenses which either do not exist in or do not translate literally into French - and vice versa. During the first year of French study, every student becomes aware of the troublesome relationship between the two main past tenses. L'imparfait [je mangeais] translates to the English imperfect [I was eating] while le passé composé [j'ai mangé] literally translates to the English present perfect [I have eaten] but can also be translated as the English simple past [I ate] or the emphatic past [I did eat]. It is extremely important to understand the distinctions between passé composé and imparfait in order to use them correctly and thus express past events accurately. Compare the uses of these two tenses in the following table. Imparfait1 Passé composé2 I. An ongoing action with no specified vs One or more events or actions completion that began and ended in the past J'allais en France - I was going to France Je suis allé en France - I went to
- 4. France Je visitais des monuments - I was visiting J'ai visité des monuments - I monuments visited some monuments II. A habitual or repeated action vs A single event Je voyageais en France tous les ans - I J'ai voyagé en France l'année traveled (used to travel) to France every dernière - I traveled in France last year year Je visitais souvent le Louvre - I often J'ai visité Paris samedi - I visited visited the Louvre Paris on Saturday III. Description/background info; set the ...when something happened, scene of how things were or what was interrupting the + happening when... (to be + -ing usually description/background. indicates this) J'étais à la banque quand... ... quand Chirac est arrivé. - I was at the bank when... - ... when Chirac arrived. Je vivais en Espagne quand... ... quand je l'ai trouvé. - I was living in Spain when... - ... when I found it. IV. General description of physical or vs Change in physical or mental mental state of being state at a precise moment or for an isolated cause J'avais peur des chiens - I was afraid of J'ai eu peur quand le chien a aboyé dogs - I was scared when the dog barked V. Expression of the time of day or age in the past Il était cinq heures du matin - It was five a.m. C'était son anniversaire; il avait douze ans - It was his birthday; he was twelve. Thus l'imparfait describes past situations, while le passé composé narrates specific events. In addition, l'imparfait can set the stage for an event expressed with the passé composé (see III, above). Compare the following passages: Quand j'avais 15 ans, je voulais être Un jour, je suis tombé malade et j'ai psychiatre. Je m'intéressais à la découvert les miracles de la médecine. J'ai psychologie parce que je connaissais fait la connaissance d'un médecin et j'ai beaucoup de gens très bizarres. Le week- commencé à étudier avec lui. Quand la end, j'allais à la bibliothèque et j'étudiais faculté de médecine m'a accepté, je n'ai pendant toute la journée. plus pensé à la psychologie. When I was 15, I wanted to be a One day, I got sick and discovered the psychiatrist. I was interested in psychology wonders of medicine. I met a doctor and because I knew a lot of really weird started studying with him. After the people. On the weekends, I used to go to medical school accepted me, I didn't think
- 5. the library and study all day. about psychology any more. The following key words and phrases can help you figure out whether to use l'imparfait or le passé composé: L'imparfait Le passé composé d'habitude usually une/deux (etc.) fois once/twice (etc.) de temps en temps from time to time plusieurs fois several times autrefois formerly soudainement suddenly le week-end on the weekends un week-end one weekend le lundi on Mondays lundi on Monday tous les jours every day un jour one day normalement usually tout d'un coup all of a sudden souvent often in general, en général generally chaque semaine, mois, every week, année... month, year le soir in the evenings Note: There is a third tense, le passé simple3, which technically translates to the English simple past tense, but is now used primarily in writing, in place of the passé composé Verbo 1ª Pª. Sing. 2ª Pª. Sing. 3ª Pª. Sing. 1ª Pª. Plur. 2ª Pª. Plur. 3ª Pª. Plur. Conditionnel avoir aurais aurais aurait aurions auriez auraient arriver arriverais arriverais arriverait arriverions arriveriez arriveraient aller irais irais irait irions iriez iraient connaître connaîtrais connaîtrais connaîtrait connaîtrions connaîtriez connaîtraient devoir devrais devrais devrait devrions devriez devraient dire dirais dirais dirait dirions diriez diraient dormir dormirais dormirais dormirait dormirions dormiriez dormiraient être serais serais serait serions seriez seraient
- 6. faire ferais ferais ferait ferions feriez feraient finir finirais finirais finirait finirions finiriez finiraient lire lirais lirais lirait lirions liriez liraient mettre mettrais mettrais mettrait mettrions mettriez mettraient naître naîtrais naîtrais naîtrait naîtrions naîtriez naîtraient partir partirais partirais partirait partirions partiriez partiraient pouvoir pourrais pourrais pourrait pourrions pourriez pourraient prendre prendrais prendrais prendrait prendrions prendriez prendraient regarder regarderais regarderais regarderait regarderions regarderiez regarderaient savoir saurais saurais saurait saurions sauriez sauraient sortir sortirais sortirais sortirait sortirions sortiriez sortiraient voir verrais verrais verrait verrions verriez verraient The French conditional mood is very similar to the English conditional mood. It describes events that are not guaranteed to occur; often they are dependent on certain conditions. While the French conditional mood has a full set of conjugations, the English equivalent is just the modal verb "would" + main verb. The French conditional is mainly used in si clauses1, to express what would happen if a condition were met: Il mangerait s'il avait faim. He would eat if he were hungry. Si nous étudiions, nous serions plus intelligents. If we studied, (then) we would be smarter. The verb vouloir2 is used in the conditional to express a polite request3: Je voudrais une pomme. I would like an apple. Je voudrais aller avec vous. I would like to go with you. However, you can't say "si vous voudriez"4 to mean "if you would like," because the French conditional can never be used after si. The verb aimer5 is used to express a polite desire, sometimes one that cannot be fulfilled: J'aimerais bien le voir ! I would really like to see it! J'aimerais y aller, mais je dois travailler I would like to go, but I have to work.
- 7. There is only one set of endings for all verbs, and most of them - even many which are irregular in the present tense - use their infinitive as the root. There are only about two dozen stem-changing1 or irregular verbs which have irregular conditional stems but take the same endings:* acheter > achèter- similar verbs: achever, amener, emmener, lever, promener appeler > appeller- similar verbs: épeler, jeter, projeter, rappeler aller > ir- avoir > aur- devoir > devr- envoyer > enverr- essayer > essaier- similar verbs: employer, ennuyer, nettoyer, payer être > ser- faire > fer- pleuvoir > pleuvr- pouvoir > pourr- savoir > saur- venir > viendr- similar verbs: devenir, parvenir, revenir voir > verr- similar verb: revoir vouloir > voudr- *Notes: 1. The conditional stem always ends in R. 2. The exact same verbs are irregular in the future2 and use the same stems. Verbo 1ª Pª. Sing. 2ª Pª. Sing. 3ª Pª. Sing. 1ª Pª. Plur. 2ª Pª. Plur. 3ª Pª. Plur.
- 8. Futur avoir aurai auras aura aurons aurez auront arriver arriverai arriveras arrivera arriverons arriverez arriveront aller irai iras ira irons irez iront connaître connaîtrai connaîtras connaîtra connaîtrons connaîtrez connaîtront devoir devrai devras devra devrons devrez devront dire dirai diras dira dirons direz diront dormir dormirai dormiras dormira dormirons dormirez dormiront être serai seras sera serons serez seront faire ferai feras fera ferons ferez feront finir finirai finiras finira finirons finirez finiront lire lirai liras lira lirons lirez liront mettre mettrai mettras mettra mettrons mettrez mettront naître naîtrai naîtras naîtra naîtrons naîtrez naîtront partir partirai partiras partira partirons partirez partiront pouvoir pourrai pourras pourra pourrons pourrez pourront prendre prendrai prendras prendra prendrons prendrez prendront regarder regarderai regarderas regardera regarderons regarderez regarderont savoir saurai sauras saura saurons saurez sauront sortir sortirai sortiras sortira sortirons sortirez sortiront voir verrai verras verra verrons verrez verront future tense the French future tense is very similar to the English future tense: it talks about upcoming events. While the French future tense has a full set of conjugations, the English equivalent is just the modal verb "will" + main verb. J'irai au magasin demain I will go to the store tomorrow. Ils mangeront dans l'avion They will eat on the plane. The French future tense can also be used in si clauses1, to express what will happen if a condition is met: Si j'ai le temps, je le ferai If I have time, I will do it. Je le ferai si j'ai le temps I will do it if I have time.
- 9. There are some differences between the French and English future tenses. 1. When the action of the verb after certain constructions* will take place in the future, the future tense is used in French, whereas in English the present tense is used. *après que (after), aussitôt que (as soon as), dès que (as soon as), espérer que (to hope that), lorsque (when), quand (when), une fois que (once): Quand il arrivera, nous mangerons. When he arrives, we will eat. Je vous téléphonerai dès que je pourrai. I'll call you as soon as I can. 2. In journalism and other factual narration, the future is often used in French even though the events are in the past. Né en Martinique, Aimé Césaire étudiera à Paris et redécouvrira l'Afrique Born in Martinique, Aimé Césaire studied in Paris and rediscovered Africa. 3. In French, the future can also be used for polite orders and requests2, in place of the vous form of the imperative: Vous fermerez la porte, s'il vous plaît. Close the door, please. To express something that is going to occur very soon, you can use the near future / futur proche3.
