Taxonomy and Classification Lesson PowerPoint
- 1. Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Archaea Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 11. • RED SLIDE: These are notes that are very important and should be recorded in your science journal. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 12. -Please make notes legible and use indentations when appropriate. -Example of indent. -Skip a line between topics -Don’t skip pages -Make visuals clear and well drawn.
- 13. • RED SLIDE: These are notes that are very important and should be recorded in your science journal. • BLACK SLIDE: Pay attention, follow directions, complete projects as described and answer required questions neatly. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 14. • Keep an eye out for “The-Owl” and raise your hand as soon as you see him. – He will be hiding somewhere in the slideshow “Hoot, Hoot” “Good Luck!” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 18. • Remember! – Humans share, and are deeply connected to the millions of species that exist on this planet. Without them, the systems that support life on this planet would fail. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 19. Taxonomy and Classification Unit Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 20. • Let’s go around the room and share where we live.
- 21. • Let’s now break it down from large to small or from broad to specific. ––––––––- This unit belongs to Ryan P. Murphy Copyright 2010 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 22. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States New Hampshire Merrimack County Andover Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 23. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States New Hampshire Merrimack County Andover Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 24. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States New Hampshire Merrimack County Andover Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 25. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States New Hampshire Merrimack County Andover Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 26. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States New Hampshire Merrimack County Andover Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 27. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States New Hampshire Merrimack County Andover Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 28. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States New Hampshire Merrimack County Andover Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 29. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States Our State Merrimack County Andover Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 30. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States Our State Our County Our Town Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 31. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States Our State Our County Our Town Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 32. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States Our State Our County Our Town Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 33. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States Our State Our County Our Town Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 34. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States Our State Our County Our Town Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 35. • You live, from broad to specific… – – – – – – – – – – The Cosmos The Milkyway Galaxy The Sol System (solar system) Planet Earth North American Continent United States Our State Our County Our Town Address • Number on road • Apartment at this number. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 36. • Please classify the organization of your grade at school. Include how the school organizes you, and how you organize yourselves. (work in table groups) (Must be respectful of others!) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 37. • You are classified by… – U.S Citizens – State Residents – County Residents – Town Residents – By Age – By homeroom • Gender – By peer groups • Umm Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 38. • You are classified by… – U.S Citizens – State Residents – County Residents – Town Residents – By Age – By homeroom • Gender – By peer groups • Umm Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 39. • You are classified by… – U.S Citizens – State Residents – County Residents – Town Residents – By Age – By homeroom • Gender – By peer groups • Umm Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 40. • You are classified by… – U.S Citizens – State Residents – County Residents – Town Residents – By Age – By homeroom • Gender – By peer groups • Umm Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 41. • You are classified by… – U.S Citizens – State Residents – County Residents – Town Residents – By Age – By homeroom • Gender – By peer groups • Umm Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 42. • You are classified by… – U.S Citizens – State Residents – County Residents – Town Residents – By Age – By homeroom • Gender – By peer groups • Umm Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 43. • You are classified by… – U.S Citizens – State Residents – County Residents – Town Residents – By Age – By homeroom • Gender – By peer groups • Umm Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 44. • You are classified by… – U.S Citizens – State Residents – County Residents – Town Residents – By Age – By homeroom • Gender – By peer groups • Umm Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 45. • Taxonomy and Classification Available Sheet. – Follows slideshow for classwork.
- 46. • Taxonomy and Classification Available Sheet. – Follows slideshow for classwork.
- 47. • Activity! Pile of Sneakers. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 48. • Activity! Pile of Sneakers. – Take off one of your sneakers / footwear and place it in a pile in the middle of the classroom. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 49. • Activity! Pile of Sneakers. – Take off one of your sneakers / footwear and place it in a pile in the middle of the classroom. – Classify the types of footwear into different groups based on their similarities and differences. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 50. • Activity! Pile of Sneakers. – Take off one of your sneakers / footwear and place it in a pile in the middle of the classroom. – Classify the types of footwear into different groups based on their similarities and differences. – Describe the physical features of each group, why are they placed where they are? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 51. • Other Option. Nuts and Bolts Classification. – Please arrange the bolts into groups that have similar characteristics (a few groups). – Describe the physical features of each group, why are they placed where they are? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 52. “Has anyone seen my shoes?” “I left them somewhere.”
- 53. Taxonomy: The science of classification. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 54. • Modern taxonomic classification, based on the natural concepts and system of the Swedish botanist Carolus Linnaeus. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 55. • Modern taxonomic classification, based on the natural concepts and system of the Swedish botanist Carolus Linnaeus. Learn more about Carolus Linnaeus at.. http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/history/linnaeus.html Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 56. • Which portrait is of Carolus Linnaeus?
- 57. • Which portrait is of Carolus Linnaeus?
- 58. • Which portrait is of Carolus Linnaeus? • King Phillip of Spain
- 59. • Which portrait is of Carolus Linnaeus? • King Phillip of Spain
- 60. • Which portrait is of Carolus Linnaeus? • King Phillip of Spain Carolus Linnaeus
- 61. • Which portrait is of Carolus Linnaeus? • Carolus Linnaeus King Phillip of Spain
- 62. • Which portrait is of Carolus Linnaeus? • Carolus Linnaeus King Phillip of Spain
- 63. • Which portrait is of Carolus Linnaeus? • Carolus Linnaeus King Phillip of Spain
- 64. • Which portrait is of Carolus Linnaeus? • Carolus Linnaeus King Phillip of Spain
- 65. • Which portrait is of Carolus Linnaeus? • Carolus Linnaeus King Phillip of Spain
- 66. Classification is a very broad term which simply means putting things into groups. Taxonomy means giving names to things. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 67. Classification is a very broad term which simply means putting things into groups. Taxonomy means giving names to things. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 68. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 69. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 70. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 71. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 72. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 73. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 74. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 75. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 76. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 77. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 78. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 79. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 80. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 81. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 82. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 83. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 84. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 85. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 86. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 87. • How well do you know some common wildlife by their taxonomic names? Danaus plexippus Micropterus salmoides Bos taurus Marmota monax Notophthalmus viridescens Meleagris gallopavo Cyanocitta cristata Rana Catesbiana Odocoileus virginianus Groundhog White Tailed Deer Largemouth Bass Domestic cow Blue Jay Turkey Newt Bull Frog Monarch Butterfly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 88. • Class Poll, Which naming system do you prefer, common names or scientific names? Common Names Science Names • Should we use the science system or the common system? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 89. • Note: The next hundred slides are going to be a bit silly.
- 90. • Note: The next hundred slides are going to be a bit silly. – Only by exposing the silliness of common names will you see the importance of a naming and classification system.
- 91. • Note: The next hundred slides are going to be a bit silly. – Only by exposing the silliness of common names will you see the importance of a naming and classification system.
- 92. • Note: The next hundred slides are going to be a bit silly. – Only by exposing the silliness of common names will you see the importance of a naming and classification system.
- 93. • These are the birds that border forests near grasslands in the central United States. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 94. • Which bird do you think is the Red Breasted Black Bird? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 95. • Answer! Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 96. • Which bird is the Brown Bird?
- 97. • Answer! Umm Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 98. • What animal is this? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 99. • Answer – Black bear (Ursus Americanus) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 100. • What animal is this? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 101. • Answer – Brown Bear (Ursus arctos) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 102. • What animal is this? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 103. • Answer – I’m not quite sure but I would guess White Bear. – Aren’t we using colors to identify? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 104. • Having simple descriptive names for a species doesn’t work. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 105. • Having simple descriptive names for a species doesn’t work. I see five black colored bears, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 106. • Having simple descriptive names for a species doesn’t work. I see five black colored bears, and three brown colored bears. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 107. • Having simple descriptive names for a species doesn’t work. I see five black colored bears, and three brown colored bears. One white bear, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 108. • Having simple descriptive names for a species doesn’t work. I see five black colored bears, and three brown colored bears. One white bear, and one black and white bear, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 109. • Having simple descriptive names for a species doesn’t work. I see five black colored bears, and three brown colored bears. One white bear, and one black and white bear, and a few kinda of brown and black with some white. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 110. • What animal is this? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 111. • Answer – Koala Marsupial (Phascolarctos cinereus) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 112. • Answer – Koala Marsupial (Phascolarctos cinereus) It’s not a bear. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 113. • Which one is the Daddy Long Legs?
- 114. • Which one is the Daddy Long Legs?
- 115. • Which one is the Daddy Long Legs?
- 116. • Which one is the Daddy Long Legs?
- 117. • Which one is the Daddy Long Legs?
- 118. • Which one is the Daddy Long Legs? Science Name Pholcus phalangioides
- 119. • How can you use simple descriptive features to name single celled organisms like this ciliate? – There are millions of different singled celled species. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 120. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 121. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 122. • The Catfish (Ictiobus bubalus) is not a mammal like a cat. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 123. • The Catfish (Ictiobus bubalus) is not a mammal like a cat. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 124. • Am I also a cat since I have whiskers?
- 125. • Am I also a cat since I have whiskers? Mammalian Order Pinnipedia, in the family Odobenidae.
- 126. • Star fish (Asterias Forbesii) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 127. • Star fish (Asterias Forbesii) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 128. • Star fish (Asterias Forbesii) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 133. • Seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis)
- 134. • What am I?
- 135. • What am I?
- 136. • What am I? Clownfish
- 137. • What are these? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 138. • What are these? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 139. • What will happen when I type cat tails on the internet? Which will I get? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 140. • Water flea
- 141. • Water flea Cat Flea
- 142. • Water flea Cat Flea
- 143. • What animal is this? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 144. • Answer – Mountain Lion Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 145. • What animal is this? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 146. • Answer – Puma Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 147. • What animal is this? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 148. • Answer – Catamount. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 149. • What animal is this? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 150. • Answer – Cougar Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 151. • What animal is this? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 152. • Answer – Panther Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 153. • What animal is this? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 154. • Answer – Silberlöwe (German) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 155. • What animal is this? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 156. • Answer – пума (Russian) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 157. • What animal are all of these? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 158. • Are you ready for the very confusing science name? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 159. One name, for the whole planet. Puma concolor
- 160. One name, for the whole planet.
- 161. One name, for the whole planet.
- 162. • Science classification uses characteristics to name species. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 163. • Science classification uses characteristics to name species. • Puma concolor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 164. • Science classification uses characteristics to name species. • Puma concolor Felis Catus domesticus Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 165. • Science classification uses characteristics to name species. • Puma concolor Felis Catus domesticus Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 166. • The science name becomes the universal name for the whole world to study and understand. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 167. • There are about 1.3 million known species of living organisms Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 168. • There are about 1.3 million known species of living organisms Neat news article about the number of species on planet earth at… http://www.nytimes.com/2011/08/30/science/30species.html?_r=0 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 169. • Estimates range the number of species on this planet between 10-100 million. – Imagine 100 million common names based on…? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 170. • Taxonomy and Classification Available Sheet. – Follows slideshow for classwork.
- 171. • Which naming system makes more sense? Common Names Science Names • Should we use the science system or the common system? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 172. A species… Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 173. Is a group of organisms with similar characteristics. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 174. Must produces fertile offspring. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 175. • A mule is the offspring of a male donkey and a female horse. A mule is almost always sterile. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 176. • A mule is the offspring of a male donkey and a female horse. A mule is almost always sterile. – Donkey Equus assinus has 62 chromosomes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 177. • A mule is the offspring of a male donkey and a female horse. A mule is almost always sterile. – Donkey Equus assinus has 62 chromosomes. – Horse Equus caballus 64 chromosomes Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 178. • A mule is the offspring of a male donkey and a female horse. A mule is almost always sterile. – Donkey Equus assinus has 62 chromosomes. – Horse Equus caballus 64 chromosomes • Doesn’t make an embryo well. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 179. • A mule is the offspring of a male donkey and a female horse. A mule is almost always sterile. – Donkey Equus assinus has 62 chromosomes. – Horse Equus caballus 64 chromosomes • Doesn’t make an embryo well. Note: Some hybrids such as the Coywolf (Coyote X Wolf) can reproduce. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 180. • A mule is not a species but a hybrid between a horse and a donkey. – The correct scientific classification is hybrid (Equus caballus x Equus assinus). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 181. • Can these two mate? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 182. • Horse zebra hybrid (sterile), called a Zebroid. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 183. • What is a Tigon?
- 187. “Pretend I’m a female lion.”
- 189. • Tigon: Offspring of a male tiger Panthera tigris and a female lion Panthera leo. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 190. • What is a Liger?
- 194. “Pretend I’m a female Tiger.”
- 196. • Liger: Offspring of a male lion Panthera leo and a female tiger Panthera tigris. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 197. • Which name is real and which is made up for this Polar Bear x Grizzly Bear Hybrid? – Grolar Bear of Polgrizz Bear
- 198. • Which name is real and which is made up for this Polar Bear x Grizzly Bear Hybrid? – Grolar Bear of Polgrizz Bear
- 199. • Which name is real and which is made up for this Polar Bear x Grizzly Bear Hybrid? – Grolar Bear of Polgrizz Bear
- 200. • Which name is real and which is made up for this Polar Bear x Grizzly Bear Hybrid? – Grolar Bear of Polgrizz Bear
- 201. • Which name is real and which is made up for this Polar Bear x Grizzly Bear Hybrid? – Grolar Bear of Polgrizz Bear
- 202. • Which name is real and which is made up for this Polar Bear x Grizzly Bear Hybrid? – Grolar Bear of Polgrizz Bear as a pizzly bear or grizlar, Also known
- 203. • Which name is real and which is made up for this Polar Bear x Grizzly Bear Hybrid? – Grolar Bear of Polgrizz Bear as a pizzly bear or grizlar, Also known Ursus × inopinatus
- 210. Domestic Cow Bos taurus, and the American bison, Bison bison
- 211. Domestic Cow Bos taurus, and the American bison, Bison bison
- 212. Cross of the yak (Bos grunniens) and the American bison (Bison bison)
- 213. Cross of the yak (Bos grunniens) and the American bison (Bison bison)
- 217. Has similar DNA. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 218. • Can a bird and a dog mate?
- 221. • Why two very different species generally can’t mate. – Chromosomal differences • If closely related then can happen (hybrids) – Most of the time the differences are large. – Behavioral differences • Mating behaviors, times, seasons, locations are different. • Structure differences between the two species. – Internal chemistry differences • Hormones, ovulation, sperm and egg enzyme differences.
- 222. • Why two very different species generally can’t mate. – Chromosomal differences • If closely related then can happen (hybrids) – Most of the time the differences are large. – Behavioral differences • Mating behaviors, times, seasons, locations are different. • Structure differences between the two species. – Internal chemistry differences • Hormones, ovulation, sperm and egg enzyme differences.
- 223. • It doesn’t work like this
- 224. • It doesn’t work like this (Hippocrab)
- 225. • Or this… (Crocodillafrog)
- 226. • Or Croc-A-fly
- 227. • Or this Zebrant
- 228. • Or Rhinochicken
- 229. • Or Doggyhorse
- 230. • Or this Dorse
- 231. • Or Pugrilla
- 232. • Or Gerbilon
- 233. • Or the Squirolf
- 234. • Or the turteraffe
- 235. • Or Dogman
- 236. • Or Sharkbird
- 237. • Or thankfully this…
- 238. • Or thankfully this… Shark-A-kitty
- 239. Phylogeny -The history of a species as they change through time. Who came from whom? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 240. • Phylogenetic tree: A tree like chart showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 241. • A clade is a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all descendants of that ancestor.
- 242. • A clade is a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all descendants of that ancestor.
- 243. • A clade is a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all descendants of that ancestor.
- 244. • A clade is a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all descendants of that ancestor.
- 245. • A clade is a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all descendants of that ancestor.
- 246. • A clade is a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all descendants of that ancestor.
- 247. • A clade is a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all descendants of that ancestor.
- 248. • A clade is a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all descendants of that ancestor.
- 249. • A clade is a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all descendants of that ancestor.
- 250. • Which colored clades are correct?
- 251. • Which colored clades are correct?
- 252. • Which colored clades are correct?
- 253. • Which colored clades are correct?
- 254. • Which colored clades are correct?
- 255. • Which colored clades are correct?
- 256. • Which colored clades are correct?
- 257. • Which colored clades are correct?
- 258. • Which colored clades are correct?
- 259. • Which colored clade is incorrect?
- 260. • Which colored clade is incorrect?
- 261. • Who is more closely related to the Coyote? – The Gray Wolf or the Red Fox?
- 262. • Who is more closely related to the Coyote? – The Gray Wolf or the Red Fox?
- 263. • Who is more closely related to the Crab Eating Fox? – The Gray Fox or the Maned Wolf ?
- 264. • Who is more closely related to the Crab Eating Fox? – The Gray Fox or the Maned Wolf ?
- 265. • Who is more closely related to the Cape Hunting Dog? – The Domestic Dog or the Bush Dog?
- 266. • Who is more closely related to the Cape Hunting Dog? – The Domestic Dog or the Bush Dog?
- 267. • Which species is the oldest?
- 268. • Which species is the oldest?
- 269. • Which species is the youngest?
- 270. • Which species is the youngest?
- 271. • Which species evolved from SCYPHOZOA?
- 272. • Which species evolved from SCYPHOZOA?
- 273. • Which two species are considered TRIPLOBLAST?
- 274. • Which two species are considered TRIPLOBLAST?
- 275. • Which two species are considered TRIPLOBLAST?
- 277. Learn more about phylogeny at… http://tolweb.org/tree/learn/concepts/whatisphylogeny.html
- 278. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 279. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 280. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 281. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 282. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 283. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 284. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 285. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 286. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 287. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 288. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 289. • Taxonomy and Classification Available Sheet. – Follows slideshow for classwork.
- 290. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs?___________ – I have feathers but don’t swim?________ – I have no feathers or legs?______ – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 291. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim?________ – I have no feathers or legs?______ – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 292. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim?________ – I have no feathers or legs?______ – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 293. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim? Hen – I have no feathers or legs?______ – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 294. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim? Hen – I have no feathers or legs?______ – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 295. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim? Hen – I have no feathers or legs? Snake – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 296. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim? Hen – I have no feathers or legs? Snake – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 297. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim? Hen – I have no feathers or legs? Snake – I have feathers and swim? Duck Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 298. Based on characteristics and uses process of comparison and elimination. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 299. • Which shark fin fits the following description? – Tail not separated into a top and bottom fin. End of tail is blunt instead of pointy? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 300. • Which shark fin fits the following description? – Tail not separated into a top and bottom fin. End of tail is blunt instead of pointy? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 301. • Which shark fin fits the following description? – Tail not separated into a top and bottom fin. End of tail is blunt instead of pointy? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 302. • Which two shark fins fit the following description? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 303. • Which two shark fins fit the following description? – Upper part of tail extends far beyond the bottom. Tip of top tail fin curved. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 304. • Which two shark fins fit the following description? – Upper part of tail extends far beyond the bottom. Tip of top tail fin curved. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 305. • Which shark fin fits the following description? – Trunk before tail fin has small fin. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 306. • Which shark fin fits the following description? – Trunk before tail fin has small fin. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 307. • Use constant characteristics rather than ones that disappear or vary with the season or other environmental factor. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 308. • Use constant characteristics rather than ones that disappear or vary with the season or other environmental factor. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 309. • Use characteristics which can be directly observed. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 310. • Use characteristics which can be directly observed. Black and White color with orange around neck… Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 311. • Use characteristics which can be directly observed. And they love each other… Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 312. • Use characteristics which can be directly observed. And they love each other… Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 313. • Use characteristics which can be directly observed. And they love each other… “They form mating pairs is a better description.” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 314. • What is a big insect to you?
- 315. • What is a big insect to you?
- 316. • What is a big insect to you?
- 317. • Use quantitative (numbered) measurements with an amount or dimension rather than vague terms like… Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 318. • Use quantitative (numbered) measurements with an amount or dimension rather than vague terms like… "big" and "small." Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 319. • Use quantitative (numbered) measurements with an amount or dimension rather than vague terms like… "big" and "small." Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 320. • Use quantitative (numbered) measurements with an amount or dimension rather than vague terms like… "big" and "small." Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 321. • Use quantitative (numbered) measurements with an amount or dimension rather than vague terms like… "big" and "small." Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 322. • Use quantitative (numbered) measurements with an amount or dimension rather than vague terms like… "big" and "small." “OH?” “That’s not very Big.” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 323. • Rules to Follow When Using a Dichotomous Key – Always read both choices, even if the first seems to be the logical. – Understand the meaning of the terms involved in the key. – When measurements are given, use a scale to measure the specimen. Do not guess at a measurement. – Living things are always variable, so do not base your organism identification in the field on a single observation. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 324. • Rules to Follow When Using a Dichotomous Key – Always read both choices, even if the first seems to be the logical. – Understand the meaning of the terms involved in the key. – When measurements are given, use a scale to measure the specimen. Do not guess at a measurement. – Living things are always variable, so do not base your organism identification in the field on a single observation. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 325. • Rules to Follow When Using a Dichotomous Key – Always read both choices, even if the first seems to be the logical. – Understand the meaning of the terms involved in the key. – When measurements are given, use a scale to measure the specimen. Do not guess at a measurement. – Living things are always variable, so do not base your organism identification in the field on a single observation. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 326. • Rules to Follow When Using a Dichotomous Key – Always read both choices, even if the first seems to be the logical. – Understand the meaning of the terms involved in the key. – When measurements are given, use a scale to measure the specimen. Do not guess at a measurement. – Living things are always variable, so do not base your organism identification in the field on a single observation. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 327. • Rules to Follow When Using a Dichotomous Key – Always read both choices, even if the first seems to be the logical. – Understand the meaning of the terms involved in the key. – When measurements are given, use a scale to measure the specimen. Do not guess at a measurement. – Living things are always variable, so do not base your organism identification in the field on a single observation. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 328. • Activity! Guess Who / 7 Questions? – Create a series of questions to find the three secret members of the class that I have written on note cards. – Use yes / no questions based on characteristics. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 329. • Activity! Wacky People Available Sheet – Use a dichotomous key to find the names for various humanoids. – Assignment is to correctly identify each character with the correct name. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 330. • Activity! Wacky People Available Sheet – Use a dichotomous key to find the names for various humanoids. – Assignment is to correctly identify each character with the correct name. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 331. Start here every time Y / N and then go where directed until you find the species name.
- 334. Patterned Mulywumpus Lugio Wirum Eggur Ondy Tri D. Duckt Elle E. Funk Tunia petalos Grif Leon Rita Nita C. Nile Cue Kide Quadrumenox Mosk Cara Giggles Hex Oculate Ru-ela Brella
- 335. • Activity – EEK Dichotomous Key – http://www.dnr.state.wi.us/org/caer/ce/eek/veg/ treekey/treestart.htm Collect a leaf and use the online dichotomous key at… http://oregonstate.edu/trees/dichotomous_key.html Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 336. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 337. • Leaf for EEK Dichotomous key. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 338. • Activity Worksheet! Salamander (Order Caudata) Dichotomous Key. – Use a dichotomous key to identify salamanders Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 340. Slimy Salamander Jefferson Salamander Spotted Newt Two Lined Mud puppy Tiger Four toed Red-backed Siren Marbled
- 341. • You should be close to page 4/5 in your bundle.
- 342. Classification uses… Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 343. Homology: Similarities between organisms Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 344. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 345. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 346. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 347. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 348. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 349. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 350. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 351. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 352. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 353. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 354. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 355. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 356. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 357. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 358. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 359. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 360. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 361. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 362. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 363. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 364. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 365. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 366. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 367. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 368. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 369. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 370. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 371. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 372. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 373. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 374. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 375. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 376. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 377. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 378. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 379. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 380. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 381. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 382. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 383. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 384. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 385. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 386. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 387. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 388. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
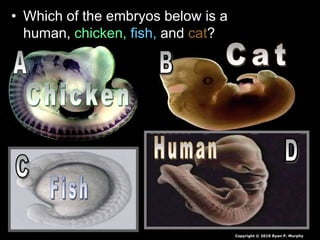
- 389. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 390. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 391. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 392. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 393. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 394. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 395. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 396. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 397. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Learn more about homology at… http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/lines_04 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 398. DNA: Similar genes aid in classification Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 399. • DNA provides insight into how similar and how different organisms are. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 400. • DNA provides insight into how similar and how different organisms are. This allows taxonomist to classify organisms more accurately. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 401. • DNA provides insight into how similar and how different organisms are. This allows taxonomist to classify organisms more accurately. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 402. • Humans and Chimpanzee share 94% of the same genes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 403. • Humans and Chimpanzee share 94% of the same genes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 404. • Humans and Chimpanzee share 94% of the same genes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 405. • Humans and Chimpanzee share 94% of the same genes. – We can get a blood transfusion from a chimp. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 406. • Red Pandas
- 407. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas
- 408. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo.
- 409. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to…
- 410. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to… – Red Pandas more closely related to…
- 411. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to… – Red Pandas more closely related to…
- 412. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to… – Red Pandas more closely related to…
- 413. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to… – Red Pandas more closely related to…
- 414. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to… – Red Pandas more closely related to…
- 415. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to… – Red Pandas more closely related to…
- 416. The 3 Domains of Life. All life is either… Archaeabacteria Eubacteria Eukarya Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 417. The 3 Domains of Life. All life is either… Archaea Eubacteria Eukarya Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 418. The 3 Domains of Life. All life is either… Archaea Bacteria Eukarya Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 419. The 3 Domains of Life. All life is either… Archaea Bacteria Eukarya Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 420. The 3 Domains of Life. All life is either… Archaea Bacteria Eukarya Learn more about the Domains of Life at… http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/alllife/threedomains.html Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 421. “Excuse Me” “Does anyone know where I can find some good food.”
- 422. The Kingdoms of life. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 423. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 424. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 425. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Note: The use of Archaeabacteria is a bit dated. Now called just Archaea Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 426. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Note: The use of Archaeabacteria is a bit dated. Now called just Archaea and Eubacteria is just Bacteria. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 427. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Note: The use of Archaeabacteria is a bit dated. Now called just Archaea and Eubacteria is just Bacteria. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 428. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 429. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. ea Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 430. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Blue Green Algae now called Cyanobacteria ea Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 431. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Blue Green Algae now called Cyanobacteria ea Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 432. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Blue Green Algae now called Cyanobacteria ea Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 433. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Blue Green Algae now called Cyanobacteria ea Learn more about the Kingdoms and Domains of Life at… http://biology.about.com/od/evolution/a/aa091004a.htm Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 434. “I’m dressed as King Phillip.” “Am I late for the spaghetti dinner?”
- 435. • Taxonomy and Classification Available Sheet. – Follows slideshow for classwork.
- 436. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 437. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 438. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 439. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 440. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 441. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 442. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 443. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 444. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 445. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 446. Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 447. Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 448. Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 449. Bacteria Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 450. Bacteria Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 451. Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 452. Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 453. Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Archaea Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 454. Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Archaea Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 455. Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Archaea Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 456. Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Archaea Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 457. Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Archaea Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 458. Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Archaea Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 459. Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Archaea Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 460. Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Archaea Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 461. Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Archaea Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 462. Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Archaea Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 463. Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Bacteria Eukarya share more in common with Archaea than Bacteria Archaea Universal Ancestor Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 464. • Until recently (1984), scientists believed all life got its energy from the sun. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 465. • Until recently (1984), scientists believed all life got its energy from the sun. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 466. • Until recently (1984), scientists believed all life got its energy from the sun. A whole new system existed on the ocean floor. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 467. • Until recently (1984), scientists believed all life got its energy from the sun. A whole new system existed on the ocean floor. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 468. • Until recently (1984), scientists believed all life got its energy from the sun. A whole new system existed on the ocean floor. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 469. • Until recently (1984), scientists believed all life got its energy from the sun. A whole new system existed on the ocean floor. 12H2S + 6CO2 → C6H12O6 (=carbohydrate) + 6H2O + 12S Learn more about the differences between chemosynthesis and photosynthesis at... http://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/facts/photochemo.html Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 470. • Some bacteria can create energy without light at the bottom of the ocean under enormous pressures, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 471. • Some bacteria can create energy without light at the bottom of the ocean under enormous pressures, hot and cold temperatures and without light. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 472. • Archaebacteria can create energy without light at the bottom of the ocean under enormous pressures, hot and cold temperatures and without light. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 473. • Video Link! Hydrothermal Vents. (5 min) – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D69hGvCsW gAwithout light. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 474. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 475. Learn more about Archaea at… http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/archaea/archaea.html Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 476. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 477. • Bacteria can also be found in extreme places. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 478. • Bacteria can also be found in extreme places. (Extremophiles) Their cell membrane is a bit different which allow them to survive in harsh places. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 479. • Bacteria can also be found in extreme places. (Extremophiles) – Many scientists think this type of life may be found in the harsh environments on other planets as well as the start of life on Earth. Their cell membrane is a bit different which allow them to survive in harsh places. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 480. • Video Link! Archaea – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W25nI9kpxtU Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 481. “By the way, I really enjoy eating Spaghetti.”
- 483. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular
- 484. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular
- 485. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular
- 486. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular
- 487. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular
- 488. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular
- 489. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia
- 490. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Gets Energy from.. Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia
- 491. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Gets Energy from..
- 492. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Gets Energy from.. Much Smaller
- 493. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Cell Wall Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Cell Wall Varies Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Cell Wall (Chitin) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) No Cell Wall Single or MultiCellular Gets Energy from.. Plant Cell Wall Cell Wall Cell Wall No Cell Wall
- 494. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Gets Energy from..
- 495. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Most are Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Some are multicellular Varies
- 496. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from..
- 497. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Heterotrophic Autotrophic Heterotrophic
- 498. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archaebacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Heterotrophic Autotrophic Heterotrophic Autrophic: Can make its own food (chemo or photsynthesis)
- 499. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archaea Kingdom Eubacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Auto / Hetero Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Heterotrophic Chemotroph Varies Varies Auto / Auto / Hetero Hetero Autotrophic Heterotrophic Autrophic: Can make its own food (chemo or photsynthesis)
- 500. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Heterotrophic Autotrophic Heterotrophic Heterotrophic: Must consume food (eat or absorb)
- 501. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Heterotrophic Autotrophic Heterotrophic Heterotrophic: Must consume food (eat or absorb)
- 502. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food
- 503. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism that absorbs its food?
- 504. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Heterotrophic Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism that absorbs its food? Fungi (Heterotrophs)
- 505. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a single celled organism that has a nucleus?
- 506. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a single celled organism that has a nucleus? Protista
- 507. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism that can make it’s own food?
- 508. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Autotrophic Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism that can make it’s own food? Plantae (Autotroph)
- 509. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a unicellular organism without a nucleus?
- 510. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a unicellular organism without a nucleus? Bacteria or Archaea
- 511. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism that eats other organisms?
- 512. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Heterotrophic I’m a multicellular organism that eats other organisms?
- 513. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism?
- 514. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism? Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia
- 515. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m an autroph?
- 516. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m an autroph? Bacteria, Archaea, some Protista, and Plantae (Varies)
- 517. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m only a heterotroph?
- 518. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m only a heterotroph? Fungi and Animalia, they must eat or absorb food.
- 519. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m heterotrophic?
- 520. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m heterotrophic? Fungi and Animalia, and Bacteria, Archaea, Protista (Varies)
- 521. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I don’t have a cell wall?
- 522. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I don’t have a cell wall? Animalia
- 523. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I have a cell wall but it’s made of chitin?
- 524. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I have a cell wall but it’s made of chitin? Fungi
- 525. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan?
- 526. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan? Bacteria
- 527. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I am a bacteria but lack peptidoglycan in my cell wall?
- 528. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or MultiCellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I am a bacteria but lack peptidoglycan in my cell wall? Archaea
- 529. • Video Link! Hank Explains Bacteria, Archaea, and Protists – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vAR47-g6tlA Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 530. “Can I come over for good spaghetti”
- 531. • Taxonomy and Classification Available Sheet. – Follows slideshow for classwork.
- 532. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 533. • Does anyone know King Phillip? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 534. • Does anyone know King Phillip? – Will someone invite him over for dinner? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 535. • Does anyone know King Phillip? – Will someone invite him over for dinner? – He likes spaghetti? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 536. • Does anyone know King Phillip? – Will someone invite him over for dinner? – He likes spaghetti? – Make sure the spaghetti is good, King Phillip only likes top quality pasta. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 537. The 8 Taxonomic ranks. All living things have 8 names. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 538. Domain - Did Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 539. Kingdom - King Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 540. Phylum - Phillip Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 541. Class - Come Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 542. Order - Over Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 543. Family - For Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 544. Genus - Good Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 545. Species – Spaghetti Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 546. • What does “Did King Phillip Come Over For Good Spaghetti” stand for? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 547. • Answer! – 1) Domain – 2) Kingdom – 3) Phylum – 4) Class – – 5) Order – 6) Family – 7) Genus – 8) Species – Did King Phillip Come Over For Good Spaghetti Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 548. • Answer! – 1) Domain – 2) Kingdom – 3) Phylum – 4) Class – – 5) Order – 6) Family – 7) Genus – 8) Species – Did King Phillip Come Over For Good Spaghetti Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 549. • Answer! – 1) Domain – 2) Kingdom – 3) Phylum – 4) Class – – 5) Order – 6) Family – 7) Genus – 8) Species – Did King Phillip Come Over For Good Spaghetti Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 550. • Answer! – 1) Domain – 2) Kingdom – 3) Phylum – 4) Class – – 5) Order – 6) Family – 7) Genus – 8) Species – Did King Phillip Come Over For Good Spaghetti Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 551. • Answer! – 1) Domain – 2) Kingdom – 3) Phylum – 4) Class – – 5) Order – 6) Family – 7) Genus – 8) Species – Did King Phillip Come Over For Good Spaghetti Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
