Water Cycle Lesson PowerPoint, Hydrological Cycle, Biogeochemical Cycles Lesson
- 1. • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 3. • This will be the big concept in ecology that will be addressed in this portion of the unit. – or artificial.
- 4. • This will be the big concept in ecology that will be addressed in this portion of the unit. – or artificial.
- 5. • This will be the big concept in ecology that will be addressed in this portion of the unit. – Note: The cycles that we will learn move between the living and non-living world. r artificial.
- 6. • This will be the big concept in ecology that will be addressed in this portion of the unit. – Note: The cycles that we will learn move between the living and non-living world. r artificial.
- 7. • This will be the big concept in ecology that will be addressed in this portion of the unit. – Note: The cycles that we will learn move between the living and non-living world. r artificial.
- 8. New area of focus: Biogeochemical Cycles. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 9. Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 10. Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 11. Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 12. Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 13. Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 14. Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 15. Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 16. Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 17. Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 18. Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 26. Hydrosphere interacts with atmosphere (Water cycle) The atmosphere interacts with the ecosphere. (Plants and animals breath -Carbon Cycle and nitrogen cycle
- 27. Hydrosphere interacts with atmosphere (Water cycle) The atmosphere interacts with the ecosphere. (Plants and animals breath -Carbon Cycle and nitrogen cycle Living things change the lithosphere, become rock, erode the land. (Phosphorus Cycle)
- 28. Hydrosphere interacts with atmosphere (Water cycle) The atmosphere interacts with the ecosphere. (Plants and animals breath -Carbon Cycle and nitrogen cycle Living things change the lithosphere, become rock, erode the land. (Phosphorus Cycle) The Hydrosphere, Atmosphere, Ecosphere and Lithosphere all interact within the biosphere.
- 29. • Ecosphere: The surface of the earth and all the ecosystems. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 30. • Lithosphere: Below the surface, in the crust and mantle. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 31. • Hydrosphere: All waters not in atmosphere and lithosphere. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 32. • Atmosphere: The area of gases that surround the planet. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 33. A general theme for all of the biogeochemical cycles we will study. They go from the living world (biotic) to the non- living (abiotic). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 34. A general theme for all of the biogeochemical cycles we will study. They go from the living world (biotic) to the non- living (abiotic). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 35. The biogeochemical cycles we will study. Water cycle. Carbon cycle. Phosphorus cycle. Nitrogen cycle. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 36. The biogeochemical cycles we will study. Water cycle. Carbon cycle. Phosphorus cycle. Nitrogen cycle. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 37. The biogeochemical cycles we will study. Water cycle. Carbon cycle. Phosphorus cycle. Nitrogen cycle. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 38. The biogeochemical cycles we will study. Water cycle. Carbon cycle. Phosphorus cycle. Nitrogen cycle. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 39. The biogeochemical cycles we will study. Water cycle. Carbon cycle. Phosphorus cycle. Nitrogen cycle. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 40. • What is so special about the water in this photograph? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 41. • What is so special about the water in this photograph? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 42. • What is so special about the water in this photograph? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 43. • What is so special about the water in this photograph? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 44. • What is so special about the water in this photograph? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 45. • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter.
- 46. • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter. Water commonly exists in all three states of matter
- 47. • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter. Water commonly exists in all three states of matter Water exists commonly in its solid state
- 48. • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter. Water commonly exists in all three states of matter Water exists commonly in its solid state
- 49. • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter. Water exists commonly in its solid state
- 50. • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter. Water exists commonly in its solid state
- 51. • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter.
- 52. • On Mars, we can see that water is most abundant in its solid form of ice.
- 53. Planet that was believed to have no water at all
- 59. This next part helps when we study the water cycle
- 60. • Solid (s) has a definite shape and volume. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 65. • Liquid (l) Has definite volume but not shape. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 69. • Gas (g) No definite shape or volume. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 70. • Gas (g) No definite shape or volume. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 71. • Gas (g) No definite shape or volume. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 72. • Gas (g) No definite shape or volume. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 76. • Water can exist on earth as a solid, liquid, and gas. – Water is a liquid between 0 and 100 degrees Celsius. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 77. • Water can exist on earth as a solid, liquid, and gas. – Water is a liquid between 0 and 100 degrees Celsius. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 78. • Video! Simulation of water in a liquid form turning into a solid (ice). – How are the molecules behaving in a liquid state and solid state? – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SVR7tfsjPO0 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 79. • Activity! State your Matter – Teacher to give each group of students a solid block (Maybe ice), glass of water, and balloon filled with gas.
- 80. • Activity! State your Matter – Teacher to give each group of students a solid block (Maybe ice), glass of water, and balloon filled with gas.
- 81. • Activity! State your Matter – Teacher to give each group of students a solid block (Maybe ice), glass of water, and balloon filled with gas.
- 82. • Activity! State your Matter – Teacher to give each group of students a solid block (Maybe ice), glass of water, and balloon filled with gas.
- 83. • Activity! State your Matter – Teacher to give each group of students a solid block (Maybe ice), glass of water, and balloon filled with gas.
- 84. • Activity! State your Matter – Teacher to give each group of students a solid block (Maybe ice), glass of water, and balloon filled with gas.
- 85. • Activity! State your Matter – Teacher to give each group of students a solid block (Maybe ice), glass of water, and balloon filled with gas.
- 86. • Activity! State your Matter – Teacher to give each group of students a solid block (Maybe ice), glass of water, and balloon filled with gas.
- 87. • Activity! State your Matter – Teacher to give each group of students a solid block (Maybe ice), glass of water, and balloon filled with gas.
- 88. • Activity! State your Matter – Teacher to give each group of students a solid block (Maybe ice), glass of water, and balloon filled with gas.
- 89. • Activity! State your Matter – Teacher to give each group of students a solid block (Maybe ice), glass of water, and balloon filled with gas.
- 90. • Activity / video link (Extremely Optional) – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p440QWpHui8 – Assign three students to each hold a poster with the three states of matter. (Solid, Liquid, Gas) • When Zebra is dancing and singing fast person with gas poster must wave it around quickly. • When zebra is dancing normal wave the liquid poster at a normal speed. • When zebra is dancing slowly wave the solid poster extremely slow.
- 91. • Activity / video link (Extremely Optional) – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p440QWpHui8 – Assign three students to each hold a poster with the three states of matter. (Solid, Liquid, Gas) • When Zebra is dancing at a fast pace the person with gas poster must wave it around quickly / dance. • When zebra is dancing normal wave the liquid poster at a normal speed / slower dance. • When zebra is dancing slowly wave the solid poster extremely slow / slow dance.
- 92. • Based on the video, which is a solid, liquid, and gas.
- 93. • Based on the video, which is a solid, liquid, and gas.
- 94. • Based on the video, which is a solid, liquid, and gas.
- 95. • Based on the video, which is a solid, liquid, and gas.
- 96. • Based on the video, which is a solid, liquid, and gas.
- 97. • Based on the video, which is a solid, liquid, and gas.
- 98. • Based on the video, which is a solid, liquid, and gas.
- 99. • Based on the video, which is a solid, liquid, and gas.
- 100. • Based on the video, which is a solid, liquid, and gas.
- 101. • Based on the video, which is a solid, liquid, and gas.
- 102. • Based on the video, which is a solid, liquid, and gas.
- 103. • Activity / video link (Extremely Optional) – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p440QWpHui8 – Assign three students to each hold a poster with the three states of matter. (Solid, Liquid, Gas) • When Zebra is dancing and singing fast person with gas poster must wave it around quickly. • When zebra is dancing normal wave the liquid poster at a normal speed. • When zebra is dancing slowly wave the solid poster extremely slow.
- 104. • Activity / video link (Extremely Optional) – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p440QWpHui8 – Assign three students to each hold a poster with the three states of matter. (Solid, Liquid, Gas) • When Zebra is dancing and singing fast person with gas poster must wave it around quickly. • When zebra is dancing normal wave the liquid poster at a normal speed. • When zebra is dancing slowly wave the solid poster extremely slow.
- 105. • Activity / video link (Extremely Optional) – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p440QWpHui8 – Assign three students to each hold a poster with the three states of matter. (Solid, Liquid, Gas) • When Zebra is dancing and singing fast person with gas poster must wave it around quickly. • When zebra is dancing normal wave the liquid poster at a normal speed. • When zebra is dancing slowly wave the solid poster extremely slow.
- 106. • Activity / video link (Extremely Optional) – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p440QWpHui8 – Assign three students to each hold a poster with the three states of matter. (Solid, Liquid, Gas) • When Zebra is dancing and singing fast person with gas poster must wave it around quickly. • When zebra is dancing normal wave the liquid poster at a normal speed. • When zebra is dancing slowly wave the solid poster extremely slow.
- 107. • Activity / video link (Extremely Optional) – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p440QWpHui8 – Assign three students to each hold a poster with the three states of matter. (Solid, Liquid, Gas) • When Zebra is dancing and singing fast person with gas poster must wave it around quickly. • When zebra is dancing normal wave the liquid poster at a normal speed. • When zebra is dancing slowly wave the solid poster extremely slow.
- 108. • Activity / video link (Extremely Optional) – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p440QWpHui8 – Assign three students to each hold a poster with the three states of matter. (Solid, Liquid, Gas) • When Zebra is dancing and singing fast person with gas poster must wave it around quickly. • When zebra is dancing normal wave the liquid poster at a normal speed. • When zebra is dancing slowly wave the solid poster extremely slow.
- 109. • Activity / video link (Extremely Optional) – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p440QWpHui8 – Assign three students to each hold a poster with the three states of matter. (Solid, Liquid, Gas) • When Zebra is dancing and singing fast person with gas poster must wave it around quickly. • When zebra is dancing normal wave the liquid poster at a normal speed. • When zebra is dancing slowly wave the solid poster extremely slow.
- 110. • Video Link! (Optional) TMBG States of Matter – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=btGu9FWSPtc
- 119. Water is being continually created by many biophysicochemical processes. As such, water can be viewed as being constantly “refreshed” or “rejuvenated.”
- 120. Water is being continually created by many biophysicochemical processes. As such, water can be viewed as being constantly “refreshed” or “rejuvenated.” The water in dinosaur pee is not the same water that we drink. The H’s and O’s that make up H2O are the same ones present when the dinosaurs roamed the Earth.
- 121. New Area of Focus: The Water Cycle Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 122. New Area of Focus: The Water Cycle AKA – The Hydrologic Cycle Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 123. New Area of Focus: The Water Cycle AKA – The Hydrologic Cycle Driven by the sun and gravity. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 124. New Area of Focus: The Water Cycle AKA – The Hydrologic Cycle Driven by the sun and gravity. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 125. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 126. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Driven by the Sun
- 127. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Driven by the Sun
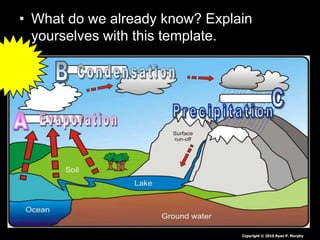
- 128. • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Driven by the Sun
- 129. • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 130. • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 131. • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 132. • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 133. • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 134. • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 135. • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 136. • Which of the other terms are we unsure of.. – Condensation – Evaporation – Precipitation – Percolation – Transpiration – Sublimation – Infiltration – Ocean Storage – Ground Water Storage – Freshwater discharge – Surface run-off Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 137. • Which of the other terms are we unsure of.. – Condensation – Evaporation – Precipitation – Percolation – Transpiration – Sublimation – Infiltration – Ocean Storage – Ground Water Storage – Freshwater discharge – Surface run-off Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 138. • Which of the other terms are we unsure of.. – Condensation – Evaporation – Precipitation – Percolation – Transpiration – Sublimation – Infiltration – Ocean Storage – Ground Water Storage – Freshwater discharge – Surface run-off Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 139. The hydrologic cycle (Water Cycle): Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 140. The hydrologic cycle (Water Cycle): The continuous movement of water on, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 141. The hydrologic cycle (Water Cycle): The continuous movement of water on, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 142. The hydrologic cycle (Water Cycle): The continuous movement of water on, above, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 143. The hydrologic cycle (Water Cycle): The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the earth. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 144. • Water Cycle Available Sheet
- 145. • Water Cycle Available Sheet
- 146. • Step by step drawing of the water cycle.
- 201. Evaporation: Substance changes from a liquid state to gas state (requires energy). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 202. Evaporation: Substance changes from a liquid state to gas state (requires energy). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 203. Evaporation: Substance changes from a liquid state to gas state (requires energy). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 204. • We usually think about oceans, but clouds also evaporate. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 205. Condensation: Water vapor (gas) turns back to a liquid. (Energy needs to be removed) - Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 206. Condensation: Water vapor (gas) turns back to a liquid. (Energy needs to be removed) Cloud formation. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 207. • Water Cycle Available Sheet
- 208. • Activity! Condensation – Teacher provides ice cold can of soda to table groups and students record temperature. – Students should observe each can for evidence of condensation.
- 209. • Activity! Condensation Questions. – Why did condensation droplets form on the cold soda can? • Where did the water come from?
- 210. • Activity! Condensation Questions. – Why did condensation droplets form on the cold soda can? • Where did the water come from? – Condensation formed on the cold soda can because water vapor near the soda can turned from a gas to a liquid.
- 211. • Cloud formation occurs with water vapor and condensation nuclei. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 213. Precipitation: Water that is so heavy it falls as liquid / solid. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 214. Precipitation: Water that is so heavy it falls as liquid / solid. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 215. • Precipitation can also be a solid in the form of snow, hail, or ice pellets. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 216. • Link! Water Cycle Flash Animation Tour – http://www.epa.gov/safewater/kids/flash/flash_ watercycle.html
- 217. • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 10 cm from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water about 10 cm. • Add food coloring if you wish. – Slide cup into the bottle to just above the warm water with cap on. – Fill top bottle (cup) with ice cubes. • Do not overfill. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) – Visual on next slide.
- 218. • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation)
- 219. • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) Soda bottle cut by teacher,
- 220. • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) Soda bottle cut by teacher,
- 221. • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) Soda bottle cut by teacher, Next fill bottle with very warm water and food coloring.
- 222. • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) Soda bottle cut by teacher, Next fill bottle with very warm water and food coloring.
- 223. • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) Soda bottle cut by teacher, then flipped, Next fill bottle with very warm water and food coloring.
- 224. • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) Soda bottle cut by teacher, then flipped, and filled with ice cubes by students. Next fill bottle with very warm water and food coloring.
- 225. • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) Soda bottle cut by teacher, then flipped, and filled with ice cubes by students. Next fill bottle with very warm water and food coloring.
- 226. • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) Soda bottle cut by teacher, then flipped, and filled with ice cubes by students. Next fill bottle with very warm water and food coloring. Strange kind of creepy video of water molecules in the hydrologic cycle as we wait (Optional 2 min) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=StPobH5ODTw
- 227. • Activity! Stranded on a Desert Island.
- 228. • Activity! Stranded on a Desert Island. – You and your group must use the materials provided (and the water cycle) to turn salt water into freshwater over the next several days in order to survive. Use the sun as the energy source. – Each group gets a clear plastic box, glass cup, plastic wrap, marbles / pebbles, salt water mixed with sand, and a bungee cord / large elastic. – Visual of materials on next slide. – Video Link of set-up. – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4sqRvUzqDCE
- 229. • Materials for the set-up. Saltwater and Sand Cup Marbles Elastic Plastic wrap
- 230. • Materials for the set-up. Saltwater and Sand Cup Marbles Elastic Plastic wrap
- 231. • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater.
- 232. • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater.
- 233. • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater. Saltwater evaporates from sun energy into vapor.
- 234. • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater. Saltwater evaporates from sun energy into vapor.
- 235. • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater. Saltwater evaporates from sun energy into vapor.
- 236. • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater. Saltwater evaporates from sun energy into vapor Leaves salt behind.
- 237. • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater. Colder temperatures on edge of container cause…
- 238. • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater. Colder temperatures on edge of container cause… Condensation
- 239. • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater. Water adheres to the plastic wrap, travels down and falls into the cup as freshwater…
- 240. • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater. Water adheres to the plastic wrap, travels down and falls into the cup as freshwater… Precipitation
- 241. • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater. Water adheres to the plastic wrap, travels down and falls into the cup as freshwater… Precipitation
- 242. • Sublimation: Solid state turns directly to a gas state skipping liquid phase. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 243. • Sublimation: Solid state turns directly to a gas state skipping liquid phase. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy See neat dry Ice Bubble: Sublimation (solid to gas) at… https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=76CNkxizQuc 2 min
- 247. Transpiration – Water released by plants into air. Non-living to the living, and back again. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 248. Transpiration – Water released by plants into air. Non-living to the living, and back again. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 249. Transpiration – Water released by plants into air. Non-living to the living, and back again. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 250. Transpiration – Water released by plants into air. Non-living to the living, and back again. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 251. Transpiration – Water released by plants into air. Non-living to the living, and back again. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 252. • Does this animation look like a water molecule leaving the leaf or a face? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 253. • Evapotranspiration is a vital component to the rainforest ecosystem. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 254. • Evapotranspiration is a vital component to the rainforest ecosystem. – Evapotranspiration describes water that is turned into a gas by evaporation, and water vapor released by plants (transpiration). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 255. • Activity! Transpiration. – Place a clear plastic bag over a section of plant. – Secure bag at base of stem so it is relatively tight. – Water plant and set in the sun. – Observe water droplets / evidence of transpiration the next day.
- 256. • Activity! Transpiration. – Place a clear plastic bag over a section of plant. – Secure bag at base of stem so it is relatively tight. – Water plant and set in the sun. – Observe water droplets / evidence of transpiration the next day.
- 257. • Activity! Transpiration. – Place a clear plastic bag over a section of plant. – Secure bag at base of stem so it’s relatively tight. – Water plant and set in the sun. – Observe water droplets / evidence of transpiration the next day.
- 258. • Activity! Transpiration. – Place a clear plastic bag over a section of plant. – Secure bag at base of stem so it’s relatively tight. – Water plant and set in the sun. – Observe water droplets / evidence of transpiration the next day.
- 259. • Activity! Transpiration. – Place a clear plastic bag over a section of plant. – Secure bag at base of stem so it’s relatively tight. – Water plant and set in the sun. – Observe water droplets / evidence of transpiration the next day.
- 261. Alternative method / extension at… http://gcuonline.georgian.edu/wootton/transpiration.htm
- 262. Surface run-off: The water flow which occurs when soil is full to capacity and excess water travels over the land. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 263. Surface run-off: The water flow which occurs when soil is full to capacity and excess water travels over the land. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Capacity: ?
- 264. Surface run-off: The water flow which occurs when soil is full to capacity and excess water travels over the land. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Capacity: The maximum amount that can be obtained in a body.
- 265. • Storage of water in vegetation. – Plants soak up and hold water. They are very good flood preventers. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 266. • Storage of water in vegetation. – Plants soak up and hold water. They are very good flood preventers. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Trees can hold enormous amounts of water.s
- 267. • Storage of water in vegetation. – Plants soak up and hold water. They are very good flood preventers. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Trees can hold enormous amounts of water.s
- 268. • Storage of water in vegetation. – Plants soak up and hold water. They are very good flood preventers. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 269. • Storage of water in vegetation. – Plants soak up and hold water. They are very good flood preventers. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Trees help control flooding by holding water in their tissues.
- 270. • Percolation: The slow movement of water through the soil. Cleans and purifies. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 271. Filtering Water Activity / Infiltration
- 272. Soda bottle cut by teacher or parent, Filtering Water Activity / Infiltration
- 273. Soda bottle cut by teacher or parent, invert the top like so. Filtering Water Activity / Infiltration
- 274. Soda bottle cut by teacher or parent, invert the top like so. Add cap Filtering Water Activity / Infiltration
- 275. Soda bottle cut by teacher or parent, invert the top like so. Add cap Filtering Water Activity / Infiltration Teacher is going to create nasty water with coffee grounds, garlic powder, and vegetable oil, and salt.
- 276. Soda bottle cut by teacher or parent, invert the top like so. Add cap Your group must brainstorm methods to filter water, bring in the materials as a group and assemble tomorrow. Filtering Water Activity / Infiltration Teacher is going to create nasty water with coffee grounds, garlic powder, and vegetable oil, and salt.
- 277. Soda bottle cut by teacher or parent, invert the top like so. Add cap Your group must brainstorm methods to filter water, bring in the materials as a group and assemble tomorrow. Filtering Water Activity / Infiltration Teacher is going to create nasty water with coffee grounds, garlic powder, and vegetable oil, and salt. Teacher will add dirty water to the top.
- 278. Soda bottle cut by teacher or parent, invert the top like so. Add cap Your group must brainstorm methods to filter water, bring in the materials as a group and assemble tomorrow. Filtering Water Activity / Infiltration Teacher is going to create nasty water with coffee grounds, garlic powder, and vegetable oil, and salt. Teacher will add dirty water to the top. Filtering Materials
- 279. Soda bottle cut by teacher or parent, invert the top like so. Add cap Your group must brainstorm methods to filter water, bring in the materials as a group and assemble tomorrow. Filtering Water Activity / Infiltration Teacher is going to create nasty water with coffee grounds, garlic powder, and vegetable oil, and salt. Teacher will add dirty water to the top. Filtering Materials How clear can your group get the water?
- 280. • Answer: Percolation trapped the larger particles as the water moves through the soil.
- 281. • Answer: Percolation trapped the larger particles as the water moves through the soil.
- 283. • Groundwater discharge: Water that has been underground seeps back into the oceans, or into rivers or lakes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 284. • Groundwater is a very important source of clean water. – It can be obtained by digging a well, or when it comes to the surface as a spring. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 285. • Groundwater is a very important source of clean water. – It can be obtained by digging a well, or when it comes to the surface as a spring. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 286. • Water can be stored in… – Oceans – Ice / snow – Surface water – Groundwater – Soil and Organisms – Atmosphere Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 287. • Water can be stored in… – Oceans – Ice / snow – Surface water – Groundwater – Soil and Organisms – Atmosphere Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 288. • Water can be stored in… – Oceans – Ice / snow – Surface water – Groundwater – Soil and Organisms – Atmosphere Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 289. • Water can be stored in… – Oceans – Ice / snow – Surface water – Groundwater – Soil and Organisms – Atmosphere Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 290. • Water can be stored in… – Oceans – Ice / snow – Surface water – Groundwater – Soil and Organisms – Atmosphere Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 291. • Water can be stored in… – Oceans – Ice / snow – Surface water – Groundwater – Soil and Organisms – Atmosphere Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 292. • Water can be stored in… – Oceans – Ice / snow – Surface water – Groundwater – Soil and Organisms – Atmosphere Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 293. • Activity! Not Smart Board. – Teacher on next slide to minimize out of slideshow. – Students should drag the terms to the correct position on the picture. – Answer revealed after.
- 299. Possible Answer
- 300. • Video Song! (Optional) The Water Cycle. – Very strange but extremely catchy. – Teacher should preview prior as it contains some strange parts. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Zejk_iNFfPA Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 301. • Water Cycle Available Sheet
- 302. 7. 8.) Which term is not shown. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 303. 7. 8.) Which term is not shown. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Driven by the Sun
- 304. • Quiz 1-7 The hydrologic cycle. Please record the numbers and the correct term. 7. 8.) Which term is not shown. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 305. • Quiz 1-7 The hydrologic cycle. Please record the numbers and the correct term. 7. 8.) Which term is not shown. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 306. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 307. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 308. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 309. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 310. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 311. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 312. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 313. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 314. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 315. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Runoff Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 316. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Runoff Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 317. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface RunoffPercolation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 318. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface RunoffPercolation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 319. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface RunoffPercolation Ground Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 320. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface RunoffPercolation Ground Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy What terms was missing that we learned?
- 321. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Run-offPercolation Ground Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sublimation #8 Sublimation
- 323. “For those who haven’t contributed yet…”
- 324. • Quiz 1-8 The hydrologic cycle. Please record the numbers and the correct term. 7. 8.) Which term is not shown. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 325. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 326. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 327. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Evapotranspiration Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 328. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Evapotranspiration Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 329. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 330. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 331. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 332. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 333. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Run-off Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 334. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Run-off Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 335. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Run-offPercolation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 336. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Run-offPercolation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 337. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Run-offPercolation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 338. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Run-offPercolation Ground Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 339. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Run-offPercolation Ground Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy What terms was missing that we learned?
- 340. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Run-offPercolation Ground Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sublimation #8 Sublimation
- 342. “There are a few who still haven’t gone.”…
- 343. • Quiz 1-8 The hydrologic cycle. Please record the numbers and the correct term. 7. 8.) Which term is not shown. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 344. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 345. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 346. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 347. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 348. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 349. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 350. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 351. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 352. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Runoff Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 353. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Runoff Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 354. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface RunoffPercolation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 355. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface RunoffPercolation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 356. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface RunoffPercolation Ground Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 357. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface RunoffPercolation Ground Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy What terms was missing that we learned?
- 358. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Run-offPercolation Ground Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sublimation #8 Sublimation
- 359. • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. 7. Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Surface Run-offPercolation Ground Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Sublimation #8 Sublimation Learn more about the hydrologic cycle at… http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/watercycle.html
- 369. • You can now complete this question on the bundled homework package on page 6
- 370. • You can now complete this question on the bundled homework package on page 6
- 372. • Please label the picture below. – Just in case on page 7.
- 373. • Please label the picture below. – Just in case on page 7.
- 375. • Try and identify the picture beneath the squares. – Raise your hand when you think you know. You only get one guess. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 387. • Try and identify the picture beneath the squares. – Raise your hand when you think you know. You only get one guess. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 402. • Try Again! Try and identify the picture beneath the squares. – Raise your hand when you think you know. You only get one guess. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 417. • Video Link! Water and Carbon Cycle Crash Course. – Advanced and Optional – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2D7hZpIYlCA&l ist=PL8dPuuaLjXtNdTKZkV_GiIYXpV9w4WxbX
- 419. • More Units Available at… Earth Science: The Soil Science and Glaciers Unit, The Geology Topics Unit, The Astronomy Topics Unit, The Weather and Climate Unit, and The River Unit, The Water Molecule Unit. Physical Science: The Laws of Motion and Machines Unit, The Atoms and Periodic Table Unit, The Energy and the Environment Unit, and The Introduction to Science / Metric Unit. Life Science: The Diseases and Cells Unit, The DNA and Genetics Unit, The Life Topics Unit, The Plant Unit, The Taxonomy and Classification Unit, Ecology: Feeding Levels Unit, Ecology: Interactions Unit, Ecology: Abiotic Factors, The Evolution and Natural Selection Unit and The Human Body Systems and Health Topics Unit. Copyright © 2011 www.sciencepowerpoint.com LLC.
- 420. • “AYE” Advance Your Exploration ELA and Literacy Opportunity Worksheet – Visit some of the many provided links or.. – Articles can be found at (w/ membership to NABT and NSTA) • http://www.nabt.org/websites/institution/index.php?p= 1 • http://learningcenter.nsta.org/browse_journals.aspx?j ournal=tst Please visit at least one of the “learn more” educational links provided in this unit and complete this worksheet
- 421. • “AYE” Advance Your Exploration ELA and Literacy Opportunity Worksheet – Visit some of the many provided links or.. – Articles can be found at (w/ membership to NABT and NSTA) • http://www.nabt.org/websites/institution/index.php?p=1 • http://learningcenter.nsta.org/browse_journals.aspx?jo urnal=tst
- 422. • This PowerPoint is one small part of my Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit. This unit includes… • A 4 Part 2,400+ Slide PowerPoint • 14 page bundled homework packaged that chronologically follows PowerPoint, + modified version • 16 pages of unit notes with visuals • 2 PowerPoint review games • Rubrics, Answer Keys, games, and much more. • http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Abiotic_F actors_Unit.html
- 424. Areas of Focus within The Ecology: Abiotic Factors Unit Abiotic Factors, Biotic Factors, The Big 7 Abiotic Factors, Organisms Range of Tolerance, Light, How light affects Organisms, Photosynthesis, Factors in the Environment that Affect the Amount of Light, How Organisms Movements are affected by light, Bioluminescence, How temperature affects organisms, Thermoregulation, Physiological Regulation, Behavioral Regulation, Adaptation, Hypothermia, Hyperthermia, Warm-Bloodedness (endothermy), Cold-Bloodedness, Hibernation / Torpor, Advantages of Warm-Bloodedness, Disadvantages of Warm-Bloodedness, Advantages of Cold-Bloodedness, Disadvantages of Cold- Bloodedness, Water, Water Requirements and Plants, Adaptations of Plants and Water, Adaptations of Animals and Water, Wind, Positives and Negatives of Wind to Organisms, How animals use Wind, How Plants use Wind, Wind Dispersal, Water Dispersal, McArthur- Wilson Island Biogeography Theory, Animal Seed Dispersal, Fire Ecology, Fire Dependence, Biogeochemical Cycles, Water Cycle, Carbon Cycle, Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration, Oxygen-Carbon Dioxide Balance, Nitrogen Cycle, Phosphorus Cycle, Importance of Phosphorus, Nutrients, Nutrient Pollution and Aquatic Systems, Eutrophification. Full Unit can be found at… http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Abiotic_Factors_Unit.html
- 430. • More Units Available at… Earth Science: The Soil Science and Glaciers Unit, The Geology Topics Unit, The Astronomy Topics Unit, The Weather and Climate Unit, and The River Unit, The Water Molecule Unit. Physical Science: The Laws of Motion and Machines Unit, The Atoms and Periodic Table Unit, The Energy and the Environment Unit, and The Introduction to Science / Metric Unit. Life Science: The Diseases and Cells Unit, The DNA and Genetics Unit, The Life Topics Unit, The Plant Unit, The Taxonomy and Classification Unit, Ecology: Feeding Levels Unit, Ecology: Interactions Unit, Ecology: Abiotic Factors, The Evolution and Natural Selection Unit and The Human Body Systems and Health Topics Unit. Copyright © 2011 www.sciencepowerpoint.com LLC.
- 431. • Please visit the links below to learn more about each of the units in this curriculum – These units take me about four years to complete with my students in grades 5-10. Earth Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Geology Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Geology_Unit.html Astronomy Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Astronomy_Unit.html Weather and Climate Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Weather_Climate_Unit.html Soil Science, Weathering, More http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Soil_and_Glaciers_Unit.html Water Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Water_Molecule_Unit.html Rivers Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/River_and_Water_Quality_Unit.html = Easier = More Difficult = Most Difficult 5th – 7th grade 6th – 8th grade 8th – 10th grade
- 432. Physical Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Science Skills Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Science_Introduction_Lab_Safety_Metric_Methods. html Motion and Machines Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Newtons_Laws_Motion_Machines_Unit.html Matter, Energy, Envs. Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Energy_Topics_Unit.html Atoms and Periodic Table Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Atoms_Periodic_Table_of_Elements_Unit.html Life Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Human Body / Health Topics http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Human_Body_Systems_and_Health_Topics_Unit.html DNA and Genetics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/DNA_Genetics_Unit.html Cell Biology Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Cellular_Biology_Unit.html Infectious Diseases Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Infectious_Diseases_Unit.html Taxonomy and Classification Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Taxonomy_Classification_Unit.html Evolution / Natural Selection Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Evolution_Natural_Selection_Unit.html Botany Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Plant_Botany_Unit.html Ecology Feeding Levels Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Feeding_Levels_Unit.htm Ecology Interactions Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Interactions_Unit.html Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Abiotic_Factors_Unit.html
- 433. • The entire four year curriculum can be found at... http://sciencepowerpoint.com/ Please feel free to contact me with any questions you may have. Thank you for your interest in this curriculum. Sincerely, Ryan Murphy M.Ed www.sciencepowerpoint@gmail.com
- 434. • Thank you for your time and interest in this curriculum tour. Please visit the welcome / guide on how a unit works and link to the many unit previews to see the PowerPoint slideshows, bundled homework, review games, unit notes, and much more. Thank you for your interest and please feel free to contact me with any questions you may have. Best wishes. • Sincerely, • Ryan Murphy M.Ed • ryemurf@gmail.com
