Tb08
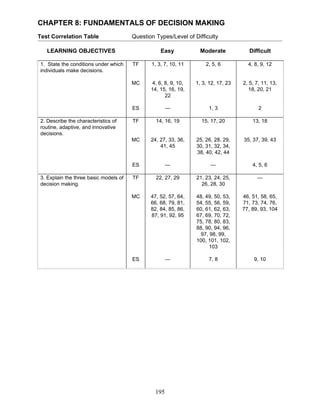
- 1. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING Test Correlation Table Question Types/Level of Difficulty LEARNING OBJECTIVES Easy Moderate Difficult 1. State the conditions under which TF 1, 3, 7, 10, 11 2, 5, 6 4, 8, 9, 12 individuals make decisions. MC 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 1, 3, 12, 17, 23 2, 5, 7, 11, 13, 14, 15, 16, 19, 18, 20, 21 22 ES — 1, 3 2 2. Describe the characteristics of TF 14, 16, 19 15, 17, 20 13, 18 routine, adaptive, and innovative decisions. MC 24, 27, 33, 36, 25, 26, 28, 29, 35, 37, 39, 43 41, 45 30, 31, 32, 34, 38, 40, 42, 44 ES — — 4, 5, 6 3. Explain the three basic models of TF 22, 27, 29 21, 23, 24, 25, — decision making. 26, 28, 30 MC 47, 52, 57, 64, 48, 49, 50, 53, 46, 51, 58, 65, 66, 68, 79, 81, 54, 55, 56, 59, 71, 73, 74, 76, 82, 84, 85, 86, 60, 61, 62, 63, 77, 89, 93, 104 87, 91, 92, 95 67, 69, 70, 72, 75, 78, 80, 83, 88, 90, 94, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103 ES — 7, 8 9, 10 195
- 2. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING True/False Questions Learning Objective 1 1. Decision making includes defining problems, gathering information, generating alternatives, and choosing a course of action. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 208 2. Intel’s CEO illustrates the planning and administration competency in the comment: “Occasionally it is more important to get the decision made than it is to collect more data.” ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 209 3. Decision making underlies most managerial competencies. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 208 4. The conditions under which individuals in an organization make decisions are influenced by developments and events that they can’t control but that may in the future influence the results of their decisions. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 209 5. Mark Meadows, an employee of Texas Instruments, is making decisions under a condition of being fully informed, as well as having alternative solutions the results of which are totally predictable. He is operating under the condition of certainty. ANSWER: T, Application, Moderate, p. 210 6. Decision making under the condition of certainty is the norm for most managers. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 210 7. Risk is the condition under which individuals can define a problem, specify the probability of certain events, identify alternative solutions, and state the probability of each solution leading to the desired results. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 210 8. Risk generally means that the problem and the alternative solutions fall somewhere between the extremes of being unknown and ambiguous. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 210 9. Susie Contreras is determining the type, amount, and reliability of information that influences the level of risk. She should look at whether she can use objective or subjective probability in estimating the outcome. ANSWER: T, Application, Difficult, pp. 210–211 196
- 3. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 10. Uncertainty is the condition under which an individual doesn’t have the necessary information to assign probabilities to the outcomes of alternative solutions. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 211 11. Dealing with uncertainty is an important facet of the jobs of many managers and other professionals, including research and development engineers. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 211 12. Managers, teams, and other professionals often need to absorb uncertainty by using their intuition, creativity, and all available information to make a judgment regarding the course of action to take. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 211 Learning Objective 2 13. The considerations of certainty, risk, and uncertainty provide an underpinning to the basic types of decision—routine, adaptive, and innovative. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 213 14. Decisions may be classified as routine, innovative, and comprehensive. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, p. 213 15. The bank teller with an out-of-balance cash drawer at the end of the day faces an ambiguous situation. ANSWER: F, Application, Moderate, p. 213 16. Alternative solutions range from the known and well defined to the untried and ambiguous. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 214 17. Adaptive decisions are choices made in response to fairly common and routine problems. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 215 18. Continuous improvement requires commitment toward occasional improvements year after year. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 217 19. Innovative decisions are based on the discovery, identification, and diagnosis of unusual and ambiguous problems and/or the development of unique or creative alternative solutions. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 218 20. Because innovative decisions usually represent a sharp break with the past, they 197
- 4. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING normally happen in a logical, orderly sequence. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 218 Learning Objective 3 21. The bounded rationality model prescribes a set of phases that individuals or teams should follow to increase likelihood that their decisions will be logical and optimal. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 219 22. There are seven phases in the rational decision making model. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 219 23. Ryan Keeley, a plant manager, has agreed to select an acceptable goal or alternative solution rather than searching for the best available goal or alternative solution. This concept is known as satisficing. ANSWER: T, Application, Moderate, p. 228 24. The law of large numbers bias refers to the tendency to view a few incidents or cases as representative of a larger population even when they aren’t. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 227 25. The political model describes the decision-making process in terms of the self-interests and goals of powerful external and internal shareholders. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 228 26. Organizational politics is the ability to influence or control individual, team, departmental, or organizational decisions and goals. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 228 27. Scapegoating is the casting of blame for problems or shortcomings on an innocent or only partially responsible individual, team, or department. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 229 28. Miguel Del Toro recognizes that he must balance the conflicting goals among his various stakeholder groups as he seeks to make an important decision. Miguel will likely use the political model of decision making. ANSWER: T, Application, Moderate, pp. 228–229 29. Stakeholders within an organization often use power as a major source of information. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, p. 230 30. Co-optation refers to bringing new stakeholder representatives into the strategic decision-making process as a way to avert threats to an organization’s stability or existence. 198
- 5. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 230 Multiple Choice Questions Preview 1. In the Preview Case, Craig Barrett of Intel considers three big steps in his decision- making process which include all of the following except __________. a. free discussion among participants b. determination of risks c. clear decision from the discussion d. everyone must “buy in” ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 208 2. Before Craig Barrett, CEO of Intel finalizes a decision, he finds it important to __________. a. understand all of the data b. collect any missing data c. make sure there are no major blind spots d. All of the above are steps in Barrett’s decision-making process. ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 208 Learning Objective 1 3. Every day, managers typically make decisions using a process that includes all of the following basic elements except __________. a. implement strategies b. generate alternatives c. define the problem d. choose a course of action ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 208 4. _________ underlies most managerial competencies. a. Common Sense b. Decision making c. Managerial input d. Forward thinking ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Easy, p. 208 199
- 6. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 5. The conditions under which decision are made can be broadly classified as __________. a. certainty and risk b. certainty, risk, and uncertainty c. uncertainty and risk d. certainty and uncertainty ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 209 6. As information dwindles and becomes ambiguous, the condition of __________ enters into decision making. a. certainty b. satisficing c. loss d. risk ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, pp. 209–210 7. The condition of certainty means that the __________ and __________ are known. a. problem; decision b. problem; alternative solutions c. opportunities; threats d. strengths; weaknesses ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 210 8. Dewann Everett is president of Halray Industries. His decision is to choose a marketing plan. He knows all about the problem, alternative plans are obvious, and the results of each plan are clear. Everett will make his decision under a condition of __________. a. risk b. guarantee c. loss d. certainty ANSWER: D, Application, Easy, p. 210 9. Jim Iverson has been asked to schedule 10 of his employees for overtime. Jim can determine the cost of the overtime in an environment of __________. a. certainty b. guarantee c. loss d. risk ANSWER: A, Application, Easy, p. 210 10. When Kirsten Colbert has full knowledge of a problem, its alternative solutions, and the results of those solutions, she makes decisions under a condition of __________. a. risk aversion b. complexity c. uncertainty d. certainty ANSWER: D, Application, Easy, p. 210 200
- 7. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 11. When Robert Gibbs has to make decisions concerning problems that are both ambiguous and exceptional, he makes decisions under a condition of __________. a. risk b. uncertainty c. subjective probability d. objective probability ANSWER: B, Application, Difficult, p. 211 12. __________ is the percentage of time that a specific outcome would occur if an individual were to make a particular decision a large number of times. a. Satisficing b. Optimizing c. Probability d. Risk ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 210 13. Risk generally means that the problem and alternative solutions fall somewhere between the extremes of being __________ and __________. a. common; usual b. certain; ambiguous c. routine; non-routine d. certain; uncertain ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 210 14. The National Highway Safety Administration concluded that the probability of a seat- belted driver’s death in an accident is reduced by 50 percent in a car equipped with a driver’s side airbag. This statistic is an example of __________. a. satisficing b. a routine decision c. a probability d. an adaptive decision ANSWER: C, Application, Easy, p. 210 15. The likelihood that a specific outcome will occur, based on hard facts and numbers, is known as __________ probability. a. rational b. subjective c. predicted d. objective ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 210 201
- 8. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 16. The likelihood that a specific outcome will occur, based on personal judgment and beliefs, is known as __________ probability. a. objective b. subjective c. strategic d. rational ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Easy, p. 211 17. Life insurance underwriters cannot determine which of their clients will die this year. However, their business success depends upon their ability to predict how many of those clients will die, based on population death rates in categories of age, gender, etc. Life insurance companies are using __________ to make their decisions about whom to insure and the premiums to charge. a. uncertainty b. alternative risk c. objective probabilities d. subjective probabilities ANSWER: C, Application, Moderate, p. 210 18. Nancy Barnes decided to become a flight attendant when she graduates from college in two years. She liked the regular hours and substantial benefits. Recently, the news has reported that benefits will no longer be offered to flight attendants, and that they will have to work standby hours. Barnes decides to become a teacher. Barnes has changed her decision in part because __________. a. the conditions under which she made her initial decision changed b. she is certain that the employment conditions will not improve c. she did not have information about the job when she made her initial decision d. she did not know how to make decisions ANSWER: A, Application, Difficult, p. 209 19. When an individual does not have the necessary information to assign probabilities to the outcomes of alternative solutions, a decision is made under the condition of __________. a. risk b. subjectiveness c. probability d. uncertainty ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 211 20. Uncertainty suggests that the problem and the alternative solutions are both __________ and __________. a. ambiguous; highly unusual b. risky; opportunities c. problems; opportunities d. strengths; weaknesses ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 211 202
- 9. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 21. All of the following are listed in the text as types of crises that may be sources of uncertainty and risk except __________. a. criminal crises b. economic crises c. management crises d. reputation crises ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 212 22. Hyundai experienced a business crisis in 1998 as a result of its __________. a. import restrictions b. product quality c. harassment scandals d. unattractive styling ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Easy, pp. 212–213 23. In responding to Hyundai’s business crisis, CEO Finbarr O’Neill identified __________ as the company’s biggest problem. a. worried customers b. lack of profits c. dealers shutting down d. none of the above ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 213 Learning Objective 2 Basic Types of Decisions 24. The considerations of __________ provide an underpinning to the basic types of decisions that managers make. a. certainty b. risk c. uncertainty d. all of the above ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 213 25. In general, the decision maker should begin by defining the problem and then ________. a. compare it to existing problems b. move on to generating and evaluating alternative solutions c. collect all available information d. immediately choose a satisfactory solution ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 213 203
- 10. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 26. Decisions may be classified as __________. a. routine, adaptive, or innovative b. routine or non-routine c. known or unknown d. risky or certain ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 213 27. Pamela Kay is a bank teller. At the end of her shift, her cash drawer is short by $100. Pam faces a(n) __________ problem. a. accounting b. bookkeeping c. common d. uncommon ANSWER: C, Application, Easy, p. 213 28. Faisal Karim, a management professor, attempts to decide why women and minorities are not moving faster into management positions. Karim is faced with a(n) __________ problem. a. common b. discrimination c. racial d. ambiguous ANSWER: D, Application, Moderate, pp. 213–214 29. The types of __________ that managers and other employees deal with range from the relatively common and well defined to the unusual and ambiguous. a. risks b. uncertainties c. decisions d. problems ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 213 30. The types of __________ available to managers in trying to solve problems range from the known and well defined to the untried and ambiguous. a. information b. solutions c. routines d. human resources ANSWERS: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 214 204
- 11. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 31. __________ is the rigid devotion to the status quo by attempting to do more of the same thing, only better. a. Active inertia b. Inactive Response Mode (IRM) c. Passive management d. Idle Management Syndrome (IMS) ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 215 32. A manager of a restaurant located in a shopping center that is losing popularity says, “Let’s spend more on advertising because sales jumped in the last half of 2002 when we did that.” This manager __________. a. may be making a routine decision when a problem calls for an adaptive or innovative decision b. is using known facts to make an adaptive decision c. should use a routine decision d. should receive a raise for seeing the connection between advertising and sales ANSWER: A, Application, Moderate, pp. 214–215 33. A(n) __________ decision is a standard choice made in response to relatively well- defined and common problems and alternative solutions. a. strategic b. adaptive c. expert d. routine ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 215 34. Dexter Humphreys has a problem. He wants to travel to London and pay the lowest possible price. His travel agent uses the computerized airline reservation system to find a flight for $1,000 and a flight for $700. Dexter’s choice of which flight to take is a(n) __________ decision. a. financial slack b. routine c. imitable d. adaptive ANSWER: B, Application, Moderate, p. 215–216 35. Choices made in response to a combination of moderately unusual problems and alternative solutions are called __________ decisions. a. strategic b. flexible c. adaptive d. non-routine ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 216 205
- 12. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 36. __________ improvement involves streams of adaptive decisions made over time that result in a large number of small, incremental enhancements year after year. a. Functional b. Corporate-level c. Continuous d. Market leader ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 217 37. Continuous improvement is driven by all of the following goals except __________. a. providing better quality b. improving efficiency c. being responsive to customers d. simplifying decision making ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 227 38. Adaptive decisions often reflect the concept of __________. This is a business shift in which two connections with the customer that were previously viewed as competing (e.g., bricks-and mortar stores and Internet stores) come to be seen as complementary. a. union b. convergence c. concurrence d. concentration ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 216–217 39. VisaNet engages in a continuous effort to __________. a. reduce system down time b. increase reliability to 100% c. meet new demands and threats d. create satisfied customers ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 217 40. Visa’s processing system requires enough capacity to handle __________ merchant and bank transactions per day. a. 2 million b. 20 million c. 50 million d. 100 million ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 217 206
- 13. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 41. Choices based on the discovery, identification, and diagnosis of unusual and ambiguous problems and/or the development of unique or creative alternative solutions are called __________ decisions. a. primary b. operational c. innovative d. adaptive ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 218 42. Otis Hawkins is an engineer in the R&D department of KennelCare Foods. During the ten years he has worked for the company, he has made a series of small, interrelated decisions as part of the development of novel new pet stores. Hawkins’ decision making at KennelCare illustrates __________. a. market segmentation b. innovative decisions c. economies of scale d. efficiency ANSWER: B, Application, Moderate, p. 218 43. Christina Culbert is a judge. Her decision on the Hanover case represents a sharp break with past decisions and she has been very careful to define the problem in the case and review prior court decisions. In this example, Culbert makes a(n) __________ decision. a. risky b. innovative c. judgmental d. adaptive ANSWER: B, Application, Difficult, p. 218 44. __________ involves individuals or organizations who change the bases for industry competition or change the economic efficiency of an industry. a. Convergence strategy b. Adaptive decision making c. Radical innovation d. Transformational leadership ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 218 45. __________ is an example of radical innovation. a. Akami Technologies b. AmeriScan c. Phillips Consumer Electronics d. Xerox Corporation ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Easy, p. 219 207
- 14. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING Learning Objective 3 Models of Decision Making 46. Which of the following is not one of the decision-making models discussed in the decision making chapter? a. rational b. bounded rationality c. political d. value chain ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 219 47. The __________ decision-making model prescribes a set of phases that individuals or teams should follow to increase the likelihood that decisions will be logical and optimal. a. rational b. bounded rationality c. political d. goal setting ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, p. 219 48. Marco Hernandez is a city manager. Morale at the new water treatment plant is at an all time low due to a succession of incompetent facility managers. As Marco is called into the hiring process, it is essential that a successful job search take place this time. He is making a __________ decision. a. rational b. bounded rational c. political d. goal setting ANSWER: A, Application, Moderate, p. 219 49. When making __________ decisions under near certain conditions, individuals don’t need to follow all of the phases in the rational decision making model. a. continuous b. routine c. core d. adaptive ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 219 50. When making adaptive or innovative decisions, individuals __________ follow the seven phases of rational decision making sequentially. a. pretend to b. never c. frequently d. rarely ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 219 208
- 15. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 51. Problem definition and diagnosis involves the skills of noticing, interpreting and incorporating, which are part of the manager’s __________ competency. a. communication b. teamwork c. planning and administrative d. strategic action ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 219 52. The first phase in the rational decision-making model is __________. a. strategy formulation b. stating the vision resource definition define and diagnose the problem ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 219 53. Phase 1 in the rational decision-making model includes the skill of __________, which involves identifying and monitoring numerous external and internal environmental factors and deciding which ones are contributing to the problem. a. interpreting b. noticing c. communication d. teamwork ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 219 54. Phase 1 in the rational decision-making model includes the skill of __________, which involves assessing the environmental factors noticed and determining which are causes, not merely symptoms, of the real problem. a. noticing b. interpreting c. communication d. teamwork ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 219 55. Phase 1 in the rational decision-making model includes the skill of __________, which involves relating those interpretations to the current or desired goals of the department or organization. a. interpreting b. noticing c. communication d. incorporating ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 219 209
- 16. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 56. In the rational decision-making model, the phase that immediately follows “define and diagnose the problem” calls for the manager to ___________. a. interpret the problem b. notice solutions c. communicate the problem d. set goals ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 220 57. ___________ are results to be attained and thus indicate the direction that decisions and actions should be aimed. a. Goals b. Objectives c. Aims d. Outcomes ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, p. 221 58. Goals may be stated in either __________ or __________ terms. a. attainable; unattainable b. objective; subjective c. qualitative; quantitative d. abstract; concrete ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 221 59. __________ goals are stated in qualitative terms while __________ goals are stated in quantitative terms. a. Subjective; objective b. Long-term; short-term c. Team; individual d. General; operational ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 221 60. Microsoft has the goal of becoming the world’s leading developer of computer software applications. This is an example of a(n) __________ goal. a. operational b. general c. tactical d. long-term ANSWER: B, Application, Moderate, p. 221 61. Microsoft has the goal of increasing sales of its Windows 2000 software packages by 40% over the next three years. This is an example of a(n) _________ goal. a. operational b. general c. strategic d. long-term ANSWER: A, Application, Moderate, p. 221 210
- 17. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 62. After individuals or teams have defined a problem, they __________. a. are stuck unless they have complete information b. can move directly to a solution c. have completed the rational decision-making model d. can set goals that are intended to lead its elimination ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 220 63. Sally Powers wants to get a job as an international currency trader. Powers begins to think creatively about the ways in which she could obtain this job. She is at the __________ step of the rational decision-making model. a. setting goals b. search for alternative solutions c. comparing alternative solutions d. choosing alternatives ANSWER: B, Application, Moderate, p. 223 64. In the rational decision-making model, the phase that immediately follows goal setting is __________. a. search for alternative solutions b. develop strategies c. engage in teamwork d. analyze the internal environment ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, p. 223 65. In the rational decision-making model, during the “search for alternative solutions” phase, individuals or teams might engage in all of the following except _____________. a. seek additional information b. think creatively c. consult experts d. analyze the environment ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 223 66. In the rational decision-making model, the phase that immediately follows the search for alternative solutions is __________. a. implement the chosen solution b. develop imitability c. compare and evaluate alternative solutions d. identify customers ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 220 211
- 18. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 67. Managers often complain that recent college graduates present and discuss only one solution when they receive project assignments. The college graduates are doing a poor job of __________. a. strategy implementation b. defining the problem c. strategy formulation d. comparing and evaluating alternative solutions ANSWER: D, Application, Moderate, p. 223 68. After individuals or teams have searched for alternative solutions, they must then __________. a. compare and evaluate alternative solutions b. choose among alternative solutions c. implement the solution selected d. follow-up and control ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, p. 220 69. Choosing among alternative solutions may prove to be difficult when the problem is __________. a. complex b. ambiguous c. involves a high level of risk d. all of the above ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 223 70. In the rational decision-making model, the phase that immediately follows “choosing among alternative solutions” is __________. a. implementing the solutions selected b. evaluating the selection c. analyzing the environment d. follow-up and control ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 220 71. In phase 7 of the rational decision-making model, individuals and teams must __________ implementation activities and __________ by evaluating results. a. manage; act b. follow up; control c. control; follow up d. explore; change ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 220 212
- 19. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 72. John Mayberry, CEO of Dofasco, says he has placed decision-making accountability right where it belongs: at the __________ level. a. individual b. executive c. manager d. team ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 225 73. Dofasco’s decision making process has resulted in a team decision to install new steel furnaces that do all of the following except __________. a. consume less energy b. reduce air pollution c. produce higher volumes d. produce higher quality ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 225 74. Which of the following is not an individual tendency in the bounded rationality model of decision making? a. engage in an extended search for alternative solutions b. select less than the best goal c. select less than the best alternative solution d. have inadequate information and control over environmental forces ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 227 75. Talia and Eliza Sinkinson are on vacation in New York City. They would like to go to a good Chinese restaurant for lunch. There are at least 200 Chinese restaurants in Chinatown. Talia and Eliza will probably use the __________ model of decision making to select a restaurant. a. bounded rationality b. decision tree c. rational d. probability ANSWER: A, Application, Moderate, pp. 226–228 76. The bounded rationality model of decision making is particularly useful because it emphasizes the __________, thus providing a better picture of the day-to-day decision- making processes used by most people. a. rational steps in decision making b. uncertainty of decision making c. limitations of rationality in decision making d. goal setting nature of decision making ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 226 213
- 20. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 77. The level of satisficing can be raised by all of the following except __________. a. using computer-based decision-making techniques b. setting lower organizational expectations c. setting higher individual standards d. personal determination ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 228 78. In the bounded rationality model, individuals stop searching for alternatives as soon as they __________. a. find an acceptable one b. find the best one c. get tired of searching d. have explored the maximum alternatives ANSWER: A, Application, Moderate, p. 227 79. A person who easily recalls specific instances of an event may overestimate how frequently the event occurs. This is an example of __________ bias. a. law of small numbers b. availability c. gambler’s fallacy d. memorization ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Easy, p. 227 80. Jerry Taylor was in a serious car accident last year. The National Safety Transportation Board says that 1 percent of all drivers will be in car accidents each year. However, Taylor thinks that the actual frequency is 5 percent. He has most likely fallen prey to the __________ bias. a. belief b. concrete information c. critical thinking d. availability ANSWER: D, Application, Moderate, p. 226 81. The idea that what people expect to see often is what they do see is an example of the __________ bias. a. availability b. limitation c. certainty d. selective perception ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, pp. 226–227 214
- 21. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 82. __________ bias means that vivid, direct experience usually prevail over abstract information. a. Availability b. Personal experience c. Concrete information d. Law of experiences ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 227 83. Amy Ingram works for a large toy manufacturing company. Her first supervisor, Alice Fredrich, was unfair, unsupportive, and often used Amy’s ideas without giving her credit. Amy’s current supervisor, Libby Valentine, is supportive and friendly, but Amy is unwilling to trust Valentine. Amy appears to be applying the __________ bias. a. concrete information b. abstract information c. intrasender role d. law of experience ANSWER: A, Application, Moderate, p. 227 84. When a few incidents or cases are viewed as representative of a larger population, even when they aren’t, the law of _________ bias exists. a. population concentration b. large numbers c. incidents d. small numbers ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 227 85. The __________ bias occurs when an unexpected number of similar events leads to the conviction that an event not seen will occur. a. probability b. law of association c. law of expected outcomes d. gambler’s fallacy ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 227 86. Bubba Barnett has seen his favorite college football team unexpectedly lose six games in a row but he is convinced that his team will win this coming weekend. Barnett is guilty of the __________ bias. a. probability b. gambler’s fallacy c. law of expected outcomes d. law of association ANSWER: B, Application, Easy, p. 227 215
- 22. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 87. Satisficing is __________. a. the practice of selecting an acceptable goal or alternative solution b. the inability to select an acceptable goal or alternative solution c. the unwillingness to select an acceptable goal or alternative solution d. applying decision making to routine decisions ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, p. 228 88. Which of the following is not one of the factors that influence a satisficing decision? a. limited search b. inadequate information c. information processing bias d. a certain environment ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 228 89. In the text, Herbert Simon identifies assumptions that lead to satisficing which include all of the following except __________. a. limited set of alternatives b. difficulty in locating alternatives c. tendency to select lowest cost d. difficulty in evaluating alternatives ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 228 90. Cherry Cheatwood is graduating from Indiana State University in May. She wants to find a job as an elementary school teacher. It would be extremely time consuming and costly for her to evaluate every teaching job available. Most likely, Cherry will __________. a. use a routine decision making framework b. use the constrained decision-making model c. use the rational decision-making model d. use bounded rationality in making a choice ANSWER: D, Application, Moderate, p. 228 91. The __________ decision-making model is described in terms of the self-interests and goals of powerful internal and external stakeholders. a. co-optation b. governance c. political d. gambler’s fallacy ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 228 92. If an individual is able to influence or control individual, departmental, team or organizational decisions and goals, the individual has __________. a. power b. vision c. entrepreneurial skill d. the backing of the CEO ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, p. 228 216
- 23. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 93. An individual has power if she or he can influence or control all of the following except __________ during decision making. a. the definition of the problem b. goal preferences of other decision makers c. the choice of the goal d. selection of the alternative to be implemented ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 228 94. A(n) __________ decision-making process is most likely to occur when decisions involve powerful stakeholders, disagreement over goals, and the lack of search for alternative solutions. a. rational b. political c. irrational d. adaptive ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, pp. 228–229 95. In the political model, external and internal stakeholders try to __________. a. define problems to their own advantage b. define problems to the advantage of everyone c. make the decision makers process more rational d. make the decision makers process more irrational ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, p. 229 96. __________ refers to the process of casting blame for problems or shortcomings on an innocent or only partially responsible individual, team, or department. a. Politics b. Scapegoating c. Blamesharing d. Satisficing ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 229 97. Brandi Putnam often blames problems on other individuals to preserve a positive image for himself. Thus, Putnam tends to use __________. a. argumentation b. person–role augmentation c. scapegoating d. power shifting ANSWER: C, Application, Moderate, p. 229 217
- 24. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 98. The push and pull of stakeholders who have both power and conflicting goals occurs in the __________ decision-making model. a. niche b. bounded rationality c. political d. relational ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 230 99. When goals and the means to achieve them are perceived by stakeholders as a win– lose situation, the ability to make adaptive and innovative decisions is __________. a. not affected b. greatly increased c. severely limited d. related constrained ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 230 100. __________ involves bringing new stakeholder representatives into the strategic decision-making process as a way of averting threats to an organization’s stability or existence. a. Conglomeration b. Co-optation c. Competitor intelligence d. Bureaucratic control ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 230 101. The __________ model of decision making may be especially useful for resolving conflicts among stakeholders with divergent goals and/or divergent preferences for actions to be taken. a. co-optation b. rational c. bounded rationality d. political ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 230 102. Russell Finkstein's company needs to borrow money. He decides to put the president of a local bank on his board of directors. Finkstein is using the political strategy of __________. a. conglomeration b. co-optation c. competitor intelligence d. bounded rationality ANSWER: B, Application, Moderate, p. 230 218
- 25. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 103. Don Carty, CEO of American Airlines, lost his job as an outcome of miscommunications related to all of the following problem areas except __________. a. full public disclosure of the seriousness of the company’s financial condition b. full disclosure to unions about lucrative executive bonuses and protections c. offering to resign if the unions would take pay cuts d. threatening bankruptcy if unions would not take pay cuts ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 231 104. __________ was taking place in the failed political process at American Airlines? a. Satisficing b. Co-optation c. Scapegoating d. Bounded rationality ANSWER: C, Application, Difficult, pp. 229–231 Essay Questions Learning Objective 1 1. What is decision making? In the most basic sense, decision making includes: (1) defining problems (2) gathering information (3) generating alternatives (4) choosing a course of action Moderate, p. 208 2. Compare and contrast certainty, uncertainty, and risk. a. Certainty is the condition under which individuals are fully informed about a problem, alternative solutions are obvious, and the likely results of each solution are clear. The condition of certainty at least allows anticipation (if not control) of events and their outcomes. This condition means that both the problem and alternative solutions are known and well defined. b. Uncertainty is the condition under which an individual doesn’t have the necessary information to assign probabilities to the outcomes of alternative solutions. The individual may not be able to define the problem, much less identify alternative solutions and possible outcomes. Uncertainty often suggests that the problem and the alternative solutions are both ambiguous and highly unusual. c. Risk is the condition under which individuals can define a problem, specify the probability of certain events, identify alternative solutions, and state the probability of each solution leading to the desired results. Risk generally means that the problem and the alternative solutions fall somewhere between the extremes of being relatively common and well-defined and being unusual and ambiguous. Difficult, pp. 210–212 3. What is probability, and what are the different types of probability? 219
- 26. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING a. Probability is the percentage of times that a specific outcome would occur if an individual were to make a particular decision a large number of times. b. Objective probability is the likelihood that a specific outcome will occur based on hard facts and numbers such as past records. c. Subjective probability is the likelihood that a specific outcome will occur based on personal judgments and beliefs, such as intuition, previous experience, and expertise. Moderate, pp. 210–211 Learning Objective 2 4. What type of decision would be made when: (1) the problem is common and well defined, (2) the problem and alternative solutions are only moderately unusual, and (3) the problems are unusual and ambiguous? Give an example of each. a. When problems are common and well-defined, routine decisions are made. Managing guest relations at Four Seasons Hotels is an example of a routine decision process. b. When problems and alternative solutions are moderately unusual and only fairly common, adaptive decisions are made. Continuous improvement at VisaNet is an example of adaptive decision making. c. When problems and alternative solutions are unusual, ambiguous, and untried, innovative decisions are made. Michael Dell, Charles Schwab, and Jeff Bezos of Amazon.com are examples of innovators. Difficult, pp. 215–218 5. How does continuous improvement relate to decision making? What goals drive the process of continuous improvement? a. Continuous improvement involves streams of adaptive decisions made over time in an organization that result in a large number of small, incremental improvements year after year. b. The goals of continuous improvement include: (1) providing better quality (2) improving efficiency (3) being responsive to customers Difficult, p. 217 220
- 27. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 6. Describe how Richard Knight uses continuous improvement in his planning and administration competency to constantly meet new demands and threats at VisaNet. Although VisaNet can maintain 100 percent reliability in their transaction processing systems, they constantly refine their software in order to protect multiple layers of redundancy and backups. They are able to process as many as 100 million transactions per day. They periodically design testing procedures to verify the quality and control taking place within the systems. VisaNet completed a three-year overhaul of their assembler-language-based clearing application and they typically modify 2 million lines of code annually. The firm upgrades system security on an ongoing basis, as well as customer service applications. Richard Knight has assigned four risk level ratings, and reviews the system constantly according to his demanding criterion. Difficult, pp. 217–218 Learning Objective 3 7. Name four of the seven phases in the rational decision-making model. a. Define and diagnose the problem b. Set goals c. Search for alternative solutions d. Compare and evaluate alternative solutions e. Choose among alternative solutions f. Implement the solution selected g. Follow up and control the results Moderate, pp. 219–225 8. Describe the parts of the bounded rationality model. a. The individual’s tendencies to select less than the best goal or alternative solution (satisficing). b. The individual’s tendencies to engage in a limited search for alternative solutions. c. The individual’s tendencies to have inadequate information and control over external and internal environmental forces influencing the outcomes of decisions. Moderate, pp. 226–228 221
- 28. CHAPTER 8: FUNDAMENTALS OF DECISION MAKING 9. Define and give examples of two of the five kinds of information processing biases common to bounded rationality decision making. a. The availability bias means that a person easily recalls specific instances of an event and overestimates how frequently the event occurs. Example: Someone who has been in a serious automobile accident will overestimate the frequency of such accidents. b. The selective perception bias means that people see what they expect to see, tending to seek information consistent with their own views. They downplay conflicting information. Example: Some people are willing to bungee jump but are unwilling to live next to a superfund cleanup site. c. The concrete information bias means that vivid, direct experience usually prevails over abstract information. Example: If one manager is difficult, all managers are difficult. d. The law of small numbers bias means that a few incidents or cases may be viewed as representative of a larger population even when they aren’t. Example: After a few well-publicized events of the use of excessive force by police officers, some people may believe that all police use excessive force. e. The gambler’s fallacy bias means that seeing an unexpected number of similar events can lead to the conviction that an event not seen will occur. Example: After 9 successive reds on a roulette wheel, a player believes the odds of a black on the next spin are greater than 50/50. Difficult, pp. 226–227 10. When does a stakeholder have power in the political model of decision making? A stakeholder has power when he or she can control or influence the: a. definition of the problem, b. choice of the goal, c. consideration of alternative solutions, d. selection of the alternative to be implemented, or e. ultimate actions and success of the organization. Difficult, p. 228 222