Formation of Large-Scale Structure and Galaxies
- 1. Formation of Large-Scale Structure and Galaxies Jeremy Lim, Associate Professor, University of Hong Kong
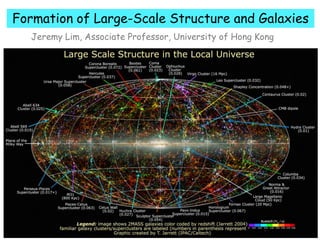
- 14. Formation of Large-Scale Structure and Galaxies Jeremy Lim, Associate Professor, University of Hong Kong How are galaxies distributed in space (large-scale structure)? How is the observed large-scale structure formed? Does our ability to reproduce (in our computers) the observed large-scale structure mean we understand galaxy formation?
- 15. Formation of Large-Scale Structure and Galaxies Jeremy Lim, Associate Professor, University of Hong Kong How are galaxies distributed in space (large-scale structure)? How is the observed large-scale structure formed? Does our ability to reproduce (in our computers) the observed large-scale structure mean we understand galaxy formation?
- 16. Distribution of Nearby Galaxies Mollweide projection of our Galaxy and the sky distribution of nearby galaxies.
- 17. Mollweide Projection of the Earth Projection of a sphere onto a 2-dimensional plane so as to accurate preserve proportions in area.
- 18. Our Galaxy Our Galaxy, also known as the Milky Way, is the bright band along the equator.
- 19. Our Galaxy Our Galaxy, also known as the Milky Way, is the bright band along the equator.
- 20. Our Galaxy Our Galaxy, also known as the Milky Way, is the bright band along the equator.
- 21. Our Galaxy We live on a planet orbiting a star at the outskirts of a spiral galaxy.
- 22. Our Galaxy We live on a planet orbiting a star at the outskirts of a spiral galaxy.
- 23. Our Galaxy Our Galaxy looks like a milky band of light across the sky.
- 24. Neighboring Galaxies The nearest galaxies are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
- 25. Neighboring Galaxies The nearest galaxies are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
- 26. Neighboring Galaxies The nearest galaxies are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
- 27. Large Magellanic Cloud Small Magellanic Cloud Neighboring Galaxies The nearest galaxies are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
- 28. Neighboring Galaxies The nearest galaxies are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
- 29. Large Magellanic Cloud Small Magellanic Cloud Neighboring Galaxies The nearest galaxies are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
- 30. Large Magellanic Cloud Small Magellanic Cloud Supernova 1987A Neighboring Galaxies The nearest galaxies are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
- 31. Neighboring Galaxies The next nearest galaxy is M31, the Andromeda galaxy. (250 m away)
- 32. Neighboring Galaxies The next nearest galaxy is M31, the Andromeda galaxy. M31 (Andromeda galaxy)
- 33. Local Group Our galaxy is part of a group of over 50 galaxies.
- 34. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters At distances up to 140 million light years, we see … (5 km away; Wan Chai)
- 35. < 140 million light years At distances up to 140 million light years, we see … More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 36. < 140 million light years Clusters comprising hundreds to thousands of galaxies such as the Virgo cluster. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 37. Virgo Cluster Clusters comprising hundreds to thousands of galaxies such as the Virgo cluster. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 38. < 140 million light years Clusters comprising hundreds to thousands of galaxies such as the Fornax cluster. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 39. Fornax Cluster Clusters comprising hundreds to thousands of galaxies such as the Fornax cluster. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 40. < 140 million light years Galaxies (individual, in groups and clusters) arranged in long filaments. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 41. < 140 million light years Galaxies (individual, in groups and clusters) arranged in long filaments (superclusters). More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 42. At distances from 140-280 million light years, we see … (5-10 km away; Wan Chai and Fortress Hill) More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 43. < 280 million light years More clusters like the Centaurus cluster. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 44. < 280 million light years Centaurus Cluster More clusters like the Centaurus cluster. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 45. < 280 million light years More superclusters. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 46. < 280 million light years The Perseus-Pisces supercluster spans the constellation Perseus to Pisces. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 47. < 280 million light years Perseus The Perseus-Pisces supercluster spans the constellation Perseus to Pisces. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 48. < 280 million light years Perseus Cluster The Perseus-Pisces supercluster is anchored by the Perseus cluster to the east. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 49. < 280 million light years More galaxies (individual, in groups and clusters) arranged in long filaments. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 50. At distances from 280-420 million light years, we see … (10-15 km away; Fortress Hill and Shau Kei Wan) More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 51. < 280 million light years< 420 million light years More clusters, such as the Coma cluster. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 52. < 280 million light years Coma Cluster More clusters, such as the Coma cluster. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 53. < 280 million light years< 420 million light years Galaxies (individual, in groups and clusters) arranged along “cell walls.” More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 54. At distances from 420-560 million light years, we see … (15-20 km away; Tai Wan and Fo Tan) More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 55. < 560 million light years More superclusters, and galaxies (individual, in groups and clusters) arranged along “cell walls”. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 56. At distances from 560-700 million light years, we see … (20-25 km away; near Lok Ma Chau) More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 57. < 700 million light years More superclusters, and galaxies (individual, in groups and clusters) arranged along “cell walls”. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 58. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters At distances from 700-840 million light years, we see … (25-30 km away; Shenzhen)
- 59. < 560 million light years< 700 million light years< 840 million light years More superclusters, and galaxies (individual, in groups and clusters) arranged along “cell walls”. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 60. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters At distances from 840-980 million light years, we see … (30-35 km away; beyond Shenzhen)
- 61. < 980 million light years More superclusters, and galaxies (individual, in groups and clusters) arranged along “cell walls”. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 62. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters At distances from 980-1220 million light years, we see … (35-44 km away; Pinghu residential district)
- 63. < 1220 million light years More superclusters, and galaxies (individual, in groups and clusters) arranged along “cell walls”. More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
- 76. Closeup of a … beads (galaxies) along a string (filament)? The Cosmic Web
- 77. Closeup of a … beads (galaxies) along strings (filaments)? The Cosmic Web < 280 million light years
- 78. Closeup of a … beads (galaxies) along connected strings (cell walls)? The Cosmic Web
- 79. You were looking at closeups of a spider’s web. The Cosmic Web
- 80. Formation of Large-Scale Structure and Galaxies Jeremy Lim, Associate Professor, University of Hong Kong How are galaxies distributed in space (large-scale structure)? In connected filaments called the Cosmic Web. How is the observed large-scale structure formed? Does our ability to reproduce (in our computers) the observed large-scale structure mean we understand galaxy formation?
- 81. Formation of Large-Scale Structure and Galaxies Jeremy Lim, Associate Professor, University of Hong Kong How are galaxies distributed in space (large-scale structure)? In connected filaments called the Cosmic Web. How is the observed large-scale structure formed? Does our ability to reproduce (in our computers) the observed large-scale structure mean we understand galaxy formation?
- 82. What is the Universe made of? The Universe is made of - 4.6% atoms (ordinary matter), such as people, Earth, Sun, stars, … - 23% Dark matter, which cannot be seen and only interact with ordinary matter through their mutual gravity - 72% Dark Energy, which repulses ordinary and Dark matter Dark matter therefore dominates gravity in the Universe.
- 83. How did the Universe begin? The Universe expanded from a dense and hot state in a “Big Bang.” Approximately 10−37 seconds into the expansion, the Universe went through a period of exponential expansion known as inflation.
- 84. State of the Universe after Inflation The Universe was almost perfectly smooth following Inflation. If draped over the Earth’s surface, the height from the deepest to tallest points would only be 850 m.
- 85. State of the Universe after Inflation The Universe was almost perfectly smooth following Inflation. If draped over the Earth’s surface, the height from the deepest to tallest points would only be 850 m.
- 86. The Cosmic Microwave Background The CMB comprises radiation from the epoch when the Universe first became transparent, ~380,000 years after the Big Bang. The CMB is smooth to about 1 part in about 100,000, but is not perfectly smooth. Regions of higher-than-average density have higher-than-average gravity, attracting both Dark and ordinary matter to form galaxies distributed in a Cosmic Web. Dunkley+09
- 87. Gravity on a Uniform Distribution of Matter If particles are uniformly distributed in space, there would be not be a net gravitational force between particles. Particles would not clump together.
- 88. Gravity on a Non-Uniform Distribution of Matter If particles are not uniformly distributed in space, there exists a net gravitational force between particles. Particles would start to clump together.
- 89. Gravity on a Non-Uniform Distribution of Matter Particles that clump together exert a stronger gravitational force on neighboring particles, attracting ever more particles towards the clump.
- 90. Modeling the Formation of Large-Scale Structure The Millennium Simulation Project, an N-body simulation comprising over 109 particles each with a mass of ~8.6 108/h M and having a spatial resolution of 5/h kpc. z Time since Big Bang 20 0.18 Gyr 15 0.27 Gyr 10 0.48 Gyr 8 0.65 Gyr 6 0.95 Gyr 5 1.20 Gyr 4 1.57 Gyr 3 2.19 Gyr 2 3.34 Gyr 1 5.94 Gyr 0.5 8.65 Gyr 0.2 11.26 Gyr 0.1 12.38 Gyr
- 92. Formation of Large-Scale Structure and Galaxies Jeremy Lim, Associate Professor, University of Hong Kong How are galaxies distributed in space (large-scale structure)? In connected filaments called the Cosmic Web. How is the observed large-scale structure formed? Through gravitational collapse of initial density inhomogeneities. Does our ability to reproduce (in our computers) the observed large-scale structure mean we understand galaxy formation?
- 93. Formation of Large-Scale Structure and Galaxies Jeremy Lim, Associate Professor, University of Hong Kong How are galaxies distributed in space (large-scale structure)? In connected filaments called the Cosmic Web. How is the observed large-scale structure formed? Through gravitational collapse of initial density inhomogeneities. Does our ability to reproduce (in our computers) the observed large-scale structure mean we understand galaxy formation?
- 94. Galaxy Formation The excellent overall agreement between observations and theoretical models of large-scale structure indicates that we understand in a global sense how galaxies form. Springel+06
- 95. Galaxy Formation The excellent overall agreement between observations and theoretical models of large-scale structure indicates that we understand in a global sense how galaxies form. Springel+06 But, theoretical models simply represent galaxies as a collection of gravitating point masses. Real galaxies contain stars and gas (along with dark matter), where gas turn into stars and stars expel gas that turn into stars … One of the frontiers of astrophysics: formation and evolution of galaxies. Andromeda galaxy
- 96. Formation of Large-Scale Structure and Galaxies Jeremy Lim, Associate Professor, University of Hong Kong How are galaxies distributed in space (large-scale structure)? In connected filaments called the Cosmic Web. How is the observed large-scale structure formed? Through gravitational collapse of initial density inhomogeneities. Does our ability to reproduce (in our computers) the observed large-scale structure mean we understand galaxy formation? No. We understand in a global sense how galaxies come into existence, but how galaxies actually form and evolve to assume their present-day properties is one of the most important frontiers in modern-day astrophysics.
- 98. < 140 million light years At distances up to 140 million light years, we see … More Distant Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters
Hinweis der Redaktion
- Say the distance between us and the center of our galaxy is the width of this room (20m)That is roughly the distance between the center of our galaxy and the LMC/SMC
- The distance between us and the Andromeda galaxy is about 16 times the width of this room (250 m away)
- Mikly Way will collide with Andromeda in about 4 billion years
- Pisces-Perseussupercluster is a long chain of galaxies that include 3 rich clusters and many groups of galaxies.Perseus cluster is at left end
- Pisces-Perseussupercluster is a long chain of galaxies that include 3 rich clusters and many groups of galaxies.Perseus cluster is at left end
- Pisces-Perseussupercluster is a long chain of galaxies that include 3 rich clusters and many groups of galaxies.Perseus cluster is at left end
- Pisces-Perseussupercluster is a long chain of galaxies that include 3 rich clusters and many groups of galaxies.Perseus cluster is at left end
- Shapley concentration = Shapley supercluster
- Distance to furthest known galaxy is roughly at shangai
- Inflation dilutes all inhomogeneities in space, as the number density of particles goes to zero.Inflation also dilutes any curvature, making the Universe flat.Even empty space can have quantum fluctuations.The Universe becomes transparent because electrons combined with protons (i.e., reducing the amount of electron scattering).
- Inflation dilutes all inhomogeneities in space, as the number density of particles goes to zero.Inflation also dilutes any curvature, making the Universe flat.Even empty space can have quantum fluctuations.The Universe becomes transparent because electrons combined with protons (i.e., reducing the amount of electron scattering).
- Inflation dilutes all inhomogeneities in space, as the number density of particles goes to zero.Inflation also dilutes any curvature, making the Universe flat.Even empty space can have quantum fluctuations.The Universe becomes transparent because electrons combined with protons (i.e., reducing the amount of electron scattering).
- Length of HK island = 15 kmAt this scale, size of our galaxy = 15m
- Length of HK island = 15 kmAt this scale, size of our galaxy = 15m
