Phase diagram notes
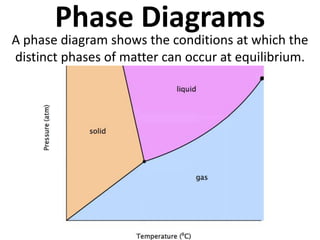
- 1. Phase Diagrams A phase diagram shows the conditions at which the distinct phases of matter can occur at equilibrium.
- 2. Phase Diagram Melting Freezing Vaporization Condensation Deposition Sublimation
- 3. Phase Diagrams Triple Point The triple point of a substance is the Liquid temperature and pressure at which Solid gas, liquid, and solid coexist in Gas thermodynamic equilibrium.
- 4. Phase Diagrams Triple Point For water, the combination of Liquid pressure and temperature are Solid exactly 0.010000 C and 0.0060373 atm. Gas At that point, the liquid can boil and freeze at the same time.
- 5. Phase Diagram According to the red line on the phase diagram, if we apply enough pressure to ice, it will melt into liquid water. What are the practical applications?
- 6. Phase Diagram According to the red line on the phase diagram, if we apply enough pressure to ice, it will melt into liquid water. Ice Skating is one application of this phenomenon.
- 7. Phase Diagrams Carbon dioxide Dry Ice
- 8. Phase Diagrams Carbon dioxide has a vapor pressure of 830 psi (56.5 atm) at 20 C. Dry Ice At 0 C the pressure inside a CO2 fire extinguisher is about 500 psi. At 30 C it is about 1000 psi.
- 9. Phase Diagrams Carbon