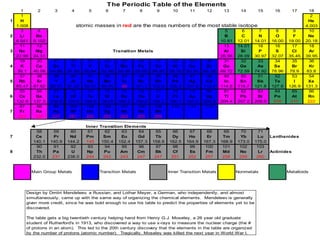
Interactive Periodic Table of Elements
- 2. ( natural ) Boiling Point: -252.77 C Freezing Point: 0 C Melting Point: -259.2 C Atomic Number: 1 Atomic Mass: 1.00797 H This element was founded by Henry Canvendish in 1776. It was confused with other gases until Cavendish demonstrated in 1776. It is used for the inflation of balloons. When hydrogen is mixed with air or oxygen it ignites. USES FOUND MIXED WITH GASES. Hydrogen Periodic Table
- 3. HE Boiling point:-268.9 Melting point:-272.2 Freeze point::20 Atomic number:2 Atomic symbol:He Atomic mass:4.0026 Helium (Natural) This Element was discovered Pierre Janssen in 1868. USES Helium is used to pressurize and stiffen the rocket engines. Periodic Table
- 4. LI Boiling Point:1342 C Melting Point:181 C Freezing Point:Not available. Atomic Number: 3 Atomic Mass: 6.941 Atomic Symbol:LI Lithium (Man made) This element was discovered by Johann A. Arfvedson in 1817. USES Lithium is used for bonding carbon dioxide in the ventilator systems of spacecraft and submarines. Also the hydride is used to inflate lifeboats and its heavy hydrogen is used in making the hydrogen bomb. Periodic Table
- 5. BE Boiling Point: 3000 C Melting Point: 1287 C Freezing Point: Not Available Atomic Number: 4 Atomic Mass: 9.012 Atomic Symbol: BE Beryllium (Natural) This element was discovered by Louis Nicolas Vauquelin in 1797. USES Beryllium is used for important use in so-called multiplexing systems. Periodic Table
- 6. B Boiling Point:3650 C Melting Point: 2180 C Freezing Point: Not available Atomic Number: 5 Atomic Mass: 10.81 Atomic Symbol: B Boron (Natural) This element was discovered by Joseph Gay-Lussie,Baron Louis Thenard and Sir Humphry Davy. USES Boron is used for bone health in humans and other vertebrates. It is also used in instruments designed to detect and count slow. Periodic Table
- 7. C Boiling Point: Not Available Melting Point: Not Available Freezing Point: Not Available Atomic Number: 6 Atomic Mass:12.011 Carbon (Man Made) This element was discovered by several scientists in 1985. Scientists vaporized graphite to produce a stable form of carbon molecules. USES Carbon is used to remove oxygen from metal. Periodic Table
- 8. N Boiling Point: -195.79 C Melting Point: -210.01 C Freezing Point: 0 C Atomic Number: 7 Atomic Mass: 14.007 Nitrogen (Natural) This element was discovered by Antoine Laurent Lavoisier in 1772. USES Nitrogen is used in the chemical industry and obtained by the fractional distillation of liquid air. Periodic Table
- 9. O Boiling Point: 182.96 C Melting Point: 218.4 C Freezing Point: 0 C Atomic Mass: 16.00 Atomic Number: 8 Oxygen (Natural) This element was discovered in 1774 by Joseph Priestely. USES This element is used for welding torches and is used for patents. Periodic Table
- 10. F Boiling Point: -188.13 C Melting Point:-219.61 C Freezing Point: 0 C Atomic Mass: 19.00 Atomic Number:9 Flourine (Natural) This element was discovered in 1886 by Henry Moissan. USES It is used to destroy the ozone layer. Periodic Table
- 11. Ne Boiling Point:-246.08 C Melting Point:-248.6 C Freezing Point:0 C Atomic Mass: 20.18 Atomic Number: 10 Neon This element was discovered in 1898 by Sir William Ramsay. USES Neon is used in neon lights and advertising. Periodic Table
- 12. NA Boiling Point:883 C Melting Point:98 C Freezing Point:0 C Atomic Mass:22.99 Atomic Number:11 Sodium (Natural) This element was discovered in 1807 by Sir Humphrey Davy. USES Sodium is used as a cooling agent in nuclear reactors. Periodic Table
- 13. MG Boiling Point: 1107 C Melting Point: 649 C Freezing Point: Not Available Atomic Number: 12 Atomic Mass: 24.31 Magnesium (Natural) This element was discovered by Sir Humphrey Davy in 1808. USES Magnesium is used in medicine and effervescent beverages. Periodic Table
- 14. AL Boiling Point - 2467c Melting Point - 660c Atomic Number - 13 Atomic Mass - 26.9815 Aluminum ( Natural ) This element was discovered in 1825 by Hans Oersted in Denmark. USES Aluminum is used in cooking utensils, railroad cars, cars, and to build aircraft, Periodic Table
- 15. SI Boiling Point - 42571f Melting Point - 2570f Atomic Number - 14 Atomic Mass - 28.086 Silicon ( Natural ) This element was discovered in 1823 by Baron Jons Jakob Berzelius. USES Silicon is used in the steel making industry as a constitute of Silicon steel, and in the making of cores of electrical transformers. Periodic Table
- 16. P Boiling point-536 f Melting point-111.4f Atomic Number-15 Atomic Mass-30.974 Phosphorus (natural) This element was discovered by Hennig Brand in 1669 when he was trying to turn silver into gold. USES Phosphorus is used in fertilizers, rat poison, and in the red part of matches. Periodic Table
- 17. S Boiling Point- 832.3F Melting Point- 239.38F Atomic Number- 16 Atomic Mass- 32.064 Sulfer (Natural) This element was discovered in the prehistoric time and mentioned in the bible. USES It is used in matches, rubber, gunpowder, sulfa drugs, and skin ointments. Periodic Table
- 18. Boiling Point -29.29f Melting Point -149.8f Atomic Number-17 Atomic Mass-35.453 Chlorine (Natural) CL This Element was discovered in 1774 by Humphry Davy. USES: It was the first substance used as a poison gas in World War 1. Periodic Table
- 19. AR Boiling Point-98 Melting Point - NONE Atomic Number-18 Atomic Mass-39.948 Argon ( Natural) This element was discovered in 1894 by William Ramsey. USES: This element is used in neon lamps that gives a red or blue light. Periodic Table
- 20. K Boiling Point - 1408f Melting Point - 145f Atomic Number - 19 Atomic Mass - 39.098 Potassium ( Natural) This element was discovered in 1807 by Sir Humphry Davy. USES: It is used in photelectric cells in matches, fireworks, dyeing, leather tanning. Periodic Table
- 21. CA Boiling Point- 2703 Melting point- 1542 Atomic Number- 20 Atomic Mass- 40.08 Calcium (Natural) This element was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy in 1808. Uses: It is used in copper, nickel, and stainless steel. Periodic Table
- 22. SC Boiling Point - 5137f Melting Point - 2806f Atomic Number - 21 Atomic Mass - 44.956 Scandium ( Natural ) This element was discovered in 1879 by a Swedish chemist Lars Fredrik. USES No uses found. Periodic Table
- 23. TI Boiling Point - 5949f Melting Point - 3020f Atomic Number - 22 Atomic Mass - 47.88 Titanium ( Natural ) This element was discovered in 1791 by William Gregor. USES This element is used in aluminum. Periodic Table
- 24. V Boiling Point - 6116f Melting Point - 3434f Atomic Number - 23 Atomic Mass - 50.941 Vanadium ( Natural ) This element was discovered in 1801 by Andres Manuel Del Rio and was rediscovered in 1830 by Nils Gabriel Sefstrom. USES This element is used in hardness, alloys, and plantinum. Periodic Table
- 25. CR Boiling Point-4842 f Melting Point-3375 f Atomic Number-24 Atomic Mass-51.996 Chromium (Natural) USES This element was discovered by a French chemist named Louis Nicolas Vanquelin in 1797. Chromium is used in alloys, iron, nickle, and cobalt. Periodic Table
- 26. MN Boiling Point - 3564f Melting Point - 2271f Atomic Number - 25 Atomic Mass - 54.938 Manganese ( Natural ) This element was discovered in 1774 by Johan Gottlicp Gahn. USES Manganese is used in copper tin, zinc, dry cell battery, paint, and varnisncils for collecting glash. Periodic Table
- 27. FE Boiling Point - 4982f Melting Point - 2795f Atomic Number - 26 Atomic Mass - 55.847 Iron ( Natural ) This element was discovered in4000B.C. by Egypt people. USES This element is used in cars, wrought iron, and castiorn steel. Periodic Table
- 28. Melting point- 2723 Boiling point-5,198 CO Atomic Number-27 Atomic Mass-58.923 Cobalt Color, silvery Structure: Rock formed It was discovered by George Brandt in 1735 Uses: unknown (Natural) Periodic Table
- 29. NI Boiling Point-2730 Melting Point-1455 Atomic Number-28 Atomic Mass-58.69 Nickel (Man made) Color, Silvery Structure: Unknown This element was discovered by Baron Axel and found in 1751 Uses Used to make nickels Periodic Table
- 30. CU Boiling point-4753 Melting point-1981 Atomic number-29 Atomic mass-63.546 Copper Color, goldish (natural) Structure: Unknown The person who discovered copper . It does not say! USES It is used in things that involve electrity. Periodic Table
- 31. ZN Boiling Point: 1665 Melting Point: 788 Atomic Number: 30 Atomic Mass: 65.38 Zinc Color, Silvery (Natural) Structure: Rock Form This element was discover by Andreas Sigismund Marggraf uses It is 5% of the worlds porducktion Periodic Table
- 32. GA Gallium Boiling point-4357 Melting point-86 Atomic number-31 Atomic mass-69.72 Color, Bluish Gray (Natural) This element was discovered by Paul Emile Leeog de Uses Unknown Periodic Table
- 33. GE Boiling point-5126 Melting point-1719 Atomic number-32 Atomic mass-72.59 Germanium Color, grayish white (natural) This element was discovered by Dmitry Nanovich. Uses It was used in world war 2. Periodic Table
- 34. AS Boiling point-Non-A Melting point-Non-A Atomic number-33 Atomic mass-74.9216 Arsenic ( man made) Color, green This element was discovered by not avalable Uses For making glasses. Periodic Table
- 35. SE Boiling point-1265 Melting point-423 Atomic number-34 Atomic mass-78.96 Selenium Color,yellowish This element was discovered by berzelivs-son jacob, Baron Uses: Unknown (natural) Periodic Table
- 36. BR Boiling point-137.8 Melting point-18.95 Atomic number-35 Atomic mass-79.9 Bromine Color,redish brown This Element was discovered by Antoine jerome Balard in 1826 Uses: Unknow (Natural) Periodic Table
- 37. KR Boiling point-244.03 Melting point-250.98 Atomic number-36 Atomic mass-83.8 Color,orange red Krypton (Natural) This Element was discovered by Norman Foster, Ramsey in 1962 Uses: For the earthes atmasfear Periodic Table
- 38. RB Boiling point-1267 Melting point-102 Atomic number:37 Atomic Mass: 85.468 Color, red Rubidium (Natural) This element was discovered by Robert Wilhelm Busen Uses Tea, Tobacco , Coffee, and other plants. Periodic Table
- 39. SR Boiling Point:2523 Melting point-1416 Atomic number-38 Atomic mass-87.62 Strontium Color silvery (natural) uses This element was discovered in 1790 unknown Periodic Table
- 40. Boiling point-6040 Melting point-2772 Atomic number-39 Atomic mass-88.91 Color silvery uses unknown (natural) Y Yttrium This was discovered by Periodic Table
- 41. ZR Boiling point-7911 Melting point-3362 Atomic number 40 Atomic mass 91.22 zirconium Color, Bluish black (natural) This Element was discovered by Martin Heinrich. Uses: The uses were for vacuum tubes, steel, and porcelain. Periodic Table
- 42. NB NB Atomic Number-41 Atomic mass-92.906 Boiling Point-5127 C Melting Point-2468 C Niobium (Natural) Found in crustal rock. Burns when heated in air. This Element was discovered in 1801 by Charles Hatchet. Found mainly in Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of Congo. USES This element is used for nuclear power plants and stainless steel. Periodic Table
- 43. MO Boiling point-4640 C Melting point-2610 C Atomic Number-42 Atomic Mass-95.94 Molybdenum (Man Made) Silvery,white, tough It’s a metal. This element was discovered in1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. USES In soils it helps contribute to the growth of plants. Used in alloying steel, for air crafts and structural work. It serves as electrodes in glass furnaces. Periodic Table
- 44. TC Atomic Number-43 Atomic Mass-98 Melting Point-2200 C Boiling Point-4567 C Technetium (Man made) This element was discovered in 1937 by Emilo Segre and Carlo Perrier by bombarding Molybdenum with Deuterons. USES Technetium is used for imaging medicines . Periodic Table
- 45. RU Boiling Point-3900 C Melting Point-2310 C Freezing Point- -263 C Atomic Number-44 Atomic Mass-107.07 Ruthenium Ruthenium was discovered in 1844 by Karl Karlovich Klaus USES Ruthenium is used for the tips of pens and in the manufacture of jewelry. Grayish white metal. Superior to Platinum in resistance to attack by acids. (Natural) Periodic Table
- 46. RH Boiling Point-3727C Melting Point-1966 C Atomic Number-45 Atomic Mass-102.905 Rhodium (Natural) Silvery white metal. Very durable. This element was discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. Rhodium is used in mirror surfaces, as plating finish in jewelry and silverware and as a black pigment for porcelain. USES Periodic Table
- 47. PD Boiling point-2970 C Melting point-1554 C Atomic number-46 Atomic mass-106.4 Palladium Rare silvery white soft metal. Fuses and welds easily. (Natural) This element was discovered by William Hyde Wollaston. It is used for nonmagnetic springs in clocks and watches. Used in jewelry, for special in mirrors, and alloyed with gold it forms white gold. Also used in Canadian nickel. USES Periodic Table
- 48. AG Boiling Point-2212 C Melting Point-962 C Atomic Number-47 Atomic Mass-107.868 Silver (Natural) Not Chemically active. Eggs tarnish it quickly. Harder than gold yet softer than copper. Date of discovery is unknown. Silver mines were probably worked in Asia before 2,500 B.C. USES Silver is used to coat smooth glass surfaces for mirrors, aluminum has replaced this though. It is also used in jewelry and used to be used in coins. Periodic Table
- 49. CD Boiling Point-1409 C Melting Point-321 C Atomic Number-48 Atomic Mass-112.41 Cadmium Burns bright when heated. USES This element is used for coating metals and is used in batteries that are used for specialized purposes. Periodic Table
- 50. IN Boiling Point-2080 C Melting Point-157 C Atomic Number-49 Atomic Mass-114.82 Indium Silvery white soft metal. (Natural) Discovered by Hieronymus Theodor Richter and Ferdinand Reich. USES This element is used in nuclear reactors control rods, and is found in certain zinc blends, tin, and iron ores. Periodic Table
- 51. SN Atomic Number-50 Atomic Mass-118.69 Boiling Point-2260 C Melting Point-232 C Tin Silvery white metal. Forms stannic acid when heated in air. Discovery date is unknown and who discovered it is also unknown. It is found in Malaysia, Brazil, Indonesia, Thailand, Bolivia, Australia, and America. USES Tin is used in hundreds of industrial processes throughout the world. It is also used as a protective coating for copper vessels, and various metals used in the manufacture of tin cans. Periodic Table
- 52. SB Boiling Point-1750 C Melting Point-630 C Atomic Number-51 Atomic Mass-121.75 Antimony Bluish white brittle semimetal. (Natural) This element was probably discovered in 1450 but was certainly discovered in 1600. It is mined in China, France, Italy,Japan, Mexico, and Western United States. USES Antimony is used in certain medicines, as a yellow pigment in glass and porcelain, used for bronzing steel, and as a mordent in dying. Periodic Table
- 53. TE Boiling Point-1390 C Melting Point-630 C Atomic Number-52 Atomic Mass-127.6 Tellurium (Natural) Silvery white semimetal. A gravity of 6.25. This element was discovered in 1782 by Franz Joseph Muller Von Reichenstein. USES Tellurium is used in the manufacture of rectifiers and thermoelectric devices. With organic substances it is used for natural and synthetic rubber, in antiknock compounds for gasoline, and as an impart for blue tints in glass. Periodic Table
- 54. I Boiling Point-185 C Melting Point-113.6 C Atomic Number-53 Atomic Mass-126.905 Iodine Chemically active. Blue black solid. (Natural) This element was first isolated from seaweed in 1811 by Bernard Courteous. USES Iodine is used in medical use and without this, stunted growth and conditions like goiter can happen. It is also used in photography, making dyes, and in cloud seeing operations. Periodic Table
- 55. XE Boiling Point-108.1 C Melting Point-111.8 C Atomic-Number-54 Atomic Mass-131.29 Xenon Colorless and odorless. This element was discovered in 1898 by Sir William Ramsey and Morris Travers. USES Xenon is used in lighting high-speed photographic tubes. Periodic Table
- 56. CS Boiling Point: 1236 F Melting Point: 82 F Atomic Number: 55 Atomic Mass: 132.905 Cesium ( Natural ) Color, White Structure, Not available Cesium was discovered in 1860 by the German chemists Robert Wilhelm Bunsen and Gustav Robert Kirchhoff through the use of a spectroscope. USES: Cerium is used to remove residual oxygen from radio vacuum tubes. Thus it is used in televisions, radios, and computers. Periodic Table
- 57. BA Boiling Point: 2984 F Melting Point: 1337 F Atomic Number: 56 Atomic Mass: 137.33 Barium Color: Soft, Silvery ( Natural ) Structure: Not available This element was discovered in 1808 by the English scientist Sir Humphrey Davy. USES: Barium is sometimes used in coating electrical conductors in electronic apparatus and in automobile ignition systems. Periodic Table
- 58. LA Boiling Point: 6267 F Melting Point: 1684 F Atomic Number:57 Atomic Mass: 138.91 Lanthanum ( Natural ) Color, Metallic Structure, not available This element was discovered by the Swedish chemist Carl Gustav Mosander in 1839. USES: Lanthanum is used in optical glass and cigarette flints. Periodic Table
- 59. CE Boiling Point: 6229 F Melting Point: 1468 F Atomic Number : 58 Atomic Mass : 140.12 Cerium Color: Soft, Gray Structure: Not available ( Natural ) Cerium was discovered in 1803 by the Swedish chemists, Baron Jons Jakob Berzelius and Wilhelm Hisinger, in the same year it was also discovered independently by the German chemist Martin Heinrich. USES: Cerium is used in small quantities in the manufacturing of glass, ceramics, arc-lamp, electrodes, and photoelectric cells. Periodic Table
- 60. PR Boiling Point: 6368 F Melting Point: 1708 F Atomic Number: 59 Atomic Mass: 140.9 Praseodymium ( Natural ) Color: Silvery Structure: Not available Extracted from Neodymium Praseodymium was discovered in 1885 by the German chemist, Carl Auer von Welsbach. USES: This element is used in magnesium alloys and in misch metal, an alloy used for cigarette-lighter flints and as a deoxidizer in alloys and vacuum tubes. Periodic Table
- 61. ND Neodymium ( Natural ) Boiling point: 5565 F Melting point : 1870 F Atomic Number : 60 Atomic Mass:144.24 Color, Silvery Structure: Not Available Extracted From Praseodymium This element was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist, Baron Carl Aver Von Welsbach. USES: Neodymium is used in the screens of color televisions. Periodic Table
- 62. PM Promethium Boiling Point: 5432 F Melting Point: 1908 F Atomic Number: 61 Atomic Mass: 145 Color, Radioactive Metallic element ( Natural ) Structure, Not available Promethium was isolated in 1945 by scientists at the nuclear research laboratory at Oak Ridge, Tennessee by the American chemists Charles DuBois Coryell, Jacob A. Marinsky, and Lawrence E. Glendenin. USES: Promethium is used in atomic batteries and as a beta-particle source in thickness gauges. Periodic Table
- 63. SM Boiling Point: 3261 F Melting Point: 1965 F Atomic Number: 62 Atomic Mass: 150.4 Samarium Color, White Structure, Not available ( Natural ) This element was discovered by the French chemist P.E Locoq de Boisbaudran in 1879. USES: Samarium oxide is used in the control rods of some nuclear reactors. Periodic Table
- 64. EU Boiling Point: 2781 F Melting Point: 1512 F Atomic Number: 63 Atomic Mass: 151.96 Europium Color, Silvery Structure, Not available ( Natural ) Europium was discovered in 1896 by the French chemist, Eugene Demorcay. USES: This element is used in the screen of a color television, and when bombarded with electrons, produces the color red. Periodic Table
- 65. GD Boiling Point: 5923 F Melting Point:2395 F Atomic Number: 64 Atomic Mass, 157.25 Gadolinium ( Natural ) Color: Silvery, White Structure: Unknown This Element was discovered in 1880, By a Swiss Chemist Jeande Marignec. Uses: It is used as a component of control rods in nuclear reactors. Periodic Table
- 66. TB Atomic Number: 65 Atomic Mass: 158.925 Boiling Point: 5846 F Melting Point: 2473 F Terbium ( Natural ) Color, Metallic Structure, Not available Terbium was discovered in 1843 by the Swedish chemist Carl Gustav Mosander. USES: Terbium is used in refactory materials, and electronic apparatus. Periodic Table
- 67. DY Dysprosium (Natural) This element was discovered in 1886 by Paul Erile Locoq de Boisbaudran. Uses He separated one of its compounds from an oxide of Holmium.It is sometimes used to control rods of nuclear reactors. Boiling point:4653 Melting point:2574 Atomic Number:66 Atomic Mass:162.5 Color,yellow or yellow green Structure: A high magnetic susceptibility Periodic Table
- 68. HO Boiling Point:4892 F Melting Point: 2683 F Atomic Number:67 Atomic Mass: 164.93 Holmium ( Natural ) Color, Silvery Structure: Not Available This element was discovered in 1878 by the Swiss chemists, Jacques Louis Soret, and Marc Delafontaine. It was also independently discovered by Per Teodor Cleve in 1879. USES: Holmium is used in some electronic devices and as a catalyst in industrial chemical reactions. Periodic Table
- 69. ER Boiling Point: 5194 F Melting Point: 2784 F Atomic Number: 68 Atomic Mass: 167.26 Erbium Color: Bright, Silvery Luster ( Natural ) Structure: Not available Erbium was discovered in 1843 by the Swedish chemist, Carl Gustav Mosander. USES: Erbium is used in experimental optical amplifiers that amplify light signals sent along fiber-optic cables. Periodic Table
- 70. Boiling Point-3542 Melting Point-2813 TM Atomic Number-69 Atomic Mass-165.934 Thulium (Natural) Color, Silvery-gray Metallic Structure: Soft, malleable ductile The element was discovered by the Swedish chemist Per Teodor Cleve in 1879. USES Thulium is used in small portable x-ray machines which utilize artificially radioactive Thulium as it’s x-ray source Periodic Table
- 71. B Boiling Point-1506 Melting Point-2185 YB Atomic Number-70 Atomic Mass-173.04 Ytterbium Color,bright silvery (Natural) Structure: Soft, malleable Ytterbium was discovered by a Swiss chemist Jean Charles De Marignac in 1878. Uses Ytterbium is used in alloys, electronics, and magnetic materials . Periodic Table
- 72. LU Boiling Point-6153 Melting Point-3025 Atomic Number-71 Atomic Mass-174.97 Lutetium (Natural) Color, Silvery White Structure: Not Available This element was discovered by a French chemist named Geoges Ubain, and a Carl Auer von Welsbach about the same time, in 1907. USES Lutetium is used in determining in meteorites in relation with the earth. Periodic Table
- 73. HF Boiling Point-8316 Melting Point-4041 Atomic Number-72 Atomic Mass-178.49 Color, Metallic Hafnium Structure: Resembles zirconium (Natural) Hafnium was discovered by the Hungarian chemist, Georg von Hevesy and Dutch physicist Dirk Coster in Copenhagen in the year 1923. USES Hafnium is used with zirconium as a structural material in nuclear power plants. Periodic Table
- 74. TA Boiling Point-5425 Melting Point-9797 Atomic Number-73 Atomic Mass-180.948 Tantalum (Natural) Color,White Structure: Acid Tantalum was discovered by Baron Jons Jakob Berzelius in 1820. USES It is used for Laboratory wear, circuits, and Camera lenses . Periodic Table
- 75. W Tungsten (Natural) Boiling Point-10,220 Melting Point-6170 Atomic Number-74 Atomic Mass- 183.85 Color, silver-steel Structure: Hard and Brittle This element was discovered Carl Wilhem Scheele, and Juan Jose and Fausto D’ Elhuyar in 1781. USES Tungsten is used in cutting tools . Periodic Table
- 76. Melting Point-5756 RE Atomic Number-75 Atomic Mass-186.207 Rhenium (Natural) Color,Silvery White Structure: Very hard This element was discovered by Walter Karl Noddack and Ida Eva Noddack in 1925. USES Rhenium is used in electrical filaments, welding rock, and photographic flashbulbs. Periodic Table
- 77. OS Melting Point-4892 Atomic Number-76 Atomic Mass-190.2 Osmium (Natural) Color, Bluish-white Structure: Brittle metallic It was discovered by Smithson Tennant in 1803 . USES It is used in standard weights and measurements. Periodic Table
- 78. IR Boiling Point-7466 Melting Point-4370 Atomic Number-77 Atomic Mass-192.22 Iridium Color, white Structure: Brittle and extremely hard It was discovered by Smithson Tennant, a British chemist in 1804. USES It is used for jewelry, fountain tip pens, compasses, and surgical tools Periodic Table
- 79. PT Boiling Point-6291 Melting Point-3222 Platinum (Natural) Color, bluish-gray Structure: Metallic Discovered sometime before the 16th century. USES Used in laboratory apparatus, contact points in electrical apparatus and in instruments used for measuring high temperatures, also used in dental fillings. Atomic Number-78 Atomic Mass-195.09 Periodic Table
- 80. AU Boiling Point-1947 Melting Point-5086 Atomic Number-79 Atomic Mass-196.97 Gold (Natural) Color, Gold Structure: Soft, Dense This element is the second most valuable mineral in the world. USES It was used for jewelry, as money, and in the form of gold leaf . Periodic Table
- 81. HG Boiling Point-675 Melting Point-38 Atomic Number-80 Atomic Mass-200.59 Mercury (Natural) Color, silvery metallic Structure: Free flowing liquid It was discovered by a French chemist Antoine Laurent Lavosier . USES Mercury is used in thermometers and it’s used in other types of scientific apparatus. Periodic Table
- 82. Boiling Point-2665 Melting Point-597 TI Atomic Number-81 Atomic Mass-204.383 Thallium (Natural) Color, bluish-gray Structure: Soft and malleable Discovered by Sir Williams Crookes an English chemist in 1861. USES It is used for rat poison and ant poison. It can also be used to diagnose some types of heart disease. Periodic Table
- 83. PB Boiling Point-3164 Melting Point-662 Lead (Natural) Atomic Number-82 Atomic Mass-207.20 Color,Bluish-Gray Structure: Soft and malleable Lead was discovered by the Romans and was mentioned the Old Testament. USES Lead is used in the storage of batteries and in sheathing electric cables, industrial lining for tanks and x-ray apparatus . Periodic Table
- 84. BI Boiling Point-2840 Melting Point-520 Atomic Number-83 Atomic Mass-208.98 Color-Pinkish tinge Bismuth Founder unknown USES Used in fluoroscopy (used to examine the internal organs.) Structure: (Artificial) Periodic Table
- 85. PO Boiling Point-1235 Melting Point-527 Atomic Number-84 Atomic Mass Polonium (Natural) Color, Blue Glow Structure: Simple Cubic This Element was discovered by Marie Curiein in 1898 in Paris USES Polonium is used for thermoelectric power. Periodic Table
- 86. AT Boiling Point-610 Melting Point-575 Atomic Number-85 Atomic Mass-210 Astatine Discovered by Corson in 1940. (Natural) Periodic Table
- 87. RN Boiling point-211 Melting Point-202 Atomic Number-86 Atomic Mass-222 Radon Discovered by Dorn in 1900 in Germany. USES Earthquake Prediction (Natural) Periodic Table
- 88. FR Francium Boiling Point- 950 Melting Point- 300.2 Atomic Number-87 Atomic Mass-223.0197 This Element was discovered by Marguerite Perey in 1939 in France. USES Structure: body centered cubic Color: (Natural) Periodic Table
- 89. RA Boiling point-1809 Melting point-973 Atomic Number-88 Atomic Mass-226.0254 Radium Color, White Structure: Body centered cubic (Natural) Isolated by the Curies and Are Debierne in 1898 in Paris USES Radium is used in Neutron sources Periodic Table
- 90. Boiling Point-3473 Melting Point-1323 Atomic Number-89 Atomic Mass-227.0278 AC Actinium Color, Silvery Structure: Face centered cube (Natural) USES Actinium is used in Thermoelectric power. Discovered by Debierne in 1899 Periodic Table
- 91. Boiling Point-5061 Melting Point-2028 Atomic Number-90 Atomic Mass-232.03804 TH Thorium Color, White Structure: Face centered cubic (Natural) Thorium was Identified in 1821and isolated by J.J. Berzelius in 1828 in Sweden. USES Thorium is used in gas lamp mantles and nuclear breeder reactors. Periodic Table
- 92. Atomic Number-91 Boiling Point----- Melting Point----- Atomic Mass-231.03588 PA Protactinium Color, Silvery Structure: Face centered cubic Discovered independently by Fajans and Gohring in Germany and by Soddy , Cranston and Fleck in Scotland in 1913. USES -------------------------- (Natural) Periodic Table
- 93. U Boiling Point:4407 Melting Point:1405 Atomic Number:92 Atomic Mass:238.029 Uranium (Natural) This element was used by the Romans for yellow pigments in glass. The element was discovered in 1789 by a German chemist, Martin Klaproth. USES Color: Silvery Structure: hex cls pkd distored Nuclear reactor fuel Periodic Table
- 94. NP Atomic Number : 93 Melting Point- 910 Boiling Point------- Atomic Mass- 237.048 Color: Silvery Structure: Complex Neptunium was produced by E.M. McMillan Neptunium (Man-Made) USES Periodic Table
- 95. Plutonium PU Atomic Number-94 Atomic Mass-244 Melting Point-913 F . Boiling Point-3503 This Element was discovered secretly by Glenn Seaborg in 1940 with Wahl and Kennedy at Berkley and publicly reported in 1946. (Man-Made) Extracted From Uranium Ore USES Plutonium is used in nuclear weapons and is used in space probe electricity sources. Color, Silvery Structure: Face centered cube Periodic Table
- 96. AM Boiling Point: 2880 Melting Point : 1268 Atomic Number: 95 Atomic Mass: 243 Structure: Face centered cubic Americium (Man-Made) This element was discovered by Glenn Seaborg in 1944 in Berkeley. USES Smoke Detector Color: Silvery White Periodic Table
- 97. CM Boiling Point----- Melting Point-1613 Atomic Number-96 Atomic Mass-247 Curium (Man-Made) Color: Silvery White Structure: Face centered cubic Discovered by James, Seaborg, and Ghiorso in 1944 USES Thermoelectric power and source Periodic Table
- 98. bk berkelium Atomic mass 247 Atomic number 97 Named after the University of California at Berkeley. Berkelium tends to accumulate in the skeletal system. Atomic weight-247 Periodic Table
- 99. Californium Cf Atomic number 98 Atomic mass 251 Named after the state of California. It has a half life of 90 years. It is a radioactive rare earth metal. Atomic weight-251 (artificial) Periodic Table
- 100. Einsteinium Es (Artificially) Atomic number 99 atomic mass 254 Named in honor of Albert Einstein. Discovered In 1952 in the debris from a hydrogen bomb explosion. Atomic weight-254 Periodic Table
- 101. fm fermium atomic Number 100 Artificially created, the element was isolated in 1952 from the debris of a hydrogen bomb explosion by the American chemist Albert Ghiorso named after Enrico Fermi Atomic mass-257 Atomic weight-257 (Artificial) Periodic Table
- 102. MD Atomic number 101 Atomic mass 258 Mendelevium is artificially created radioactive element. Discovered in 1955 and named after Dmitri Mendeleev. It has a half-life of 54 days. (Artificial) Mendelevium Atomic weight-258 Periodic Table
- 103. Nobelium No (Artificial) Atomic number-102 Atomic mass-259 Atomic weight-259 Nobelium is a radioactive metalic element named after Alfred Bernhard Nobel. It was discovered in 1957 and is not found in nature but is produced artificially in the laboratory. The properties of Nobelium are unknown and it has a half-life of a few minutes. Periodic Table
- 104. Lr Lawrencium (Artificial) Atomic number-103 Atomic mass-260 Atomic weight-260 Lawrencium is an artificially created radioactive metallic element. It was discovered in 1961 and named after Ernest Lawrence. Periodic Table
- 105. RF Rutherfordium (Artificial) Rutherfordium is an unstable chemical element named after Ernest Rutherford. In 1969 it was synthesized according to a convention adopted in 1980 for naming elements 104 and beyond, however, the element was named unnilquadium. Atomic number-104 Atomic mass-261 Atomic weight-261 Periodic Table
- 106. Db Dubnium Atomic number-105 Atomic mass-262 Atomic weight-262 (Artificial) Dubnium is an artificial element that was discovered by Ghiorso. It was named after Duba, a northern suburb. Periodic Table
- 107. Sg Seaborgium Atomic number-106 Atomic mass-263 Atomic weight-263 (Artificial) Seaborgium is an artificial element named after Glenn Seaborg. Discovered by Ghiorso. Periodic Table
- 108. Bh Bohrium Atomic number 107 Atomic mass 262 Atomic weight 262 Bohrium is a synthetic element and is not present in the environment at all. The German discoverers proposed the name Nielsbohrium after Niels Bohr. IUPAC are happy to name an element after Bohr but suggest Bohrium on the grounds that the first name of a person does not appear in the names of any other element named after a person. (Artificial) Periodic Table
- 109. HS Hassium (Artificial) Atomic number 108 atomic mass 265 Atomic weight 265 Hassium is a synthetic element that is not present in the environment at all. Periodic Table
- 110. MT Meitnerium Atomic number 109 atomic mass 266 Atomic weight 266 (artificial) Meitnerium is a synthetic element that is not present in the environment at all.There is no dispute concerning the name Meitnerium. Periodic Table