wasemann notes
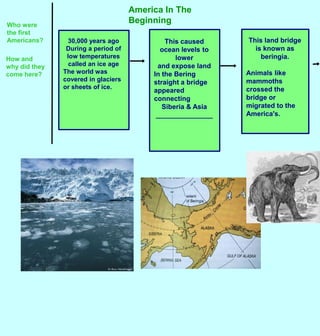
- 1. America In The Beginning Who were the first Americans? This land bridge is known as beringia. Animals like mammoths crossed the bridge or migrated to the America's. This caused ocean levels to lower and expose land In the Bering straight a bridge appeared connecting Siberia & Asia _______________ 30,000 years ago During a period of low temperatures called an ice age The world was covered in glaciers or sheets of ice. How and why did they come here?
- 2. America In The Beginning What happened when they came to America? The ice age ended covering up glaciers causing water levels to rise covering up the bridge. Some animals died off like. Living in many different parts of the Americas the Natives needed to adjust or adapt to every thing in the new surrounds that made up each of their own environment in order to survive. How did they meet their new needs? Hunter's in Asia who moved from place to place to find food or nomads followed the mammoths and spread out or migrated to the America's
- 3. How did Native Americans adjust to the new environments? America In The Beginning Different groups in different environments developed their own beliefs and ways of life or culture. Groups in the same environments adapted similar life styles, and language creating cultural region. Many Native American have these things in common. 1. Nature has a spirit. 2. No one can own land. 4. Only use what is needed. 5. trade was important to most societies Living in many different parts of the Americas the Natives used the different natural resources in their own different environments for food, clothing, and shelter. What did they have in common?
- 4. 8 Cultural Regions California Great Basin Great Plains South East North West Coast Plateau Eastern Woodlands South West
- 7. North West Coast Weather: long cold winters cool summers heavy rainfall Natural Resources: ocean/beaches thick forests of fir, spruce, and cedar rugged mountains seafood/salmon deer, moose, bear, elk, beaver, mountain goats Used cedar canoes to hunt Fenced in salmon laying eggs used cedar to make rope, mats and baskets shell needles used wedges, sledge hammers, drills, and knifes to carve wooden masks Clothing: Cedar water proof clothing like capes with decorative shell buttons Shelter: lived near the coast Cedar Long Houses with cedar bark roofs
- 8. California Weather: rainy winters hot dry summers Natural Resources: ocean/coast foothills valley's deserts mountains acorns, oak trees grass, and plants redwood trees salmon/seafood/shellfish deer, rabbits, ducks, roots berries, pine nuts Used Bows& arrows, snares, and nets, used cooking stones to heat acorn meal tools from antlers Clothing: grass/leather aprons and skirts Shelter: Cone shaped made of redwood bark, pole, and reeds woven into mats
- 9. Great Basin Weather: little rain hot during the day cold at night Natural Resources: mostly dessert low areas surrounded by mountains at the edges with valleys that had seasonal lakes and streams plants that need little water like grasses, sagebrush, pinon trees, at the outer edges pine trees, and willow small animals rabbits, lizards, grasshoppers, snakes sometimes ducks , duck eggs during certain seasons seeds,berries pine nuts, roots, cattail Tools: water baskets sealed with tree sap Floating duck decoys, nets, sharp sticks, flat baskets for catching seeds Clothing: rabbit robes in winter Shelter: Nomadic temporary cone shelters of willow, brush and reeds
- 10. Plateau Weather: long cold winters comfortable summers Natural Resources: mountains with dense forests in areas flatter in the center with drier grass lands rivers driftwood, mud, dirt, grass and sage brush fish, antelope, deer, seeds onions, carrots, camas roots, salmon Tools: woven baskets, willow digging sticks, wooden fishing platforms, nets, and spears for salmon Clothing: antelope and deer hides leggings, dresses and skirts, woven hats, seed and shell designs Shelter: near rivers, partly under ground out of driftwood, mud, sap, and reeds
- 11. Great Plains Weather: cold winters hot summers Natural Resources: mountains surrounding edges treeless grasslands in the center east more water and softer soil west drier dense grass Buffalo and smaller animals
- 12. South West Weather: high temperatures little rain dry/arid Natural Resources: mountains, canyons desserts, flat top mesas rivers, little water clay, brightly colored plants, cotton corn, beans, squash, peppers, rabbits Large thick walled houses made of bricks of adobe(sun baked clay). Up to 4 stories and had hundreds of rooms. Clothes were made of cotton that they grew. Using plants and minerals, they dyed the fabric Lived near naturally flooded areas. Men dug irrigation ditches, and also built dams to hold summer rain. Women spend most the day grinding corn kernels into cornmeal. They used clay pots to cook stews
- 13. Eastern Woodlands Weather: snowy winters , rain Natural Resources: rivers, ocean/coast lots of lakes and streams Forests, plants, maple trees, elm, deer, bears, beavers, birds, fish corn, sunflowers, tobacco, vegetables, nuts, berries Long House: Sturdy, log-framed houses covered with elm bark, about 20 feet wide and over 100 feet long. Several related families live in sections of the house. Skirts, capes, and moccasins were made out of deer skins. Women ground corn with wooden sticks . Men often paddled on the rivers and streams in log and bark canoes . They trapped beavers, hunted deer, bear, caught birds, and speared fish. For farming land, men burnt small sections of trees and underbrush. Women did the hoeing and planting. They planted many different types of corn, beans and squash. Made maple syrup and wooden storage canisters.
- 14. South East Weather: long warm humid summers mild winters Natural Resources: rivers, ocean/coast Fertile coastal plains mountains, swamps Trees, clay, shells, corn, beans, squash, pumpkins, sunflowers, sweet potatoes squirrels, rabbits, turkeys, deer, alligators, turtles, wild rice, persimmons Houses were made from strips of young trees woven into a rectangular frame, then plastered with clay. These houses had pointed roofs made of leaves. Towns included many mounds, first mounds were burial sights, but others were larger, and used as platforms for temples. It took many months, even years, to build these mounds, because they moved the dirt 1 basket full at a time. Simple clothing was made of deer skin. Jewelry made of stones, shells, feathers, pearls, bones, and clay. Women used hoes made of stone, shell or animal shoulder blades. Men hunted using small blow guns, and bows and arrows.