Uccn1003 -may10_-_lab_04_-_intro_to_layer-1_network_devices-updated_30_june2010-2
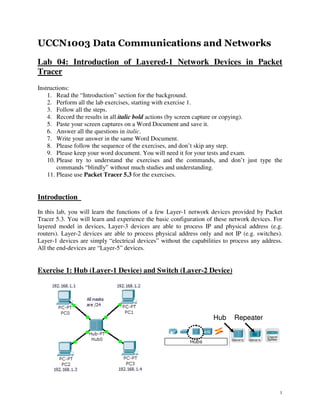
- 1. UCCN1003 Data Communications and Networks Lab 04: Introduction of Layered-1 Network Devices in Packet Tracer Instructions: 1. Read the “Introduction” section for the background. 2. Perform all the lab exercises, starting with exercise 1. 3. Follow all the steps. 4. Record the results in all italic bold actions (by screen capture or copying). 5. Paste your screen captures on a Word Document and save it. 6. Answer all the questions in italic. 7. Write your answer in the same Word Document. 8. Please follow the sequence of the exercises, and don’t skip any step. 9. Please keep your word document. You will need it for your tests and exam. 10. Please try to understand the exercises and the commands, and don’t just type the commands “blindly” without much studies and understanding. 11. Please use Packet Tracer 5.3 for the exercises. Introduction In this lab, you will learn the functions of a few Layer-1 network devices provided by Packet Tracer 5.3. You will learn and experience the basic configuration of these network devices. For layered model in devices, Layer-3 devices are able to process IP and physical address (e.g. routers). Layer-2 devices are able to process physical address only and not IP (e.g. switches). Layer-1 devices are simply “electrical devices” without the capabilities to process any address. All the end-devices are “Layer-5” devices. Exercise 1: Hub (Layer-1 Device) and Switch (Layer-2 Device) Hub Repeater 1
- 2. 1. Construct the above networks with 1 hub and 4 PCs. Put in the IP addresses and subnet masks in the PCs as indicated in the above figure. Step #4 Step #3 Step #2 Step #1 2. Click on “Simulation mode” (Step #1). Then “Edit Filters” button (Step #2). Click to uncheck “Show All/None” (Step #3), this step makes all the ‘√’ disappear. Click to check ICMP (Step #4). Click anywhere else to hide the “Edit ACL Filters” dialog box. All these steps are to create a “simulation mode” to observe ping operation (ICMP). 2
- 3. Step #4 Step #5 Step #3 Step #2 Step #1 3. Click on the “sealed envelope with a +” button (Step #1). The mouse button will change from an arrow to an envelope. Click on PC2 (192.168.1.3) (Step #2), and then click on PC1 (192.168.1.2) (Step #3). This step means PC2 is trying to ping PC1. 4. The line shown in “Step #4” appears. Click on “Capture/Forward” button (Step #5) and observe the envelope as it travels. You need to click the “Capture/Forward” button a few times and continue to observe the envelope. Step #1 Step #2 Step #3 5. The simulation finishes as you see the “envelope with a √” in PC2. Repeat the simulation by clicking the “Reset Simulation” buttion (Step #1). Click on “Auto Capture / Play” button (Step #2). After Step #2, the envelope will automatically travels by itself. If 3
- 4. you feel that the simulation runs a little slow, you may adjust the sliding bar to the right as indicated in (Step #3). 6. You should observe that the hub is a “broadcasting” device. Since it is a layer 1 device, it does not have the capabilities to process MAC address and IP address. 7. Next few steps will involve changing the hub to a 2950-24 switch. 4
- 5. Step #2 Step #3 Step #1 8. Click on “Realtime mode” button (Step #1). In “Simulation mode”, time is frozen. Click on the “X” button (Step #2) to erase the hub and change it to a switch as shown in (Step #3). Remember to re-wire the PCs to the switch. Wait until all the “bubbles” turn green. 9. Click on “Simulation mode” again. Click on “Auto Capture / Play” and observe the envelope. After the simulation finishes, you may click on the “ping envelope” and then click on PC3 and PC0 to simulate PC3 is trying to ping PC0. Repeat the procedure of “Auto Capture / Play” to observe the envelope. Step #2 Step #1 5
- 6. 10. If you want to erase a particular “pair” of ping. Click on the line of (Step #1) and then click on “Delete button” (Step #2). 11. After the simulation, ALWAYS remember to put the Packet Tracer back to Realtime mode. 12. Note: Switch only does broadcast at the first run. After that, the switch will not operate in the “broadcast” mode, because the switch has remembered all the MAC addresses that attached to its interfaces. The switch from this moment on, will only send the data from source PC to destination PC directly. Whereas hub will always “broadcast”. Exercise 2: Repeater (Layer-1 Device) 1. Start a new file and construct the above network. Ping PC1 from PC0 to ensure connectivity among the two PCs. Step #1 Step #2 2. Click on the “Physical mode” button at the top left corner of Packet Trace window (Step #1). Then, click on “Working Closet” at the top right corner (Step #2). 6
- 7. Step #2 Step #1 Step #3 Step #4 3. In the Work Closet, adjust the scroll bar until you see the two PCs (Step #1). Then, click on “Move Object” (Step #2), the mouse would change to a “cross”. Click on PC0 (Step #3), and then click on “Home City” and “Move to Home City”, as shown in Step #4. Repeat the same process for PC1. Step #1 Step #2 Step #3 4. Click on “Back” (twice) till you (Step #1) see “Home City” (Step #2). Notice that there are the two “moved” PCs hiding at the corner (Step #3). 5. Move the PCs and “Corporate office” as shown in the above figure, and then click on “Grid”. The following dialog box will appear. 7
- 8. 6. Check the three √ boxes and click on “select grid color” (choose bright green) and then click “OK”. Step #1 7. The green lines grid should appear with numbers (unit in meter). Click on “Logical mode” button as indicated in (Step #1). Green bubble 8. Make sure that the two “bubbles” are still green in Logical mode. Ping PC1 from PC0, it should be working. Now, switch back to “Physical mode”. 9. Now, in “Physical mode”, drag PC1 to the far right corner of the grid (1800, unit meters), as indicated in the above figure. Make sure that PC0 is between grid 0 to 200, and the Corporate Office is between grid 400 to 600. Switch back to “Logical mode” again. 8
- 9. 10. In “Logical mode”, try to ping PC1 from PC0. Does it work now? Have you noticed that the “bubbles” are in red color? 11. Note: In the real world, the length of Ethernet communication has a limit. When the Ethernet communication between two PCs exceeds certain length, the electrical signal will be attenuated to a “weak” state that both PCs will lost communication due to “physical and hardware” issues not software issue. Green Red bubble bubble 12. Connect a Repeater between PC0 and PC1 as indicated in the above diagram. After you have connected the Repeater, the left side bubbles are green but the right side bubbles are still red. 13. Switch back to “Physical mode”. Move the “Corporate Office” between grid 1000 to 1200. The repeater is contained inside the “Corporate Office”. It may click on the “Working Closet” to view at the physical repeater. Switch back to “Logical mode” again. 14. Now, all bubbles should be green. Try to ping PC1 from PC0, both PCs should communicate. 15. Note: Repeater is a layer-1 device that extends the length of the communication by re- shaping and re-amplifying the weakened electrical signal to a stronger signal so that the signal could travel further. Exercise 3: Wireless Access Point (Layer-1 device) 9
- 10. 1. Start a new file, and construct the network based on the above figure. a) Set the IP addresses and gateway IP according to the figure. b) Set the dynamic routes using RIP. (Refer to Lab 3 and lecture notes.) c) Set the DHCP service in Router0. (Refer to Lab 2). d) Set the DHCP service in DHCP server. e) Obtain dynamic IP in PC0 and start to ping every IP interface to check the connectivity of the network. 2. Use the access point model indicated in the above figure. Set the SSID and WEP Key (10 characters) of the access points by referring to the following figure for Access Point 1. Repeat the same process for Access Point 0 (SSID: Peter; WEP Key: 7777777777) and Access Point 2 (SSID: Mark; WEP Key: 9999999999). 3. Take two laptops from the End Devices. Change the laptop module to Linksys- WPC300N by referring to the following figure (for both laptops). 10
- 11. Use this module On/Off switch Put here 4. For Laptop0, go to “Desktop” tab, and then click on PC Wireless icon (as indicated in the above right figure). 5. The above screen should appear. Click on “Connect” tab and then “Refresh” button. The SSID of three access point should appear. 11
- 12. 6. Click on John (which means you choose to access AccessPoint1), and then click on “Connect” button. 7. Key in the WEP Key (3333333333, ten ‘3’), and click “Connect”. 8. Laptop0 should have the “wavy lines” to the Access Point1, indicating that Laptop0 is connected to Access Point1. 9. Open the “Command Prompt”, and type “ipconfig”. You should have the dynamic IP assigned by Router0. 10. Use Laptop0 to ping PC0 and DHCP Server. If the pings are not successful, please troubleshoot the network. 11. Using the same process, try to connect Laptop1 to Access Point0 (SSID: Peter; WEP Key: 7777777777). Since Access Point0 has not been set with any DHCP service, you should provide a proper static IP for Laptop1. Use Laptop1 to ping Laptop0, DHCP Server, and PC0. 12. Again, use Laptop1 to connect Access Point 2 (SSID: Mark; WEP Key: 9999999999). The DHCP server should provide you with an IP. Use Laptop1 to ping Laptop0, and PC0. Exercise 4: Modems (Cable, DSL, Dial-Up) (Layer-1 Devices) 12
- 13. 1. Construct the following network (as shown in the figure) based on the following specifications. a) One 2811 router, two Cloud-PT-Empty, five PCs, one server, two TVs, one cable- modem, one DSL-modem, and one coaxial splitter. b) PC1, PC2, PC3, and PC4 are set to obtain dynamic IP c) Public PC and Public Web Server are set in static IP. d) All subnet masks in the network are /24. e) Beware of the type of cables used in this network. f) Follow the subsequent steps to make this network functions as intended. 2. Use model 2811 for Router0. Add one NM-2FE2W module for the AIM slots and 4 WIC-1AM into the WIC slots, as shown the following figure. 3. Drag out two Cloud-PT-Empty, as shown in the following icon. . 13
- 14. 4. Change the name of one of the Could-PT-Empty to “Cable TV Company”. Insert five “PT-CLOUD-NM-1CX” modules (coaxial port) and two “PT-CLOUD-NM-1CFE” modules (FastEthernet port) into slots. Insert the modules EXACTLY as shown in the following figure. Five “PT-CLOUD-NM-1CX” on the top row, and two “PT-CLOUD- NM-1CFE” at the bottom left. This “Cloud device” is to simulate cable TV networks. Cable TV Company 5. Change the name of the remaining Could-PT-Empty to “Phone Company”. Insert five “PT-CLOUD-NM-1AM” modules (RJ-11 phone port) and two “PT-CLOUD-NM-1CFE” modules (FastEthernet port) into slots. Insert the modules EXACTLY as shown in the following figure. Five “PT-CLOUD-NM-1AM” on the top row, and two “PT-CLOUD- NM-1CFE” at the bottom left. This “Cloud device” is to simulate telephone networks. Phone Company 6. Construct the following subnet with the given IP addresses. Connect the switch to fa0/0 of the ISP router. Use Public PC to ping the server and the gateway to ensure connectivity. 14
- 15. 7. Build the following subnet with the devices indicated in the following figure. Connect the hardware ports according to the figure too (especially the Cable Company Cloud). For the coaxial splitter, connect Port 0 to the “Cable TV Company”, and connect two remaining ports to TV1 and PC1 (no preference). Set gateway IP for Fa1/0 of the ISP router. Coax1 Fa8 Fa1/0 Coax0 8. Double click on “Cable TV Company”, click on “TV Settings” tab. Load in a few JPG files as indicated. This is to simulate the Cable TV programs. 9. Turn on both TV0 and TV1, you should see pictures “changing” (depending on how many JPG files that you have put in). This is to show that the TVs are working. 15
- 16. 10. Next, we will set up the “data connectivity” for the cable modem to the ISP router. First, click on the “FastEthernet8” tab, then click to “Cable” (as shown in the left figure). Next, click on the “Cable” tab. Select “Coaxial1” < - > “FastEthernet8”, and then click on the “Add” button. Now, “Cable TV Company” should have an internal link between Coaxial1 and FastEthernet8. 11. Type in the following commands in ISP router. This is to provide DHCP service for the Cable TV network. Make sure that you have set the gateway IP on Fa1/0. Router(config)#ip dhcp pool CABLE Router(dhcp-config)#network 195.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 Router(dhcp-config)#default 195.1.1.254 Router(dhcp-config)#exit 12. Go to PC1 and obtain the dynamic IP from the ISP router. If it does not work, please troubleshoot the subnet. If the dynamic IP is successfully obtained, try to ping “Public PC” and “Public Web Server”. 13. Please note that the cable modem is a layer-1 device that helps to deliver data across the Cable TV networks (coaxial cables). The Cable TV networks is originally designed to deliver cable TV signals, not Internet data. 14. Now, we will build and connect the subnet of the “Phone Company”. Based on the following figure, connect the ports of the “Phone Company” with proper cables to the correct ports of ISP router, PCs, and DSL modem, as indicated in the figure. (e.g. Modem0 of Phone Company is connected to Modem0/0/0 of ISP router with Phone cable.) 16
- 17. Modem3 Modem4 Modem2 Modem0/1/0 Modem0/0/0 Modem0 Modem0/0/0 Modem0/1/0 Modem1 Fa1/1 Fa8 15. For PC3 and PC4, please change the module to “PT-HOST-NM-1AM” (dial-up modem with RJ-11 plug). 16. Please use the “Config” tab of ISP Router to put in the gateway IP. Modem0/0/0 = 200.1.1.254; Modem0/1/0 = 200.2.2.254; Fa1/1 = 198.8.8.254. Remember to turn on all the interfaces of ISP Router. 17
- 18. 17. Please put in the four phone numbers in the “Phone Company” cloud. Click on the “Modem0” tab and key in the phone number (4628880) as indicated. Repeat the same process for Modem1 (4628881), Modem2 (4620001), and Modem3 (4620002). Modem4 do not require phone number in this network simulation. 18. Click on “FastEthernet8” tab of “Phone Company”. Make sure that it is on “DSL”. 19. Click on “DSL” tab of “Phone Company”, repeat what we have done for “Cable TV Company”. Add an internal link between Modem4 and FastEthernet8. 18
- 19. 20. Type in the following commands in ISP router. This is to provide DHCP service for the telephone network (especially for the DSL modem). Make sure that you have set the gateway IP on Fa1/1. Router(config)#ip dhcp pool DSL Router(dhcp-config)#network 198.8.8.0 255.255.255.0 Router(dhcp-config)#default 198.8.8.254 Router(dhcp-config)#exit 21. Go to PC2 and obtain the dynamic IP from the ISP router. If it does not work, please troubleshoot the subnet. If the dynamic IP is successfully obtained, try to ping “Public PC” and “Public Web Server”. Try to ping PC1 of the “Cable TV Company” subnet too. 22. Please note that the DSL modem is a layer-1 device that helps to deliver data across the telephone networks (phone cables). Again, telephone networks is originally designed to give telephone service, not Internet data. 23. Now, we configure the Dial-up modem communication. First, go the ISP Router and key in the following commands. Router(config)#username john_tan password tan123 Router(config)#username mike_chan password chan123 Router(config)#ip dhcp pool DIAL_UP1 Router(dhcp-config)#network 200.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 Router(dhcp-config)#default 200.1.1.254 Router(dhcp-config)#exit Router(config)#ip dhcp pool DIAL_UP2 Router(dhcp-config)#network 200.2.2.0 255.255.255.0 Router(dhcp-config)#default 200.2.2.254 Router(dhcp-config)#end Router#copy run start 24. Go to PC3, click on “Desktop” tab and then “Dial-up”. 19
- 20. 25. Key in john_tan, tan123, and 4628880 according to the following diagram, and then press dial. If the connection is successful, the right figure will show up. 26. Make sure that PC has obtained its dynamic IP. Use PC3 to ping other PCs and server. 27. In PC4, use “mike_chan”, “chan123”, and 4628881 in the Dial-Up. If the communication is successful, remember to obtain the dynamic IP for PC4. Use PC4 to ping other PCs too. 28. Dial-Up modem is a 1990s technology that has fallen in popularity due to its speed. Same as other modems, Dial-up modem is a layer-1 device that delivers data across telephone network. Currently, Dial-up modem technology is being replaced by DSL modem technology. 20
