Early and feudal japan updated
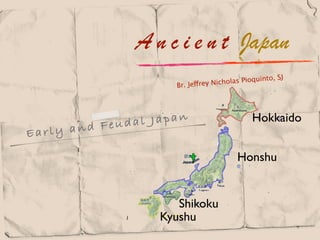
- 1. A n c i e n t Japan SJ ho las Pioquinto, Br. Jeffrey Nic Feuda l Japan Hokkaido Ear ly and Honshu Shikoku Kyushu
- 2. Yayoi Culture in Japan Han Dynasty in China Early Ties with C h i n a and Korea
- 3. Aborigines in Japan Man Woman Chief Clan A i n u Uji
- 4. The Relationship between hereditary rule and ancestral worship became an important part of a native religion - Shintoism S h i n t o “The Way of the gods”
- 5. Simple religion based on worship of the forces of nature... Kami spirits that are present in extraordinary people and things. Inspires a feeling of awe and wonder They worship waterfalls, sunset, rock formations S h i n t o i s m Religion
- 6. AMATERASU Goddess of the Sun her grandson descended to earth and brought 3 things. D e s c e n d a n t s o f t h e SUN
- 7. AMATERASU Goddess of the Sun her grandson descended to earth and brought 3 things. D e s c e n d a n t s o f t h e SUN
- 8. AMATERASU Goddess of the Sun her grandson descended to earth and brought 3 things. D e s c e n d a n t s o f t h e SUN
- 9. AMATERASU Goddess of the Sun her grandson descended to earth and brought 3 things. D e s c e n d a n t s o f t h e SUN
- 10. AMATERASU Goddess of the Sun her grandson descended to earth and brought 3 things. Bronze Mirror D e s c e n d a n t s o f t h e SUN
- 11. AMATERASU Goddess of the Sun her grandson descended to earth and brought 3 things. Bronze Mirror Carved Jewel D e s c e n d a n t s o f t h e SUN
- 12. AMATERASU Goddess of the Sun her grandson descended to earth and brought 3 things. Bronze Mirror Iron Sword Carved Jewel D e s c e n d a n t s o f t h e SUN
- 13. Yamato Clan - Descendants of Amaterasu 593 Empress Suiko chose her nephew to rule as regent Prince Shotoku drafted the 17-Article Constitution Ended the hereditary clans Introduction of centralized government based on Confucian principles Adoption of Buddhism as state religion Y a m a t o Clan
- 14. They rejected the idea of Mandate of Heaven Rejected China’s Examination System S e l e c t i v e Borrowing
- 15. They rejected the idea of Mandate of Heaven because they can be overthrown Rejected China’s Examination System S e l e c t i v e Borrowing
- 16. They rejected the idea of Mandate of Heaven because they can be overthrown Rejected China’s Examination System because it opposed to their aristocratic rule S e l e c t i v e Borrowing
- 17. They rejected the idea of Mandate of Heaven because they can be overthrown Rejected China’s Examination System because it opposed to their aristocratic rule Sons of nobles were admitted to university S e l e c t i v e Borrowing
- 18. Sent many missions to China, hoping to learn about their laws and government... Thousands of Japanese students went to China to learn about their civilization P r i n c e Shotoku
- 19. Fujiwara 7th Century Opposition leader TAIKA REFORM of 646 to model China’s political and economic institutions End large landowning established uniform tax system and measurement Assigned military governor Meant to copy the grandeur of TANG DYNASTY T a i k a Reform
- 20. Traditional Culture remained distinctively Japanese S E L E C T I V E Borrowing
- 21. 710 - The capital was NARA 794 The capital was moved to HEIAN (Kyoto) Novels replaced poetry as the most popular form of literature LADY MURASAKI SHIKIBU The first novel ever1000 AD (Japan) The Tale of Genji written The Classical age o f HEIAN JAPAN
- 22. at the end of 11th Century the Heian Courts declined LANDOWNDERS They can collect taxes Controlled productions- got wealthy Organized armies for protections P e r r e n i a l Problem
- 23. MINAMOTO FAMILY1185 AD YORIMOTO Established his government in Kamakura. far from the influence of the imperial court at Heian J a p a n e s e FEUDALISM
- 24. YORIMOTO The emperor gave Yorimoto the title: SHOGUN “Barbarian Subduing General” In theory, they ruled in the name of the emperor but in practice, real authority rested with the shogun J a p a n e s e SHOGUNATE
- 25. To gain the loyalty of the landlords Yorimoto appointed powerful lords as protector of the provinces. Moving from Civil Goverment to Military Dictatorship J a p a n e s e FEUDALISM
- 26. The lords estates were protected by the SAMURAI “Those who serve” only them were allowed to wear the two swords of the warriors Samurai inherited their position as warriors Had the right to inherit land... Rise of the SAMURAI
- 27. SAMURAI BUSHIDO“The way of the warrior” Called for the life of discipline and duty 1 They need to control their emotions 2 Loyalty to the lords 3 Loyalty was based on personal and moral obligations rather than contract vassalage. European feudalism BUSHIDO
- 28. HONOR SAMURAI If he was dishonored by capture or an act of disloyalty to his lord, he would not hesitate to commit: SEPPUKU HARA-KIRI “Belly-slitting” thrusting a short knife into his abdomen then his friend would cut off his head to complete the act of honor S e p p u k u Hara-Kiri
- 29. ZEN BUDDHISM All people were mutual in the eyes of god they need to meditate their problem for a long period of time until they suddenly reached SATORI enlightenment greater appeal on the samurai class for it emphasized discipline and authority New form of BUDDHISM
- 30. Kamakura Period Japan transformed itself into a culture very much of its own making K a m a k u r a Legacy
- 31. Kamakura Period Japan transformed itself into a culture very much of its own making Why ? K a m a k u r a Legacy
- 32. Kamakura Period Japan transformed itself into a culture very much of its own making Why ? No longer was Japan borrowing institutions and ideas from China K a m a k u r a Legacy
- 33. Kamakura Period Rejected Centralized government and ruled indirect and decentralized rule of the shogun Military leader and not the gentry ruled the nation Position of the hereditary emperor endured but the power of the emperor, weak to begin with, became even weaker K a m a k u r a Legacy
- 34. Kamakura Period Feudalism divided the lands among the samurais After few generations there was little land left to divide...hence, K a m a k u r a Legacy
- 35. Kamakura Period Feudalism divided the lands among the samurais After few generations there was little land left to divide...hence, Samurai started to sell their services to lords K a m a k u r a Legacy
- 36. Kamakura Period Feudalism divided the lands among the samurais After few generations there was little land left to divide...hence, Samurai started to sell their services to lords This weakened central authority even further K a m a k u r a Legacy
- 37. Genghis Khan - Mongol ruler who invaded China Sent 140,000 men to conquer Japan G e n g h i s K h a n Invasion
- 38. Genghis Khan - Mongol ruler who invaded China Sent 140,000 men to conquer Japan After 53 days of fighting, they were saved by natural disaster. G e n g h i s K h a n Invasion
- 39. Genghis Khan - Mongol ruler who invaded China Sent 140,000 men to conquer Japan After 53 days of fighting, they were saved by natural disaster. A typhoon from the Pacific swept the Mongol fleet with raging winds and tides G e n g h i s K h a n Invasion
- 40. Genghis Khan - Mongol ruler who invaded China Sent 140,000 men to conquer Japan After 53 days of fighting, they were saved by natural disaster. A typhoon from the Pacific swept the Mongol fleet with raging winds and tides Believing that they typhoon was a supernatural force, they started calling it a KAMIKAZI G e n g h i s K h a n Invasion
- 41. Genghis Khan - Mongol ruler who invaded China Sent 140,000 men to conquer Japan After 53 days of fighting, they were saved by natural disaster. A typhoon from the Pacific swept the Mongol fleet with raging winds and tides Believing that they typhoon was a supernatural force, they started calling it a KAMIKAZI “Divine Wind” G e n g h i s K h a n Invasion
- 42. Kamakura government that even an emperor tried to seize power. Ashikaga Shogunate Distinct They ruled without the benefit of samurai retainers This period is a warfare period among the aristocrats No family was strong enough to stop the fighting... A s h i k a g a Shogunate
- 43. Leader : Ashikaga Ruled for 250 years A s h i k a g a Shogunate
- 44. A s h i k a g a Shogunate
- 45. Problem: The Central Government had no samurai to enforce its authority. Japan during this period was torn by violence and civil disorder Asikaga Shogunate
- 46. Ashikaga Shogunate Aristocrats Were overthrown by the local lords Distinction disappeared Aristocrats Local Lords DAIMYO hired peasants - army. Who fought alongside with the samurais Breakdown of class distinction
- 47. hired peasants - army. Who fought alongside with the samurais Implication? The prestige of the samurai went down “As the common foot soldiers increased in importance, the prestige of the samurai class decreased.” T i t l e Text
- 48. the need for audition selected few will be accepted P r e s t i g e Context
- 49. Who was supporting the Emperor Emperor Ashikaga Shogunate
- 50. Who was supporting the Emperor Court Officials/Aristocrats Emperor Ashikaga Shogunate
- 51. Who was supporting the Emperor Court Officials/Aristocrats who supported the emperor, lost their estates to the daimyos Emperor Ashikaga Shogunate
- 52. Who was supporting the Emperor Court Officials/Aristocrats who supported the emperor, lost their estates to the daimyos Impoverished emperor was reducedto selling examples of his calligraphy to people on the streets. Emperor Ashikaga Shogunate
- 53. Economic Growth Agriculture Trade Cottage Industry C o n t r i b u t i o n Ashikaga Shogunate
- 54. Nothing is Absolute
- 55. Centralized Feudalism Tokugawa Early Christian Coverts Shogunate St. Francis Xavier, SJ - Landed in Kyushu 1549 Daimyo eager to trade with the Europeans - were converted to Christianity 1584-1582 ODA NABUNAGA Eliminated the power of Buddhism Thought that Christian might help in unifying Japan T o k u g a w a Shogunate
- 56. Hideyoshi 8 years after Nobunaga died, he UNITED JAPAN Ruled among the daimyos Surrounded the daimyos those who were loyalto him Destroyed the military power of the Buddhist Monasteries Tokugawa Shogunate
- 57. Tokugawa Shogunate Brought back the class system saling pusa Emperor Shogun Daimyos Samurais Commoners Hideyoshi
- 58. Ruled in Edo (Present day Tokyo) T o k u g a w a Shogunate
- 59. Ruled in Edo (Present day Tokyo) Edo period was a time of stability for the Japanese people, but there was little or no development when compared to other nations in the rest of the world during the same period. T o k u g a w a Shogunate
- 60. Ruled in Edo (Present day Tokyo) Edo period was a time of stability for the Japanese people, but there was little or no development when compared to other nations in the rest of the world during the same period. T o k u g a w a Shogunate
- 61. Ruled in Edo (Present day Tokyo) Edo period was a time of stability for the Japanese people, but there was little or no development when compared to other nations in the rest of the world during the same period. From 1852-1854, Commodore Matthew Perry negotiated a trade agreement between Japan and the United States. T o k u g a w a Shogunate
- 62. The government at Tokyo was forced to agree to the demands of the United States as they were intimidated by the technologically advanced and heavily armed fleet of steam frigates under the command of Commodore Perry. Black Ships symbolizes the threat imposed by western technology T o k u g a w a Shogunate
- 63. Given that humiliating experience with the UNITED STATES, what do you think Japan would do next to redeem itself ? M e i j i Restoration
- 64. Meiji Restoration 1889 Capital in Tokyo a new constitutional monarchy was established, headed by the Meiji Emperor. The power of the shoguns was broken. The constitution provided for new legislative bodies including the Imperial Diet, the House of Peers, and an independent cabinet directly under the Emperor. E d o - Tokyo
- 65. Imperial Diet Assembly the national legislature of Japan. was established on the basis of two houses with coequal powers. Kokkai (“National Assembly”) the House of Peers House of Representatives-Shugiin Meiji Restoration
- 66. During this time zaibatsu , large privately owned corporations, began to form. Mitsubishi Zaibatsu Japan became the first industrialized country in Asia. M e i j i Restoration
- 67. Japan wanted to conquer China Why? 1 9 3 0 Japan vs China
- 68. Japan wanted to conquer China Why? Japanese imperialist policy aimed to dominate China to acquire its vast material reserves and natural resources 1 9 3 0 Japan vs China
- 69. Japan wanted to conquer China This culminated into a full-scale war in 1937. Western powers were reluctant to provide support to the Chinese who they thought would eventually lose the war. esp United States of America 1 9 3 0 Japan vs China
- 70. Japan wanted to conquer China This culminated into a full-scale war in 1937. Western powers were reluctant to provide support to the Chinese who they thought would eventually lose the war. esp United States of Why did the Japanese want US in? America 1 9 3 0 Japan vs China
- 71. Japan wanted to conquer China This culminated into a full-scale war in 1937. Western powers were reluctant to provide support to the Chinese who they thought would eventually lose the war. esp United States of Why did the Japanese want US in? America What made the US changed their mind? 1 9 3 0 Japan vs China
- 72. World War 2
- 73. The United States entered the war in 1942 after the surprise attack on Pearl Harbor by Japanese forces. In 1945, atomic bombs were dropped on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki and Japan surrendered soon afterward. Japan's government shifted from imperial and military rule to a parliamentary democracy. Emperor Hirohito P a r l i a m e n t a r y Democroacy
Hinweis der Redaktion
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
