Overview of oceania 2012
- 2. What’s in a name? • Anthropologists look at numerous variables (such as language, mythology, religion, as well as kinship and social organization) to establish what have been termed "culture areas" in order to work with people. • In the Pacific these have been designated as Polynesia, Melanesia, and Micronesia • "The term Polynesia was coined by Charles de Brosses [1709-1777] in 1756 and applied to all the Pacific islands. At the same time he also proposed the terms Melanesia and Micronesia for the regions which still bear those names.
- 3. Continued… • The native peoples of Melanesia and Australia are quite dark-skinned, while the peoples of Micronesia and Polynesia are generally lighter. • The name of each island region is descriptive: the prefix “mela” means “dark” (because the inhabitants of Melanesia are so dark), “micro” means “small” (because the islands of Micronesia are so small), and “poly” means “many” (because the islands of Polynesia are so numerous).
- 5. Oceania • Prehistoric land bridges, lower seas permit migration • Outrigger canoes for open-sea travel • Humans in Oceania at least by 58,000 BCE • By 8,000 BCE trade between islands ceased due to the rising seas. • Early hunter-gatherer societies in Australia • Early agriculture in New Guinea by 3000 BCE – Yams, taro & raising pigs & chickens
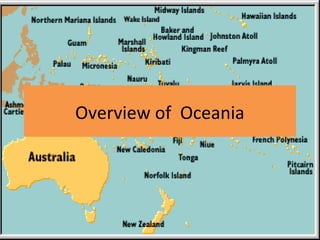
- 6. Geography of Oceania • The largest component of Oceania is Australia, which (being a continent) is not considered an island. • The next-largest land mass is New Guinea, the world’s second-largest island (after Greenland). New Guinea is by far the largest component of Melanesia. • The next-largest Oceanian islands are the south and north islands of New Zealand, which is the largest component of Polynesia.
- 7. Oceania was colonized by waves of migration emanating from Southeast Asia. •The first waves, which occurred during the Paleolithic, colonized Melanesia and Australia. • (The migrants of this period could easily reach Melanesia and Australia due to the lower sea level during the Paleolithic.)
- 8. Early Societies of Oceania, 1500 BCE – 700 CE
- 9. Austronesian • A group of languages that originated in the country of New Guinea which have adapted to modern languages such as Malayan, Indonesian, Filipino and Polynesian • - Seafaring peoples from southeast Asia who first entered New Guinea and surrounding islands about 5,000 years ago. Their skills of navigation, agriculture, and raising domestic animals helped them to people most islands of the Pacific. Also the population pressure and internal conflicts pushed these people to the Pacific islands.
- 12. The Austronesian people are a population group in Oceania and Southeast Asia who speak or had ancestors who spoke one of the Austronesian languages. They form a diverse group of peoples inhabiting roughly half the globe, ranging from Madagascar to Easter Island. Austronesian peoples consist of four primary strains: • Formosan: consists of the indigenous inhabitants of Taiwan. • Malay: consists of the inhabitants of the Malay Peninsula, Malay archipelago, Madagascar, and the Cham people. • Polynesian: consists of the inhabitants of Polynesia. ex. Maori, Hawaiian. • Micronesian: consists of the inhabitants of Micronesia, such as the Chamorros, Palauans, and Carolinians.
- 13. Lapita Peoples • Earliest Austronesian (language group of Oceania) migrants to sail into the Pacific Ocean and establish settlements in pacific islands. • Found throughout Pacific Islands • Agriculture, animal herding • Political organization based on chiefdoms – Relatives formed aristocracy • Trade over open ocean declines 500 BCE – Greater independence of
- 14. Lapita society • 1500-500 BCE from New Guinea to Tonga. Agricultural villages. • They had pottery with geometric designs. They also had trade and communication networks. (They traded potter, obsidian, shells, and tools.) These networks declined after 500 BCE. They had divine/ semi-divine chiefs who led public rituals and oversaw irrigation.
- 15. Lapita Catamarans and mask
- 16. First settlements •Australia was settled by the Indigenous Australians between 40,000 and 125,000 years ago. Oceania was first settled by Austronesians or Polynesian people at around 1800 BCE. in Fiji, then further colonized the rest of the islands by 1000 CE. •The Tu'i Tonga Empire was founded in the 10th century AD and expanded between 1200 and 1500. The Tu'i Kanokupolu is the title held by Tongan monarchs since 1600. George Tupou II of Tonga became the first king of Tonga in 1893. •From the 1850s Seru Epenisa Cakobau tried to unite the Fijian Islands, and became the first Tui Viti, or king of Fiji, a title which passed to the British Crown after 1874. The Great Council of Chiefs was established in Fiji in 1876.
- 18. Aborigine of the Naomi Tribe
- 19. Early 19th Century Aboriginal Tribe
- 20. 21 century Aboriginal People st
- 22. European exploration • Oceania was explored by Europeans from the 16th century onwards, the Spanish, with Ferdinand Magellan in the expedition achieved the circumnavigation of the world for the first time, discovered the Marianas and other islands of Oceania. • Abel Tasman's voyages in the 1640s visiting northwestern Australia, Tasmania, New Zealand, Tonga and the Fijian islands (Dutch seafarer) • James Cook explored the Pacific islands and the east coast of Australia in the 18th century. (English) • In 1789 the Mutiny on the Bounty against William Bligh led to several of the mutineers escaping the Royal Navy and settling on Pitcairn Islands, which later became a British colony.
- 25. Colonization/Imperialism • The British followed with colonies in Australia in 1788, New Zealand in 1840 and Fiji in 1872, with much of Oceania becoming part of the British Empire. • The Frenchacquired New Caledonia from 1853 and French Polynesia from 1889, • the Germans established colonies in New Guinea in 1884, and Samoa in 1900. • The United States also expanded into the Pacific, beginning with Baker Island and Howland Island in 1857, and with Hawaii becoming a U.S. territory from 1898. • Disagreements between the US, Germany and UK over Samoa led to theTripartite Convention of 1899. Among the last islands to be colonised wereTonga and Niue (1900) and Manu'a (1904).
- 27. Early 20th Century • During the First World War the German colonies in the Pacific were taken over by Allied powers. • In 1940 the administration of French Polynesia recognized the Free French Forces and many Polynesians served in World War II. • Unknown at the time to French and Polynesians, the Konoe Cabinet in Imperial Japan on 16 September 1940 included French Polynesia among the many territories which were to become Japanese possessions in the post-war world – though in the course of the war in the Pacific the Japanese were not able to launch an actual invasion of the French islands.
- 29. In the Second World War • …the Japanese invaded New Guinea, the Solomon Islands and other Pacific islands. They were turned back at the Battle of the Coral Sea and the Kokoda Track campaign before they were finally defeated in 1945. • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 1941-12-07 (12-08 Asian Time) Attack on Pearl Harbor 1941-12-08 Battle of Guam (1941) 1941-12-07 Japan declares war on the United States 1941-12-08 The United States declare war on Japan 1941-12-11 – 1941-12-24 Battle of Wake Island 1942-01-01 – 1945-10-25 Transport of POWs via hell ships 1942-01-11 – 1942-01-12 Battle of Tarakan 1942-01-23 Battle of Rabaul (1942) 1942-02-19 Air raids on Darwin, Australia 1942-02-19 - 1943-02-10 Battle of Timor (1942–43) 1942-03-31 Battle of Christmas Island 1942-04-18 Doolittle Raid 1942-05-03 Japanese invasion of Tulagi 1942-05-04 – 1942-05-08 Battle of the Coral Sea 1942-05-31 – 1942-06-08 Attacks on Sydney Harbour area, Australia 1942-06-04 – 1942-06-06 Battle of Midway
- 30. Post-war period • In 1946, Polynesians were granted French citizenship and the islands' status was changed to an overseas territory; the islands' name was changed in 1957 to Polynésie Française (French Polynesia). • Australia and New Zealand became dominions in the 20th century, adopting the Statute of Westminster Act in 1942 and 1947 respectively, marking their legislative independence from the United Kingdom. Hawaii became a U.S. state in 1959. • In 1962, France's early nuclear testing ground of Algeria became independent and the Maruroa atoll in the Tuamotu Archipelago was selected as the new testing site; tests were conducted underground after 1974.
- 31. Modern Age • Fiji and Tonga became independent in 1970, with many other nations following in the 1970s and 1980s. The South Pacific Forum was founded in 1971, which became the Pacific Islands Forum in 2000. Bougainville Island, geographically part of the Solomon Islands but politically part of Papua New Guinea, tried unsuccessfully to become independent in 1975, and a civil war followed in the early 1990s, with it later being granted autonomy. • In 1977, French Polynesia was granted partial internal autonomy; in 1984, the autonomy was extended. French Polynesia became a full overseas collectivity of France in 2004. • French nuclear testing in the Pacific was controversial in the 1980s, in 1985 French agents caused the Sinking of the Rainbow Warrior in Auckland to prevent it from arriving at the test site in Moruroa. In September 1995, France stirred up widespread protests by resuming nuclear testing at Fangataufa atoll after a three-year moratorium. The last test was on 27 January 1996. On 29 January 1996, France announced that it would accede to the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty, and no longer test nuclear weapons.
- 33. Continued Modern Era • East Timor declared independence from Portugal in 1975, but was invaded by Indonesia, before it was granted full independence in 2002. • Fiji has had a troubled recent history with coups in 1987, 2000 and 2006. • Between 2001 and 2007 Australia's Pacific Solution policy transferred asylum seekers to several Pacific nations, including the Nauru detention centre. Australia, New Zealand and other nations took part in the Regional Assistance Mission to Solomon Islands from 2003 after a request for aid. • Global warming is an issue in present day Oceania with many countries having droughts and storms.
- 35. 0 -> 14 Age Bracket 15 -> 64 Age Bracket 65+ Age Bracket 70,260 37.50% 57% 5.40% Cook Islands 240 sq km [93 sq mi] 1.3 Washington D.C. 21,008 n/a n/a n/a Fiji 18,270 [7,054 Slightly smaller than sq mi] New Jersey 868,531 32% 64.10% 3.80% 4,167 sq km [1,609 sq mi] 1/3rd Connecticut 262,125 29.30% 66.30% 5.40% 181.3 sq km [70 sq mi] ~ Washington, DC 56,429 39.10% 58.20% 2.70% 4 x Washington, D.C. 108,143 38.40% 58.50% 3.20% COUNTRY American Samoa French Polynesia Marshall Islands AREA (Sq. Km) (Comparable Area) POPULATION 199 sq km [77 sq miles] Micronesia, Federated 402 sq km [155 States of sq mi] Slightly larger than Washington, D.C. New Caledonia 19,060 [7,359] Slightly smaller than New Jersey 210,798 29.70% 64.20% 6.10% New Zealand 268,680 sq km [103,738 sq mi] About the size of Colorado 3,951,307 21.90% 66.50% 11.60% Palau 458 [177 sq mi] 2.5 x Washington, D.C. 19,717 26.70% 68.70% 4.60% 5,295,816 38.40% 57.80% 3.80% n/a n/a n/a 38.20% 57.60% 4.10% 199,414 34.80% 61.80% 3.40% 178,173 29.40% 64.60% 6.10% Papua New Guinea Pitcairn Island Tonga Vanuatu Western Samoa 463,840 sq km Slightly larger than [179,090] sq mi] California 47 sq km [18 sq mi] .3 Washington, D.C. 47 Individuals 748 sq km [289 4 x Washington, sq mi] D.C. 108,141 12,200 [4,710 sq mi] Slightly larger than Connecticut 2,944 [1,137 sq Slightly smaller than mi] Rhode Island
- 37. Arthur Frommer, age 76, author of travel books].... • "Travel teaches seven important lessons • 1. Travelers learn that all people in the world are basically alike. ... 2. Travelers discover that everyone regards himself or herself as wiser and better than other people in the world. ... 3. Travel makes us care about strangers. ... 4. Travel teaches that not everyone shares your beliefs. ... 5. Travelers learn that there is more than one solution to a problem. ... 6. Travel teaches you to be a minority. ... 7. Travel teaches humility