Tb09
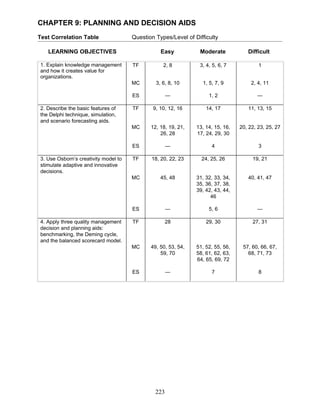
- 1. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS Test Correlation Table Question Types/Level of Difficulty LEARNING OBJECTIVES Easy Moderate Difficult 1. Explain knowledge management TF 2, 8 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 1 and how it creates value for organizations. MC 3, 6, 8, 10 1, 5, 7, 9 2, 4, 11 ES — 1, 2 — 2. Describe the basic features of TF 9, 10, 12, 16 14, 17 11, 13, 15 the Delphi technique, simulation, and scenario forecasting aids. MC 12, 18, 19, 21, 13, 14, 15, 16, 20, 22, 23, 25, 27 26, 28 17, 24, 29, 30 ES — 4 3 3. Use Osborn’s creativity model to TF 18, 20, 22, 23 24, 25, 26 19, 21 stimulate adaptive and innovative decisions. MC 45, 48 31, 32, 33, 34, 40, 41, 47 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 42, 43, 44, 46 ES — 5, 6 — 4. Apply three quality management TF 28 29, 30 27, 31 decision and planning aids: benchmarking, the Deming cycle, and the balanced scorecard model. MC 49, 50, 53, 54, 51, 52, 55, 56, 57, 60, 66, 67, 59, 70 58, 61, 62, 63, 68, 71, 73 64, 65, 69, 72 ES — 7 8 223
- 2. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS True/False Questions Learning Objective 1 1. SchlumbergerSema’s InTouch decision system features a centralized help desk in Houston. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 238 2. Creative management (CM) involves recognizing, generating, documenting, distributing, and transferring between persons useful information to improve organizational effectiveness. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, p. 238 3. Knowledge management is generally viewed as consisting of two main components: explicit knowledge and tacit knowledge. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 239 4. Enabling technologies include such things as intranets, Internet, search engines, and work-flow software. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 239 5. Knowledge is becoming more valuable than physical or financial assets, or even natural resources. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 239 6. The application of knowledge management has three natural targets: an organization’s teams, customers, and competitors. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 239 7. Organizations consistently identify cultural issues as the greatest barriers to the successful implementation of knowledge management. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 242 8. Expert systems have problem-solving capabilities within a specific area of knowledge. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 241 Learning Objective 2 9. Forecasting is primarily concerned with internal events or conditions beyond the organization’s control that are important to its survival and growth. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, p. 242 10. Extrapolation is the projection of some tendency from the past or present into the future. 224
- 3. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 242 11. In the second phase of the Delphi technique, a questionnaire is sent to a group of experts. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 244 12. A simulation is a representation of a real system. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 245 13. Spreadsheet simulations are useful for estimating the most critical aspect of venture planning which is profit and loss. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 246 14. Scenarios are quite useful in forcing those involved in planning to evaluate preliminary plans against past history. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 247 15. Scenarios often involve answering “what next” questions. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 246 16. In the planning and administrative competency in Chapter 9, the Society of Safety Engineers used computer simulations to predict the future needs of clients. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, pp. 245–246 17. A competitor scenario presents various actions that might be taken in response to competitive forces. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, pp. 246–247 Learning Objective 3 18. “Conceptual thinking” is the ability to visualize, generate, and implement new ideas. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, p. 248 19. The creative process includes five interconnected stages: preparation, concentration, incubation, illumination, and verification. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 248 20. The Osborn creativity model is intended to stimulate competition, as various groups strive to convince others that their idea is superior. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, p. 249 21. Bob is the leader of a team that is using Osborn’s creativity model to generate ways their firm can gain a competitive advantage in the industry. Currently the team is 225
- 4. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS brainstorming for ideas. Thus, they are in the fact-finding phase of the model. ANSWER: F, Application, Difficult, p. 250 22. Brainstorming is an unrestrained flow of ideas in a group or team with all critical judgments suspended. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 250 23. Quantity without concern for quality is not welcome in a brainstorming session. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, p. 250 24. The Osborn creativity model has four phases. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 249 25. At IDEO, clients are usually invited to brainstorming sessions because their knowledge is needed to complete a project. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, pp. 251–252 26. The Osborn creativity model is based on the assumption that most people have the potential for greater creativity and innovation in decision making than they use. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 252 Learning Objective 4 27. The most common definition of quality is the extent to which a good or service conforms to specifications or standards. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 252 28. Benchmarking is the continuous process of comparing an organization’s goods, services, and practices against industry leaders anywhere in the world to gain information that will help the organization improve performance. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 253 29. Benchmarking includes six stages. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 253 30. The Deming cycle is also known as the PACA cycle. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 254 31. The Deming cycle is comprised of four stages: plan, do, check, and review. ANSWER: F, Application, Difficult, p. 254 Multiple Choice Questions 226
- 5. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS Preview 1. SchlumbergerSema’s InTouch service is built on all of the following elements except __________. a. a standard computer platform for all engineers b. global network infrastructure c. satellite communication d. centralized document authoring and publishing ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 238 2. SchlumbergerSema’s InTouch system is just one example of how companies are starting to use __________. a. collaborative teams b. online decision aids c. knowledge management drivers d. expert systems ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 238 Learning Objective 1 Fostering Knowledge Management 3. __________ involves recognizing, generating, documenting, distributing, and transferring between persons useful information to improve organizational effectiveness. a. Creative management b. Information management c. Data management d. Knowledge management ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 238 4. Which of the following is not one of the uses for the seven planning and decision aids suggested in the text? a. These aids are useful at various levels in the organization. b. These aids are useful in virtually all functional areas. c. These aids can assist in the analysis essential to planning and decision making associated with many types of organizational issues and problems. d. These aids are considered general planning and decision aids. ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 238 5. Which of the following is not generally viewed as one of the main components of knowledge management (KM)? a. information knowledge b. explicit knowledge c. tacit knowledge d. enabling technologies ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 239 6. __________ knowledge consists in part of books, magazines, journals, and government data and reports. 227
- 6. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS a. Common b. Tacit c. Enabling d. Explicit ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 239 7. David Nagle is trying to teach his son Jonathan how to ride a bike. David realizes that his knowledge of bike riding was developed from his own direct experiences with a bicycle and is subconsciously understood. He’s having a difficult time explaining to Jonathan how to ride his new bike. David’s knowledge of bike riding is __________. a. explicit b. common c. enabling d. tacit ANSWER: D, Application, Moderate, p. 239 8. Which of the following is not an example of an enabling technology? a. intranets b. Internet c. search engines d. all of the above ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 239 9. Which of the following is not one of the natural targets for the application of knowledge management? a. teams b. customers c. competitors d. workforce ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 239 10. __________ are computer based programs based on the decision-making processes of human experts that store and receive data, diagnose problems, and offer solutions. a. Knowledge management systems b. Decision systems c. Expert systems d. Computer support systems ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 241 228
- 7. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 11. One of the primary characteristics of an expert system is __________. a. searching to find the best possible solution b. using line of reasoning processes c. use of fuzzy logic d. ability to solve highly generalized problems ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 241 Learning Objective 2 Fostering Forecasts 12. __________ involves projecting or estimating future events or conditions in an organization’s environment. a. Extrapolation b. Scenarios c. Decision aids d. Forecasting ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 242 13. Forecasting is concerned primarily with __________. a. external events or conditions that the organization can control b. internal events or conditions that the organization can control c. external events or conditions that the organization cannot control d. internal events or conditions that the organization cannot control ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 242 14. Much forecasting is based on __________. a. simulation b. scenarios c. extrapolation d. the Delphi technique ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 242 15. The simplest, and at times most misleading, form of extrapolation is a __________. a. linear projection of a present trend into the future b. curvilinear projection of a present trend into the future c. linear projection of a past trend into the future d. curvilinear projection of a past trend into the future ANSWER: C, Application, Moderate, p. 242 229
- 8. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 16. Duane Somers works for Porky’s Bar B Q and is attempting to make a sales forecast for fiscal year 2006. Duane knows that sales increased 4% in 2003 and 5% in 2004. He also knows that consumer preferences seem to be shifting away from pork in favor of chicken. Duane forecasts 2006 sales to increase 2% on the basis of __________. a. scenarios b. extrapolation c. the Delphi technique d. simulations ANSWER: B, Application, Moderate, p. 242 17. Rachel Cline needs to make a decision on whether to expand her business to a second location. She assembles a panel of experts including a member of her chamber of commerce, her accountant, and a professor of strategic management at a local university. The group refined their opinions, step by step, until they reached a consensus that Rachel should expand to the second location. This decision is an example of __________. a. the Delphi technique b. groupthink c. extrapolation d. scenarios ANSWER: A, Application, Moderate, p. 243 18. __________ is(are) a forecasting aid based on a consensus of a panel of experts. a. Extrapolation b. Scenarios c. Decision forecasts d. The Delphi technique ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 243 19. The American Society of Engineers used a __________ to anticipate changes in OSHA’s operations. a. Delphi study b. benchmarking model c. creativity model d. simulation ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, pp. 243–244 20. The American Society of Engineers assembled a panel of __________ to evaluate predictions in their Delphi study. a. OSHA administrators b. professional engineers c. industry executives d. chapter presidents ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 243 230
- 9. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 21. The Delphi technique involves __________ basic steps. a. two b. three c. four d. five ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Easy, p. 244 22. The number of experts who participate in the Delphi technique may range from only a few to more than 100, depending on the scope of the study. A range of __________ is recommended for a very focused issue. a. 10 to 15 b. 15 to 30 c. 30 to 40 d. 40 to 60 ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 244 23. The heart of the Delphi technique is __________. a. the qualifications of the experts b. the number of rounds c. the number of experts d. the series of questionnaires ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 243 24. The Ford Motor Company developed a system that shows how changes in external variables (e.g., inflation, price changes, unemployment) may affect Ford’s sales, profits and employment levels. This is an example of __________. a. the Delphi technique b. a simulation c. a strategic plan d. virtual reality ANSWER: B, Application, Moderate, p. 245 25. Which of the following statements about simulations is not true? a. A simulation is a representation of a real system. b. Simulation is often used to forecast the effects of environmental changes and internal management decisions on an organization. c. The goal of simulation is to experience reality. d. Most simulations are intended to let management ask numerous “what-if” questions. ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 245 231
- 10. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 26. Electric utility managers took part in a __________ to develop understanding of the new deregulated business environment they were entering. a. Delphi study b. simulation c. scenario study d. fact finding phase ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Easy, pp. 245–246 27. Taking part in an electric utilities industry restructuring simulation helped senior managers learn to do all of the following except __________. a. forecast competitive strategies b. forecast competitors’ prices c. discover that incremental cost was the main factor in determining how competitive they could be d. discover that marginal cost was the main factor in determining how competitive they could be ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 246 28. __________ is a story that helps people recognize and adapt to changing features of their environments. a. The Delphi technique b. A simulation c. A scenario d. An extrapolation ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 246 29. __________ provides a way to identify alternative paths that may exist for an organization in the future and the actions that likely are involved in going down each of those paths. a. The Delphi technique b. A scenario c. A simulation d. An extrapolation ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 246 30. Competitor scenarios present projections of __________. a. how a competitor might be defeated b. what a competitor might do c. what level of threat exists d. all of the above ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, pp. 246–247 232
- 11. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS Learning Objective 3 Fostering Creativity 31. All decision making needs to be supported strongly by __________. a. efficacy b. entropy c. rules d. creativity ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 248 32. Creativity is the ability to __________ new ideas. a. visualize b. generate c. implement d. all of the above ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 248 33. Which of the following is not one of the five stages of the creative process? a. brainstorming b. concentration c. preparation d. illumination ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 248 34. The __________ stage of the creative process involves searching for and collecting facts and ideas. a. concentration b. preparation c. brainstorming d. illumination ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 248 35. During the creative process of developing ideas for a new novel, author Jane Windham began focusing her energies and resources on identifying and solving the problem of whether her main character should be a man or a woman. Jane is in the __________ stage of the creative process. a. incubation b. concentration c. brainstorming d. actualization ANSWER: B, Application, Moderate, p. 249 233
- 12. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 36. Louis McDonald is having a difficult time deciding how to proceed on an important research project. He feels he needs to be creative in the subjects selected for the study and the way in which data is gathered from these subjects. McDonald goes for a walk to relax in hopes that he can unconsciously search for a solution. McDonald is in the __________ stage of the creative process. a. realization b. brainstorming c. incubation d. actualization ANSWER: C, Application, Moderate, p. 249 37. During the creative process of developing new software, Elvira Melendez experienced a moment of discovery, an instant recognition in which she realized what needed to be done to solve a problem. Elvira is in the __________ stage of the creative process. a. incubation b. brainstorming c. realization d. illumination ANSWER: D, Application, Moderate, p. 249 38. At the __________ stage of the creative process, confirmation and acceptance of the new approach is sought. a. verification b. confirmation c. realization d. validation ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 249 39. __________ is not a phase in Osborn’s creativity model. a. Fact finding b. Application finding c. Solution finding d. Idea finding ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 249 40. Which of the following statements is not true regarding the Osborn creativity model? a. It is designed to help overcome blockages to creativity and innovation. b. External pressure and self-generated tension are harmful. c. It can be used with all types of groups. d. Intense pressure and threats from the wrong sources can easily undermine the process. ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 249 234
- 13. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 41. Distinguishing between a symptom and an actual problem occurs in the __________ phase of the Osborn creativity model. a. fact-finding b. idea-finding c. solution-finding d. application-finding ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 249 42. Brainstorming occurs in the __________ phase of the Osborn creativity model. a. fact-finding b. solution-finding c. idea-finding d. application-finding ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 250 43. Which of the following is not one of the basic rules that should be followed in a brainstorming session? a. Criticism is encouraged. b. Freewheeling is welcomed. c. Quantity is wanted. d. Combination and improvement are sought. ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 250 44. The __________ phase of the Osborn creativity model involves generating and evaluating possible courses of action and deciding how to implement the chosen course of action. a. fact-finding b. idea-finding c. application-finding d. solution-finding ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 250 45. Skilled brainstorming facilitators at IDEO perform all of the following functions except __________. a. lead the sessions b. enforce rules c. write and record the suggestions d. All of the above are performed by facilitators. ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 252 235
- 14. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 46. In the illustration of the Teamwork Competency at IDEO, by using __________, the company’s clients gain insight and learn because they join IDEO designers in the creative process. a. fact finding b. brainstorming c. synthesis d. incubation ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, pp. 251–252 47. The Osborn creativity model is based on the assumption that __________. a. few people can be creative if the proper environment is in place b. most people have the potential for greater creativity than they use c. most people are not creative d. creativity is not natural, but can be acquired under the proper circumstances ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 252 48. __________ makes use of technology to input and automatically disseminate ideas in real time over a computer network to all team members, each of whom may be stimulated to generate additional ideas. a. Virtual reality b. Group decision support systems c. Management information systems d. Electronic brainstorming ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 252 Learning Objective 4 Fostering Quality 49. __________ is the extent to which a product or service meets and/or exceeds customers’ expectations. a. Value b. Excellence c. Quality d. Conformance to specifications ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 252 50. __________ is a systematic and continuous process of measuring and comparing an organization’s goods, services, and practices against industry leaders anywhere in the world to gain information that will help the organization improve performance. a. Benchmarking b. Quality c. Total Quality Management (TQM) d. Reengineering ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, p. 253 236
- 15. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 51. Benchmarking includes __________ stages. a. five b. six c. seven d. eight ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 253 52. __________ includes a careful study of the organization’s own products and processes that are to be compared to benchmark products and processes. a. Defining the domain b. Identifying the best performers c. Collecting and analyzing data to identify gaps d. Setting improvement goals ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 253 53. __________ is not among the functions that may be benchmarked. a. Finance b. Marketing c. Transportation d. All of the above may be benchmarked. ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 253 54. Xerox compared its warehousing and distribution process with that of L. L. Bean, the catalog sales company, because of its excellent reputation in this area. Xerox has completed which step in the benchmarking process? a. identifying the best performers b. defining the domain c. collecting and analyzing data to identify gaps d. setting improvement goals ANSWER: A, Application, Easy, p. 254 55. __________ are not usually a good source of information for learning about best-in- class organizations. a. Customers b. Suppliers c. Government agencies d. Trade journals ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 254 237
- 16. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 56. Pedro Rodriquez is a vice president with Wal-Mart. Rodriquez is interested in improving the performance of the “pet supplies” departments in all stores. He identified some of the country’s best pet stores and in the process of gathering financial data from these stores so that he can understand how to improve performance Wal-Mart. Rodriquez is using a process known as __________. a. Deming cycle b. benchmarking c. total quality management (TQM) d. reengineering ANSWER: B, Application, Moderate, p. 253 57. Which of the following statements regarding benchmarking is not true? a. Over time, the things that are benchmarked should remain the same. b. Benchmarking needs to be linked to other sources of information, such as changing customer expectations and preferences. c. Benchmarking typically looks at the present in terms of how some process or quality dimension is being achieved by others. d. Benchmarking is often used to help an organization adapt, but less commonly to innovate. ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 254 58. When benchmarking is used simply to copy the best-in-class competitors, it may lead to __________. a. sustained competitive advantage b. short-term competitive advantage c. competitive disadvantage d. competitive parity ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 254 59. The Deming cycle involves __________ stages. a. two b. three c. four d. five ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 254 60. Which of the following is not among the questions that need to be answered in the plan stage of the Deming cycle? a. What are we trying to accomplish? b. Do we have the resources for what we are trying to accomplish? c. What changes can we make that will result in improvement? d. How will we know that a change is an improvement? ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 254 238
- 17. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 61. __________ is not one of the stages of the Deming cycle. a. Plan b. Do c. Will d. Check ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 254 62. Truett Fontenot is a famous chef in New Orleans. He has tested some new recipes in a laboratory. Next he intends to establish a pilot production process and try out the recipes on a small number of customers. Truett is operating in the __________ stage of the Deming cycle. a. plan b. do c. will d. check ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, pp. 254–255 63. Anna Lyn is the production supervisor for a manufacturing company that is implementing a new quality control process. She is trying to determine if the new process is working as it was intended and whether any revisions need to be made. Anna is operating in the __________ stage of the Deming cycle. a. plan b. will c. do d. check ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 255 64. The __________ stage of the Deming cycle focuses on implementing the process within the organization or with its customers and suppliers. a. act b. will c. do d. plan ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 255 65. In the textbook example, the owner of the Deluxe diner applied __________ to solve the problem of customers having to wait too long to be seated. a. benchmarking b. reengineering c. total quality management (TQM) d. the Deming cycle ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 255 239
- 18. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 66. Which of the following was not one of the problems identified by Billie Boyd, the owner of Deluxe Diner, as she used her communication competency to solve the problem of long lines at lunchtime? a. Customers were waiting in line for as long as 15 minutes. b. Usually, tables were available. c. Many of the customers were regulars. d. All of the above were problems that Billie Boyd identified. ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 255 67. Which of the following was not one of the changes developed by Billie Boyd, the owner of Deluxe Diner, to solve the problem of long lines at lunchtime? a. Allow customers to fax their orders in ahead of time. b. Encourage customers to open corporate charge accounts. c. Install a preparation table for fax orders in the kitchen. d. Devote one of the two cash registers to handling fax orders. ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 255 68. The balanced scorecard looks at all of the following strategic perspectives except __________. a. internal perspective b. competitive perspective c. innovation perspective d. customer perspective ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 256 69. Edwin Kaycee is evaluating his motorcycle parts assembly operations in Mexico for the amount of manufacturing defects that are being caused by poor workmanship. This balanced scorecard factor is addressed in the __________. a. learning perspective b. financial perspective c. internal perspective d. quality perspective ANSWER: C, Application, Moderate, p. 256 70. __________ is a method for gaining wider perspective on strategic decisions by considering the role of finances, customers, and innovation. a. Benchmarking b. Brainstorming c. Balanced scorecard d. Knowledge management ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 256 240
- 19. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 71. Southwest Airlines took an innovative approach to using the balanced scorecard in linking operational goals, such as baggage delivery, to __________. a. internal perspectives of safety b. learning perspectives of employee training c. customer perspectives of satisfaction d. financial perspectives of profitability ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, pp. 257–258 72. Customer perspectives of Southwest Airlines’ balanced scorecard include all of the following except __________. a. seat revenue b. lowest prices c. on-time flights d. Number 1 ranking ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 258 73. The balanced scorecard is criticized because __________. a. it does not link the perspectives to each other b. innovation is internal, but it is not included in the internal perspective c. managers are not given autonomy to pursue perspective goals d. the balanced scorecard model is too technical for most managers ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 258 Essay Questions Learning Objective 1 1. What is knowledge management (KM)? What is the difference between tacit and explicit knowledge? Give examples of each. Knowledge management (KM) involves recognizing, generating, documenting, distributing, and transferring between persons useful information to improve organizational effectiveness. KM is generally viewed as consisting of three main components: explicit knowledge, tacit knowledge and enabling technologies. Explicit knowledge is knowledge that is contained in books, magazines, journals, reports and manuals. Information published by the U.S. Census Bureau is an example. Tacit knowledge is knowledge that is unconsciously understood and applied. It is difficult to express and often developed from direct experiences and action. The knowledge of how to play golf or ride a bicycle is an example. Moderate, pp. 238–239 241
- 20. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 2. Describe how SchlumbergerSema applied knowledge management to improve organizational effectiveness under challenging operating conditions. SchlumbergerSema designed the InTouch system to immediately connect on-site employees with subject-matter experts. The firm operates in remote locations in 100 countries and faces huge challenges in conducting sensitive technical operations. The InTouch system is designed to use the global Schlumberger infrastructure through a standard computer platform and a single portal into the technical resource base. Help desks are available, with just-in-time online distance learning, and a centralized document authoring and publishing system. An example of the system in operation took place on a remote location in Indonesia, late in the day. Wrong instructions programmed into a computerized drilling tool were not noticed until after drilling had started. Although it was 4 a.m. in Houston, the head of the department that oversees the specific tool was able to respond within 15 minutes and transmit a solution back to the Indonesian job. Within an hour, the job was corrected and underway again. Moderate, p. 238 Learning Objective 2 3. What is the Delphi technique? Describe in detail the use of the Delphi technique. The Delphi technique is a forecasting aid based on a consensus of a panel of experts. The experts refine their opinions, step by step, until they reach a consensus. Because the technique relies on opinions, it obviously isn’t foolproof. But the consensus arrived at tends to be much more accurate than a single expert’s opinion. The Delphi process replaces face-to-face communication and debate with a carefully planned, orderly program of sequential discussions. The Delphi technique involves three basic steps: A questionnaire is sent to a group of experts. A summary of the first round is prepared (it may show such things as the average, medium and quartile range of response). This summary, along with a revised questionnaire, is sent to those who completed the first questionnaire. A summary of the second round is prepared (this often shows that a consensus is developing). The experts are then asked in a third questionnaire to indicate whether they support this emerging consensus. Three rounds generally are recommended. Difficult, pp. 243–244 4. What is a simulation? What is the goal of a simulation and how is it used? A simulation is a representation of a real system. A simulation model usually describes the behavior of the real system (or some aspect of it) in quantitative and/or qualitative terms. Simulation often is used to forecast the effects of environmental changes and internal management decision on an organization, department, or SBU. The goal of simulation is to reproduce or test reality without actually experiencing it. Most simulations are intended to let management ask numerous “what-if” questions. Moderate, p. 245 Learning Objective 3 242
- 21. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 5. Discuss three of the five stages in the creative process. a. Preparation involves a thorough investigation to ensure that all parts of an issue or problem are identified or understood. This stage involves searching for and collecting facts and ideas. b. Concentration occurs when energies and resources are focused on identifying and solving an issue or problem. A commitment must be made in this stage to implementing a solution. c. Incubation involves an internal and unconscious ordering of gathered information. A successful incubation stage yields fresh ideas and new ways of thinking about the nature of an issue or a problem and alternative solutions. d. Illumination is the moment of discovery, the instant of recognition, as when a light seems to be turned on mentally. The mind instantly connects an issue or a problem to a solution. e. Verification is the testing of the created solution or idea. At this stage, confirmation and acceptance of the new approach is sought. Moderate, pp. 248–249 6. What are three of the rules that should be followed in a brainstorming session? A brainstorming session should include about how many people? a. Criticism is ruled out. b. Freewheeling is welcomed. c. Quantity is wanted. d. Combination and improvement are sought. e. From 5 to 12 people should be included in a brainstorming session. Moderate, p. 250 Learning Objective 4 7. What is benchmarking? What are the seven stages in the benchmarking process? Benchmarking is a systematic and continuous process of measuring and comparing an organization’s goods, services, and practices against industry leaders anywhere in the world to gain information that will help the organization improve performance. 1. Define the domain to be benchmarked. 2. Identify the best performers. 3. Collect and analyze data to identify gaps. 4. Set improvement goals. 5. Develop and implement plans to close gaps. 6. Evaluate results. 7. Repeat the evaluations. Moderate, pp. 253–254 243
- 22. CHAPTER 9: PLANNING AND DECISION AIDS 8. Describe how Billie Boyd, the owner of Deluxe Diner, applied the Deming cycle to solve the problem of customers having to wait too long to be seated during lunchtime at the diner. Billie Boyd promoted two-way communication by soliciting feedback, listening, seeking out contrary opinions; creating give and take conversations; informing employees of relevant data and activities and keeping them up to date; and appearing to be persuasive and comfortable in her managerial role. One process in the plan stage involved several team meetings with her employees. They identified four main aspects of this problem: (1) customers were waiting in line for as long as 15 minutes, (2) usually, tables were available, (3) many of the customers were regulars, and (4) people taking orders and preparing food were getting in each others’ way. Boyd developed a plan that involved the following changes: (1) customers were allowed to fax their orders in ahead of time, (2) a preparation table for fax orders was installed in the kitchen, and (3) one of the two cash registers was devoted to handling fax orders. Difficult, p. 255 244