Exercise 7 animal tissues
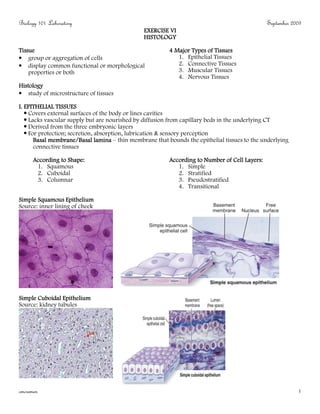
- 1. Biology 101 Laboratory September 2009 EXERCISE VI HISTOLOGY Tissue 4 Major Types of Tissues • group or aggregation of cells 1. Epithelial Tissues • display common functional or morphological 2. Connective Tissues properties or both 3. Muscular Tissues 4. Nervous Tissues Histology • study of microstructure of tissues I. EPITHELIAL TISSUES Covers external surfaces of the body or lines cavities Lacks vascular supply but are nourished by diffusion from capillary beds in the underlying CT Derived from the three embryonic layers For protection; secretion, absorption, lubrication & sensory perception Basal membrane/Basal lamina – thin membrane that bounds the epithelial tissues to the underlying connective tissues According to Shape: According to Number of Cell Layers: 1. Squamous 1. Simple 2. Cuboidal 2. Stratified 3. Columnar 3. Pseudostratified 4. Transitional Epithelium Simple Squamous Epithelium Source: inner lining of cheek Epithelium Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Source: kidney tubules cmcremen 1
- 2. Biology 101 Laboratory September 2009 Simple Columnar Epithelium Source: stomach or small intestine • highly absorptive surfaces → small intestine • secretory surfaces → stomach • may be specialized for secretion → goblet cells in the small intestine Stratified Squamous Epithelium Source: skin • Composed of epithelial tissues with more cell layers • Only cells of the lowest layer touch the basement membrane • Basal layer consists of columnar or cuboidal cells → undergoes continuous mitotic division • Cells near the surface are flattened, consists of squamous cells Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium Source: trachea • ‘pseudo’ → false • Cells appear to be arranged in more than one layer but all of them are attached to the basal membrane, thus are actually single layer of cells • Pointed structure: microvilli (hair-like structures) cmcremen 2
- 3. Biology 101 Laboratory September 2009 Transitional Epithelium Source: urinary bladder • Transition between stratified squamous & columnar epithelium • Cells change their form • Found in hollow organs subject to contraction & stretching II. CONNECTIVE TISSUES Bind, anchor, and support body parts Abundant cellular matrix Originate from the mesenchyme, the embryonic connective tissue that develops from the mesoderm 2 Types: 1. Connective Tissue Proper – for binding organs 2. Specialized Connective Tissues – binding & other specific functions Connective tissue fibers: 1. Collagen fibers – thick, un-branched, appear wavy; show resistance to stretching 2. Elastic Fibers – thin & less wavy than collagen fibers, branched; easily stretched but return to normal length when tension is released 3. Reticular Fibers – extremely fine & highly branched forming network Connective Tissue Proper Loose or Areolar Connective Tissue Dense Connective Tissue (Tendon) • Large amount of tissue fluid, many cells, few • More fibers, less ground substance & cells fibers cmcremen 3
- 4. Biology 101 Laboratory September 2009 Connective Tissue: Specialized Connective Tissue: Adipose Tissue • Store fats in the form of triglycerides • Stores nutrients, provides insulation, & acts as cushion; fills crevices in organs • Adipocytes → fat cells Cartilage • Soft & pliable 3 Types of Cartilage based on Matrices: • Chondrocytes → cartilage cells 1. Hyaline Cartilage 2. Elastic Cartilage • Lacuna → cartilage matrix 3. Fibrocartilage • The lacuna houses the chondrocytes Hyaline Cartilage: Source: trachea • Clear homogenous matrix • Perichondrium → dense connective tissue at the periphery of the cartilage • Spindle-shaped lacunae Elastic Cartilage Fibrocartilage Source: epiglottis & external ear • Resembles connective tissue proper • Contains collagen fibers, & a network of elastic • Consists of a network of collagen fibers fibers • Lacunae → round or oval cmcremen 4
- 5. Biology 101 Laboratory September 2009 Specialized Connective Tissue (continuation) Bone For support, protection, movement, forming blood cells; reservoir of calcium Lamellae → matrix Haversian canal Osteocytes → bone cells Lacunae Canaliculi → minute canals radiating from the lacunae Haversian System or Osteone – composed of haversian canal, lamellae, osteocytes, lacunae, & canaliculi Volkman’s canal – canals that runs diagonally/right angles to the Haversian canal Blood Transport medium Consists of cells, matrix, & intercellular fibers Cellular elements: erythrocytes, leucocytes, & thrombocytes Matrix: liquid called plasma Function: transporting gases & substances to and from the different parts of the body 1. Erythrocytes or Red Blood Cells Oxygen carrier carries hemoglobin 2. Leucocytes or White Blood Cells For body defense against microorganisms by their phagocytic action & antibody production a. Granular WBC ♦ have a granulated cytoplasm & multi-lobulated nucleus connected by chromatin strands ♦ function as phagocytes b. Agranular WBC ♦ cells without granules in the cytoplasm ♦ are transformed into large phagocytic cells called macrophages 3. Platelets also, thrombocytes small, non-nucleated, colorless, round or oval, non-motile corpuscles functionally related to blood clotting Human RBC Frog’s RBC Granulated WBC Agranulated WBC cmcremen 5
- 6. Biology 101 Laboratory September 2009 III. MUSCLE TISSUES • specialized for contraction • contains contractile proteins – allows them to shorten their lengths • muscle cells → muscle fibers • 3 Types of Muscle Tissues: 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle • connected to the skeleton • concerned with body movement • striated; voluntary in action • skeletal muscle cells: cylindrical, striated & multinucleated; oval nuclei are at the periphery of the cell • Fasciculi – muscle fibers grouped into bundles • Endomysium – connective tissue meshwork enveloping the muscle fiber • Perimysium – connective tissue sheath joining the fasciculi • Epimysium – holds together the whole muscle mass Smooth Muscle • found as part of the walls of the viscera (internal organs) • non-striated; involuntary in action • smooth muscle cell: spindle-shaped cells in side view with a single centrally located nucleus at the widest part of the cell • cytoplasm is homogenous cmcremen 6
- 7. Biology 101 Laboratory September 2009 Cardiac Muscle • comprises the contractile wall of the heart; also found in the roots of large blood vessels arising from the heart • specialized to contract automatically & rhythmically • striated, branched; involuntary in action • presence of intercalated discs → dark bands IV. NERVOUS TISSUES • specialized to receive stimuli from the environment or from the various organs of the body • transmit impulses to the nerve centers in the brain & spinal cord • composed of 2 Types of Cells: Neurons & Neurologia Neuron • consist of nerve cell body → soma or perikaryon 2 processes (nerve fibers): 1 axon & 1 dendrite perikaryon aryon; 1. axon thinner & longer compared to the dendrite, branches extensively gradually decreases in diameter as it furthers the cell body conveys impulses away from the cell body 2. dendrite short & confined near the cell body may be more than one process in a neuron have thorny appearance conveys impulses towards the cell body cmcremen 7
- 8. Biology 101 Laboratory September 2009 • Types of Neurons (based on Processes) a. Multipolar Neuron – 1 axon & several dendrites b. Bipolar Neuron – 1 axon & 1 dendrite; least numerous c. Unipolar Neuron – 1 process that separate into an axon & a dendrite Teased Nerve: Myelin Sheath – appears as a tube surrounding the axis cylinder (cytoplasm of the axon); produced by Schwann cells Nodes of Ranvier – regions in the myelin sheath that appears interrupted Neurologia • supporting cells of the neurons • possess several branching processes Cross Section of Nerve: Fascicle → single discrete bundle of nerve fibers & connective tissue Epineurium → connective tissue that binds several fascicles in nerve trunks Perineurium → dense connective tissue covering each fascicle Endoneurium → covers individual nerve fibers cmcremen 8
