Structure and types of pneumonia
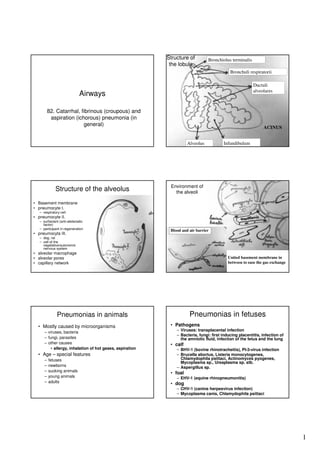
- 1. Structure of the lobule Bronchiolus terminalis Bronchuli respiratorii Ductuli alveolares Airways 82. Catarrhal, fibrinous (croupous) and aspiration (ichorous) pneumonia (in general) ACINUS Alveolus Structure of the alveolus Infundibulum Environment of the alveoli • Basement membrane • pneumocyte I. – respiratory cell • pneumocyte II. – surfactant (anti-atelectatic factor) – participant in regeneration • pneumocyta III. Blood and air barrier – dog, rat – cell of the vegetative/autonomic nervous system • alveolar macrophage • alveolar pores • capillary network United basement membrane in between to ease the gas exchange Pneumonias in fetuses Pneumonias in animals • Mostly caused by microorganisms – viruses, bacteria – fungi, parasites – other causes • allergy, inhalation of hot gases, aspiration • Age – special features – – – – – fetuses newborns sucking animals young animals adults • Pathogens – Viruses: transplacental infection – Bacteria, fungi: first inducing placentitis, infection of the amniotic fluid, infection of the fetus and the lung • calf – BHV-1 (bovine rhinotracheitis), PI-3-virus infection – Brucella abortus, Listeria monocytogenes, Chlamydophila psittaci, Actinomyces pyogenes, Mycoplasma sp., Ureaplasma sp. stb. – Aspergillus sp. • foal – EHV-1 (equine rhinopneumonitis) • dog – CHV-1 (canine herpesvirus infection) – Mycoplasma canis, Chlamydophila psittaci 1
- 2. Pneumonia in newborns Forms of pneumonias (perinatal pneumonias) • neonatal pneumonia (collective category) – Aerogenous infection before the newborn got the colostrum (in state of hypogammaglobulinaemia) – inhalation of different bacteria • calf, foal, goat Streptococcus sp. • piglet Streptococcus sp., E. coli • birds E. coli – Local process continues often to septicemia • meconium aspiration syndrome – aspiration during parturition, typical – or obturation, or pneumonia due to pathogens Bronchopneumonias: Inflammation → hyperaemia, edema → neutrophils, macrophages → epithelial gaps↑, ↑ vascular permeability↑ → ↑ plasma fluid, proteins → airspace↓ ↓ Serous bronchopneumonia Desquamative bronchopneumonia • definition – inflammatory process in the parenchyma of the lung often accompanied with the lesions of the smaller or larger bronchi • Forms – bronchoalveolar • serous, desquamative, catarrhal, suppurative, fibrinous (croupous) – interstitial – granulomatous – embolic-metastatic – aspiration – special Desquamative bronchopneumonia Desquamative bronchopneumonia 2
- 3. Serous bronchopneumonia Normal shape, slightly enlarged, darker, gland-like by palpation, doesn’t crepitate when cut, clear liquid oozes to the cut surface Desquamative pneumonia Catarrhal bronchitis Bronchoalveolar pneumonia Fibrinous (croupous) pneumonia (bronchopneumonia) • • spreads quickly → entire lobes are affected - “Lobar pneumonia” Development • Appearance – Congestion, hemorrhage, massive exudation, fibrin accumulation – Fibrin → pleural surface = sero-fibrinous pleuritis – intense redness, firmer texture, “consolidation”, hepatization (red~, gray~). – Dilation and thrombosis of lymph vessels → edema → thick septae → marbled appearance – Focal coagulative necrosis. “Sequestra”. – Histology • massive exudation → fluid obliterates airspace. Neutrophils, macrophages. Fibroblasts • Stages – initial phase Extension: • stadium incrementi s. hyperaemicum – phase of hepatisation (std. hepatisationis) lobules - lobular lobes - lobal focal - pseudolobular • red hepatisation (std. h. rubrae) • grey hepatisation (std. h. griseae) • yellow hepatisation (std. h. flavae) – phase of resolution (std. resolutionis) • Croupous (fibrinous) pneumonia nasal discharge: mucoid or mucopurulent (P. m., B. b., Str.) Croupous (fibrinous) pneumonia 3
- 4. Croupous pneumonia Croupous pneumonia – stadium incrementi Croupous pneumonia - hepatisation Grey hepatisation Croupous pneumonia – hemorrhagic character Healing of the croupous pneumonia • restitutio ad integrum – if the integrity of the tissue structure is maintained – freed enzymes of the degenerated neutrophils cause – fibrinolysis • partially absorbtion (lymph vessels) • partially expectoration – epithel layer of the acini regenerates • restitutio cum defectu – connective tissue proliferation from the wall of the respiratory ducts – carnificatio pulmonum 4
- 5. Croupous pneumonia Croupous pneumonia • Due to direct (thrombotic) effect of the pathogen – Smaller or larger necrotic foci – Sometime hemorrhagic character – Secondary ichorous pneumonia on the affected areas • Cause of death: – Suffocation or heart failure – Following croupous pneumonia • Metastatic foci – focal necrotizing-purulent-ichorous pneumonia • Allergic reaction in horses – Hemorrhagic purpura, septic pododermatitis, uveitis, urticaria Pathology of the croupous pneumonia • • • • • • shape maintained enlarged marbled liver-like (in stages of hepatisation) No crepitation on cutting! cut surface – mottled, homogenous – dry, uneven, granular Aspiration pneumonia Aspiration pneumonia • Different aspirated substances – amniotic fluid – milk, saliva, food, drinking water, blood – fluid used for gastric lavage, contrast medium used for filling the GI tract – eructated or vomited gastric content • Consequences are different according to – what type of material and what amount is aspirated – where did the substance go – if there where any putrefactive bacteria present Aspiration pneumonia 5
- 6. Aspiration pneumonia Aspiration pneumonia • Putrid bronchitis – Putrefactive bacteria colonize in the mucous membrane of the bronchi – the mucous membrane necrotizes – accompanied with putrid smell, the tissue debris becomes soft fluid – all the layers of the bronchi are affected – if there is enough time, the lungs also become affected • usually the animal dies because of the absorbed toxins Ichorous pneumonia Ichorous pneumonia • Way of infection: – Aerogenous infection (aspiration) • putrid bronchitis first, than spreading to the lungs • starts from the airways – lympho-haematogenous infection may occur • disseminated foci • from the blood vessels of the interstitium • Due to putrefactive bacteria – coagulation necrosis – secondary softening in the necrotized areas • putrid smell, histolytic tissue debris causing intoxication (sapraemia) – acute ichorous abscess, ichorous cavern (cavity) • Slow, delayed demarcation Interstitial pneumonia • Majority of the lesions – In the interstitium 83. Interstitial, suppurative and embolic pneumonias (in general) • Most typical lesions: – acute, subacute, chronic proliferative inflammation – besides proliferative processes immunpathological processes, accumulation of immune cells • Appearance: – intralobular (interalveolar) – interlobular – between the lobules – peribronchial – around the small bronchi 6
- 7. Intralobular (interalveolar) interstitial pneumonia Mild proliferation of the alveolar interstitium Intralobular (interalveolar) interstitial pneumonia Severe proliferation of the alveolar interstitium Immunpathologic process Intralobular (interalveolar) interstitial pneumonia Intralobular (interalveolar) interstitial pneumonia Peribronchial interstitial pneumonia Interstitial pneumonia • Proliferative processes in the alveoli – Epithelisation • pneumocyta II. – Pseudoepithelisation • alveolar macrophages • Age of the process – acute – histiocyte and macrophage proliferation – subacute – pronounced cell proliferation – chronic – severe fibrosis 7
- 8. Pathogen has an effect inside the alveoli Intralobular (interalveolar) interstitial pneumonia Epithelisation Pseudoepithelisation Chronic interstitial pneumonia Suppurative pneumonia (pneumonia purulenta) Purulent bronchopneumonia • Typically embolic or metastatic • If hematogenous: – Purulent process somewhere in the body → distributed abscesses in the lung (no surrounding inflammation) • If bronchiogenous: – First catarrhal or croupous pneumonia occurs and secondary purulent foci are formed • Pathogens: – cattle/pig → Arcanobacterium (Actinomyces) pyogenes – rabbit → Staphylococcus aureus – horse → Streptococcus equi, Rhodococcus equi 8
- 9. Purulent bronchopneumonia Pneumonia with granulome formation • Accompaying other disease – Lympho-hematogenous metastasis • Embolic-metastatic pneumonia • Possible nodules – necrotic foci – purulent (ichorous) abcesses – ichorous foci • Appearance: – solitaer focus (smaller - larger) – evenly disseminated foci – foci of the same age / or prolonged form Necrotic pneumonia Sequestrum formation after necrotic pneumonia Mass of necrotic lung parenchyma seprated from viable lung tissue by purulent exudate and usually encased in a fibrous capsule 9
- 10. Embolic-metastatic pneumonia Chronic purulent abscess formation (cut surface) Port of entry Purulent-ichorous pneumonia Granulomatous pneumonia Granulomatous pneumonia 10
- 11. Granulomatous pneumonia Locus minoris resistanciae Special pneumonias • Actinobacillus pleuropneumonia – serous-hemorrhagic-proliferative-necrotizing • in hours, death in 1-2 days • pronounced macrophage proliferation • extended demarcation – sero-fibrinous pleuritis • perifocal edema • Anthrax – Aerogenous infection (piglet inhales the spores) – Serous, hemorrhagic, necrotizing pneumonia – Spore reaches the deep areas of the lung, starts to proliferate → rapid course 11