Marine Sediments Types (Detailed)
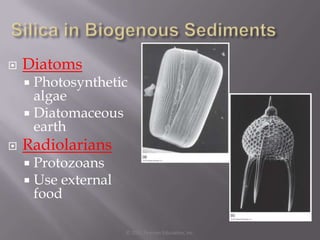
- 1. Diatoms Photosynthetic algae Diatomaceous earth Radiolarians Protozoans Use external food © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 2. Tests from diatoms and radiolarians generate siliceous ooze. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 3. Coccolithophores Also called nannoplankton Photosynthetic algae Coccoliths – individual plates from dead organism Rock chalk Lithified coccolith- rich ooze © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 4. Foraminifera Protozoans Use external food Calcareous ooze © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 5. Depends on three processes: Productivity Destruction Dilution © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 6. Dominated by lithogenous sediment, may contain biogenous sediment Carbonate Deposits Carbonate minerals containing carbon trioxide (CO3 ) Marine carbonates primarily limestone – CaCO3 Most limestones contain fossil shells Suggests biogenous origin Ancient marine carbonates constitute 25% of all sedimentary rocks on Earth. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 7. Stromatolites Fine layers of carbonate Warm, shallow- ocean, high salinity Cyanobacteria © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 8. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 9. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 10. Minerals precipitate directly from seawater Manganese nodules Phosphates Carbonates Metal sulfides Small proportion of marine sediments Distributed in diverse environments © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 11. Fist-sized lumps of manganese, iron, and other metals Very slow accumulation rates Grows ~1 centimeter over several million years Many commercial uses © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 12. Phosphates Phosphorus-bearing Occur beneath areas in surface ocean of very high biological productivity Economically useful as fertilizer Carbonates Aragonite and calcite Oolites © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 13. Metal sulfides Contain: Iron Nickel Copper Zinc Silver Other metals Associated with hydrothermal vents © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 14. Evaporites Minerals that form when seawater evaporates Restricted open ocean circulation High evaporation rates Halite (common table salt) and gypsum © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 15. Macroscopic meteor debris Microscopic iron- nickel and silicate spherules (small globular masses) Tektites Space dust Overall, insignificant proportion of marine sediments © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 16. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 17. Energy resources Petroleum Mainly from continental shelves Gas hydrates Sand and gravel (including tin, gold, and so on) Evaporative salts Phosphorite Manganese nodules and crusts © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 18. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 19. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.