Anatomy and Physiology 6 joints
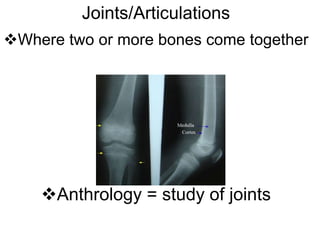
- 1. Joints/Articulations Where two or more bones come together Anthrology = study of joints
- 2. Three types of Joints A. Fibrous joint or Synarthrosis – immovable to slightly moveable • Two adjacent edges separated with a small amount of fibrous tissue or a thin layer of cartilage Examples 1. Skull – joints called sutures
- 3. Three types of Joints A. Fibrous joint or Synarthrosis – immovable to slightly moveable • Two adjacent edges separate with a small amount of fibrous tissue or a thin layer of cartilage Examples 1. Skull – joints called sutures 2. Gomphosis – tooth joins its bony socket
- 4. Three types of Joints A. Fibrous joint or Synarthrosis – immovable to slightly moveable • Two adjacent edges separate with a small amount of fibrous tissue or a thin layer of cartilage Examples 1. Skull – joints called sutures 2. Gomphosis – tooth joins its bony socket 3. Syndesmosis – joint of ulna and radius where slightly movable.
- 5. Three types of Joints A. Fibrous joint or Synarthrosis B. Cartilaginous joints or Amphiarthrosis Two adjacent bones are separated by a substantial amount of fibrocartilage or hyaline which gives them mobility Slightly movable Examples 1. Vertebrae with disk cartilage
- 6. Three types of Joints A. Fibrous joint or Synarthrosis B. Cartilaginous joints or Amphiarthrosis Two adjacent bones are separated by a substantial amount of fibrocartilage or hyaline which gives them mobility Examples Vertebrae with disk cartilage 2. Pubic symphysis – pubic portions of pelvic bone
- 7. Three types of Joints A. Fibrous joint or Synarthrosis B. Cartilaginous joints or Amphiarthrosis Two adjacent bones are separated by a substantial amount of fibrocartilage or hyaline which gives them mobility Examples 1. Vertebrae with disk cartilage 2. Pubic symphysis – pubic portions of pelvic bone 3. Sacroiliac joint – where sacrum joins the illium
- 8. c. Synovial joints or Diarthrosis Freely movable There are 6 kinds of synovial joints Characteristic – ends of bones covered with articular cartilage
- 9. c. Synovial joints or Diathrosis Freely movable There are 6 kinds of synovial joints Characteristic – ends of bones covered with articular cartilage Anatomy of the Synovial Joint Joint is surrounded by an outer joint capsule called the fibrous capsule which is an extension of the periosteum which forms ligaments.
- 10. Anatomy of the Synovial Joint Joint is surrounded by an outer joint capsule called the fibrous capsule which is an extension of the periosteum which forms ligaments Bursa = articular capsule extends way beyond the joint and is filled with fluid to cushion Bursitis = inflammation of the bursa
- 11. Anatomy of the Synovial Joint Synovial Membrane – inner membrane that produces the synovial fluid which is a slipper liquid to reduce friction
- 12. Six major types of synovial joints: 1. Ball and socket joint: Has most freedom of movement can move in all directions and also rotate Example – hip and shoulder
- 14. Six major types of synovial joints: 1. Ball and socket joint 2. Hinge joint The convex surface of one bone fits into the concave surface of another Permits movement in one plane only Ex. Elbow, phalanges, knee
- 16. Six major types of synovial joints: 1. Ball and socket joint 2. Hinge joint 3.Saddle joint Both bones have articulating concave and convex regions One bone fits the complementary surface of the other Variety of movement in two planes, all but rotation Examples: Carpal and Metacarpel of thumb More motion than hinge, less ball/socket
- 18. Six major types of synovial joints: 1. Ball and socket joint 2. Hinge joint 3. Saddle joint 4. Ellipsoid Ovoid condyle of one bone fits into the elliptical cavity of another Movement forward and backwards, left and right, but no rotation Ex. Metacarpals to phalanges, mandible to temporal bone
- 20. Six major types of synovial joints: 1. Ball and socket joint 2. Hinge joint 3. Saddle joint 4. Ellipsoid 5. Pivot The cylindrical surface of one bone rotates within a ring of bone and fibrous tissue of a ligament Permits rotational movement only Ex. Atlas and axis of neck and radius and ulna
- 22. Six major types of synovial joints: 1. Ball and socket joint 2. Hinge joint 3. Saddle joint 4. Ellipsoid 5. Pivot 6. Gliding The articulating surfaces are flat or nearly curved. Allows bones to move a little bit in all directions by sliding over each other. Ex. Wrist, ankle, vertebra
- 23. gliding
- 24. Anatomical terms: Anatomical position – the body is assumed to be standing, the feet together, the arms to the side, and the head and eyes and palms of the hands facing forwards. Anterior = front Posterior = back
- 25. Motion and terms of motion: Midline – imaginary line that runs down center of the body Midsagital plane – runs through the body at the midline Lateral – way from the midline Medial – toward the midline
- 27. Terms of Movement of joints: Extension – straighten joint – increasing the angle between the two bones Flexion – decreasing the angle between the two bones
- 29. Movement of joints Plantar flexion –movement of the ankle so that you can stand on your toes. Dorsiflexion – movement of the ankle to decrease the angle between your foot and tibia.
- 31. Terms of Movement of joints Abduction - moving body part away from the midline of the body Adduction – moving the body part toward the midline of the body
- 33. Terms of Movement of joints : Circumduction – circular rotation of a ball and socket joint
- 34. : Terms of Movement of joints Rotation – movement in which a body part moves about an axis Medial rotation – rotation towards the midline Lateral rotation – rotation away from the midline
- 36. Movement of joints : Pronation - rotating the palm of the hand backward or opposite the anatomical position Supination – rotating the palm of the hand forward or into anatomical position
- 37. pronation supination
- 38. Movement of joints: Inversion – rotation of the sole of the foot inward Eversion- rotation of the sole of the foot outward
