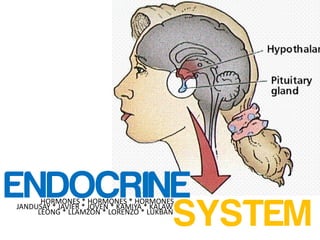
PH 131 - Endocrine Pathophysiology Report
- 1. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM HORMONES * HORMONES * HORMONES JANDUSAY * JAVIER * JOVEN * KAMIYA * KALAW LEONG * LLAMZON * LORENZO * LUKBAN
- 2. WHAT TO EXPECT: REPORT OBEJECTIVES SHORT REVIEW DISORDERS and DISEASES REPORT SUMMARY
- 3. To provide a short review on the Endocrine System To present preventive measures and cures REPORT OBEJECTIVES To discuss common & rare Endocrine diseases & disorders To familiarize students with Endocrine processes To discuss the effects on normal physiology To provide a short summary on the topics discussed REPORT*OBEJECTIVES
- 4. REVIEW
- 5. REVIEW ENDOCRINOLOGY VS. neurons hormones
- 6. REVIEW ENDOCRINOLOGY VS. long-lasting nervous endocrine fast
- 7. REVIEW ENDOCRINOLOGY NEGATIVE FEEDBACK MECHANISM
- 10. DISEASES&DISORDERS PITUITARY GLAND THYROID GLAND PARATHYROID GLAND ADRENAL GLAND PANCREATIC ISLET SEX HORMONES
- 11. PITUITARY GLAND DWARFISM & GIANTISM DIABETES INSIPIDUS
- 12. PITUITARY GLAND DWARFISM & GIANTISM DIABETES INSIPIDUS
- 13. Pituitary Gland Disorders Diabetes Insipidus
- 14. Diabetes Insipidus -(“diabetes”= overflow, “insipidus”= tasteless) -most common abnormality associated with the dysfunction of the posterior pituitary -due to defects in antidiuretic hormone receptors or inability to secrete ADH -can be neurogenic (or central) or nephrogenic
- 15. Diabetes InsipidusHow does the normal physiology is disrupted?
- 16. Diabetes Insipidus Symptoms: - excretion of large volumes of urine with resulting dehydration and thirst - bed-wetting
- 18. Subcutaneous injection or nasal application of ADH analogs
- 21. Usually causes Type 2 diabetes
- 22. Occurs when there is reduced sensitivity of diabetics who undergo insulin therapy
- 25. 3. Hyperinsulinism How can normal physiology be regained? - immediate intravenous administration of large quantities of glucose - administration of glucagon (or, less effectively of epinephrine) can cause glycogenolysis in the liver and thereby increase blood glucose level extremely rapidly **Permanent damage to the neuronal cells of the nerous system usually occurs when treatment is not given immediately.
- 26. DISEASES&DISORDERS PITUITARY GLAND THYROID GLAND PARATHYROID GLAND ADRENAL GLAND PANCREATIC ISLET SEX HORMONES
- 27. THYROID GLAND GOITER HYPERTHYROIDISM HYPOTHYROIDISM
- 28. GOITER WHY, YES. THIS IS A…. GOITER? WHAT IS A GOITER? ENLARGEMENT OF THE THYROID.
- 29. GOITER SYMPTOMS NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Thyroid Hormones (T3 & T4) - produced by cells in thyroid gland - regulated by thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) - produced through the attachment of iodine atoms to ring structures of T3 and T4 AHEM! AHEM! Breathing and swallowing difficulties Coughing and hoarseness
- 30. CAUSES TREATMENT POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS GOITER HYPERTHYROIDISM Surgery- thyroidectomy Lugol’s Iodine Radiocative Iodine HYPOTHYROIDISM
- 31. WHAT OVERACTIVE TISSUE IN THE HYPERTHYROIDISM THYROID GLAND PRODUCING T3 TOO MUCH T4 AND TRIIODOTHYRONINE & THYROXINE
- 32. CAUSES GRAVE’S DISEASE TOXIC THYROID ADENOMA NORMAL? THYROIDITIS WHAT WHAT WHAT SYMPTOMS? HIGH EXCITABILITY; METABOLISM MILD TO EXTREME WEIGHT LOSS MUSCLE WEAKNESS; TREMORS
- 33. DEVELOPMENT OF PROTRUSION OF EYEBALLS exophthalmos EDEMATOUS TISSUES & DEGENERATIVE MUSCLES TREATMENT! SURGICAL REMOVAL OF GLAND LESSEN IODINE INTAKE
- 34. HYPOTHYROIDISM T3 T4 TOO LITTLE AND
- 35. AUTOIMMUNITY AGAINST THE THYROID =DETERIORATION AUTOIMMUNITY CAUSES ASSOCIATED WITH THYROID GOITER
- 36. IODINE DEFICIENT ENDEMIC COLLOID & IDIOPATHIC NONTOXIC GOITER NOT IODINE DEFICIENT THYROID GOITER
- 37. SYMPTOMS? FATIGUE; SLEEPINESS; SLUGGISH WEIGHT GAIN; CONSTIPATION FAILURE OF TROPHIC FUNCTIONS myxedema AND TREATMENT! MORE IODINE ORAL MEDICATON
- 38. DISEASES&DISORDERS PITUITARY GLAND THYROID GLAND PARATHYROID GLAND ADRENAL GLAND PANCREATIC ISLET SEX HORMONES
- 39. PARATHYROID GLAND HYPOPARATHYROIDISM HYPERPARATHYROIDISM
- 40. FUNCTION &NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY PARATHYROID GLAND * control calcium within the blood. * control how much calcium is in the bones, and therefore, how strong and dense the bones are! * As the blood filters through the parathyroid glands, they detect the amount of calcium present in the blood making more or less parathyroid hormone (PTH). Calcium level in the blood is too low: the parathyroid cells make more parathyroid hormone.
- 41. PARATHYROID GLAND …occurs when your parathyroid glands make too much PT and cause you to have too much calcium in the bloodstream. CAUSES OF TOO MUCH PTH: Growth on the parathyroid glands! Enlargement of 2 or more of the parathyroid glands! OR medical conditions (like, lessay, kidney failure and rickets...) HYPOPARATHYROIDISM HYPERPARATHYROIDISM
- 42. HYPERPARATHYROIDISM Normally, the amount of calcium going into your bones matches the amount of calcium passing out of your bones. This means that the amount of calcium in your bones should stay about the same all the time. If you have hyperparathyroidism, more calcium is coming out of your bones than is going back in. When this happens, your bones might hurt, ache or become weak. Weak bones break more easily and heal slower than normal bones. PHYSIOLOGY&IMPLICATIONS
- 43. HYPERPARATHYROIDISM Feeling weak or tired most of the time General aches and pains Frequent heartburn Nausea & Vomiting; Loss of appetite An increase in bone fractures or breaks Confusion and memory loss Kidney stones; Excessive urination High blood pressure THE SYMPTOMS
- 44. HYPERPARATHYROIDISM SURGERY DRINK PLENTY OF WATER LIMIT INTAKE OF CALCIUM AND VITAMIN D DO NOT SMOKE EXERCISE DAILY TREATMENT
- 46. PARATHYROID GLAND HYPOPARATHYROIDISM HYPERPARATHYROIDISM
- 47. HYPOPARATHYROIDISM Hypoparathyroidism is a rare conditionin which your body secretes abnormally low levels of parathyroid hormone (parathormone). This hormone plays a key role in regulating and maintaining a balance of your body's levels of two minerals — calcium and phosphorus. The low production of parathyroid hormone in hypoparathyroidism leads to abnormally low ionized calcium levels in your blood and bones and to an increased amount of phosphorus. PHYSIOLOGY&IMPLICATIONS
- 48. HYPOPARATHYROIDISM Tingling or burning (paresthesias) Muscle aches or cramps; Twitching or spasms Fatigue or weakness Painful menstruation Patchy hair loss, such as thinning of your eyebrows Dry, coarse skin; Brittle nails Headaches; Depression, mood swings Memory problems THE SYMPTOMS
- 49. HYPOPARATHYROIDISM RESTORE THE CALCIUM AND MINERAL BALANCE IN THE BODY. Treatment involves calcium carbonate and vitamin D supplements, which usually must be taken for life. Blood levels are measured regularly to make sure that the dose is correct. A high-calcium, low-phosphorous diet is recommended. TREATMENT
- 51. HEP! HEP! HEP! HAVE YOO BEEN LISTENING? Test your knowledge and try your luck… With our game!
- 52. DISEASES&DISORDERS PITUITARY GLAND THYROID GLAND PARATHYROID GLAND ADRENAL GLAND PANCREATIC ISLET SEX HORMONES
- 53. CUSHING’S SYNDROME CUSHING’S DISEASE ADRENAL GLAND ADDISON’S DISEASE
- 56. Characterized by high plasma levels of ACTH and cortisol
- 58. Can occur from multiple causes including:Adenomas of the anterior pituitary that secrete large amounts of ACTH Abnormal function of the hypothalamus that causes high levels of corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) “ectopic secretion” of ACTH by a tumor elsewhere in the body Adenomas of the adrenal cortex CUSHING’S
- 59. High blood pressure. High blood sugar. Suppressed immunity (and more infections). Insulin resistance Suppressed sex hormones and reduced libido. Suppressed thyroid hormones. - A round, red, full face, often called a "moon" face. - Muscle weakness and thin limbs. - Growth of fine hair on the face, upper back, or arms. - A lump of fat (buffalo hump) on the back of the neck. - Stretch marks over abdomen. CUSHING’S SYMPTOMS
- 61. CUSHING’S Cushing's syndrome is treated by restoring a normal balance of hormones. This may involve surgery, radiation treatments or drugs. Tumors on the adrenal glands are removed by surgery. If there is a tumor on just one adrenal gland, the other gland usually shrinks and ceases normal productivity. TREATMENT
- 63. Addison's disease results from damage to the adrenal cortex. This damage may be caused by the following: The immune system mistakenly attacking the gland (autoimmune disease) Infections such as tuberculosis, HIV, or fungal infections Hemorrhage, blood loss Tumors Use of blood-thinning drugs (anticoagulants) A disorder that occurs when your body produces insufficient amounts of certain hormones produced by your adrenal glands. It may be due to : a disorder of the adrenal glands themselves (primary adrenal insufficiency) or inadequate secretion of ACTH by the pituitary gland (secondary adrenal insufficiency) ADDISON’S
- 65. Chronic diarrhea
- 66. Darkening of the skin ; Paleness
- 67. Extreme Weakness
- 69. Mouth lesions on the inside of a cheek
- 71. Salt craving
- 73. ADDISON’S Taking hormones to replace the insufficient amounts being made by your adrenal glands (glucocorticoids (cortisone or hydrocortisone) and mineralocorticoids (fludrocortisone)) TREATMENT
- 74. DISEASES&DISORDERS PITUITARY GLAND THYROID GLAND PARATHYROID GLAND ADRENAL GLAND PANCREATIC ISLET SEX HORMONES
- 75. DIABETES MELLITUS PANCREATIC ISLET
- 77. PANCREAS retroperitoneal Exocrine gland Endocrine gland -98% of the secreting cells in the pancreas make digestive enzymes -2% of the cells make hormones that are secreted into the portal vein
- 79. Normal Physiology Circulating glucose is derived from three sources: 1. intestinal absorption during the fed state 2. glycogenolysis -breakdown of glycogen 3. gluconeogenesis -formation of glucose primarily from lactate and amino acids during the fasting state insulin is the key regulatory hormone of glucose disappearance (hypoglycemic hormone), and glucagon is a major regulator of glucose appearance (extremely potent hyperglycemic agent)
- 82. Insulin and glucagon antagonistic interaction humoral stimuli potent regulators of glucose metabolism bi-hormonal definition of diabetes: diabetic state = insulin deficiency + glucagon excess
- 86. NOTE: TYPE1 – noticeable early symptoms TYPE2 – may occur without or gradual development of symptoms
- 90. DISEASES&DISORDERS PITUITARY GLAND THYROID GLAND PARATHYROID GLAND ADRENAL GLAND PANCREATIC ISLET SEX HORMONES
- 91. KLINEFELTER’S DISEASE POLYCYSTIC OVARIES SEX HORMONES
- 92. PCOS polycystic ovary syndrome
- 98. very light or very heavy bleeding during your period
- 99. mild to moderate abdominal discomfort
- 100. excessive hair growth on your face, chest and lower abdomen
- 101. acne
- 102. Infertile
- 104. Too much production of LH compared to FSH follicles on the ovaries produce more of the male hormone testosterone than the female hormone estrogen adrenal glands start to produce increased amounts of testosterone
- 105. Too much testosterone prevents ovulation
- 106. Estrogenis still produced deficiency in progesterone
- 107. one of the most common female endocrine disorders
- 108. a health problem caused by hormonal system imbalance: increase in ovarian production and insulin resistancepolycystic ovary syndrome
- 110. also known as XXY Syndrome or 47, XXY
- 113. Osteoporosis (in young or middle-age men)
- 114. Motor delay or dysfunction
- 115. Speech and language difficulties
- 116. Attention deficits
- 118. Dyslexia or reading dysfunction
- 119. Psychosocial or behavioural problemsManagement and Treatment Educational guidance Therapeutic Options Medical Options e.g. Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
- 120. HEP! HEP! HEP! HAVE YOO BEEN LISTENING? Test your knowledge and try your luck… By giving me a hand with these case studies!
- 121. She had puffiness around her nose and eyes. Her menses gegan at age 16 and were irregular with scant flow. She had no interest in the opposite sex. There was an absence of pubic hair. She was constipated, gained weight easily, had dry skin and hair, had anemia, and she tired easily. What can she be suffering from?
- 122. What can she be suffering from?
- 123. References: Elaine N. Marieb, KatjaHoehn. Human Anatomy & Physiology 7th edition Aronoff, S. et al. Glucose Metabolism and Regulation: Beyond Insulin and Glucagon. Retrieved from http://spectrum.diabetesjournals.org/content/17/3/183.full http://www.hormone.org/Diabetes/diabetes.cfm Photos from Google images
- 124. References: Guyton, A. & Hall, J. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 11th Edition Tortora, G. & Derrickson, B. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology. 11th Edition http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/117648-overview