Melden
Teilen
Empfohlen
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Ähnlich wie Thermo#2
Ähnlich wie Thermo#2 (20)
Thermodynamics ,types of system,formulae ,gibbs free energy .pptx

Thermodynamics ,types of system,formulae ,gibbs free energy .pptx
Diploma_I_Applied science(chemistry)U-V Thermodynamics 

Diploma_I_Applied science(chemistry)U-V Thermodynamics
Which of the following is true An open thermodynamic system can gai.pdf

Which of the following is true An open thermodynamic system can gai.pdf
Mehr von gbsliebs2002
Mehr von gbsliebs2002 (20)
Thermo#2
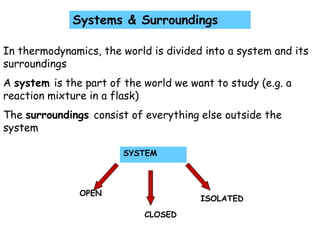
- 1. SYSTEM OPEN ISOLATED CLOSED Systems & Surroundings In thermodynamics, the world is divided into a system and its surroundings A system is the part of the world we want to study (e.g. a reaction mixture in a flask) The surroundings consist of everything else outside the system
- 2. OPEN SYSTEM: can exchange both matter and energy with the surroundings (e.g. open reaction flask, rocket engine) CLOSED SYSTEM: can exchange only energy with the surroundings (matter remains fixed) e.g. a sealed reaction flask ISOLATED SYSTEM: can exchange neither energy nor matter with its surroundings (e.g. a thermos flask)
- 3. Exothermic A chemical reaction or a physical change that releases heat -energy flows out as a result of a temperature difference between the system and the surroundings Exothermic processes have negative q reaction
- 4. Endothermic A chemical reaction or a physical change in which heat is absorbed - energy flows into a system from the surroundings. Endothermic processes have positive q reaction
- 5. Exothermic and Endothermic Processes