Smart metering infrastructure Architecture and analytics
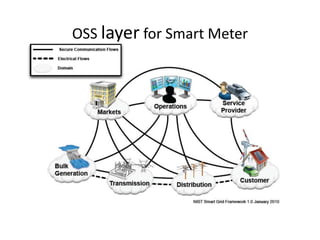
- 1. OSS layer for Smart Meter
- 2. Smart metering OSS layer
- 3. Electric Utility Communications Architecture Customer PremisesGeneration Transmission Distribution Smart Meter Field Devices Power Plant Communications Networks Control/Operations Centers Regional Interconnection Wide Area Network Backhaul/WAN Neighborhood Area Network Distribution Access Point Grid Energy Resources Field Area Network Field Devices Field Devices Field Devices Consumer Electric Products Energy Management System Public Networks 3rd Party Services Workforce Mobile Network Home Area Network
- 4. AMI top priority in Smart Grid
- 6. AMI topology
- 7. Metering Infrastructure Blue Print Legend • DSO Distribution System Operator • NAN Neighbourhood Area Network • Wireless
- 9. 3G Vs LTE support for Metering Apps
- 10. Smart meter Communication • Smart Meter: as traffic generator assigned with a global IPv6 address ,receives demand response data from the collector. • Router: takes the responsibility of relaying packets from both smart meters and collectors. determines the next hop for the packet to reach the final destination. • Collector: serves interconnection between a NAN and a WAN in the SG and aggregates all meter reading information. collector node collects all meter reading data and sends acknowledgement back to corresponding meters.
- 11. Wireless Communication for Smart Grid • Wireless Communication Technologies: – IEEE 802.15.4 – Z-wave – IEEE 802.11 – IEEE 802.16 – LTE/LTE-A – IEEE 802.22 – Cellular 3G/4G – MBWA
- 12. Communication for NAN,HAN • NANs are supposed to cover large geographical areas where the user and/or field devices are distributed. To cover large geographical devices for communication purposes generally traditional infrastructure based networks such as Wi MAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) or 3G/4G based standards such HSPA (High Speed Packet Access) or LTE (Long Term Evolution) based networks are preferred. • Smart meter Act as router for Home Area Network HAN supporting bi-directional Demand mgmt.
- 13. IEEE 802.15.4- Zigbee • ZigBee is a short-range, low-data rate, energy- efficient wireless protocol , support star, tree mesh topology and suitable for WSN.
- 14. ZigBee Advantage & Challenges -1 • ZigBee utilizes – 16 channels in the 2.4GHz ISM band worldwide – 13 channels in the 915MHz band in North America – one channel in the 868MHz band in Europe – It supports data rates of 250 kbps, 100kbps, 40 kbps, and 20 kbps • ZigBee Smart Energy Profile (SEP) aims to support the needs of smart metering and AMI, and provide communication among utilities and household devices
- 15. ZigBee Advantage & Challenges -2 Advantage: • Control of home appliances: ZigBee end devices connected with relay can control power supply switch of home appliances. ZigBee Coordinator manage configuration, exchange info. Between appliance and local HAN control. • Direct Load Control Local HAN auto control locally or remotely using AMI infrastructure. • Challenges: limited battery energy Supply, memory and processing power
- 16. Z-wave • Z-Wave is a proprietary, short-range, low-data rate wireless RF mesh networking standard • Z-wave uses the 908MHz ISM band in the Americas, and its data rate is 40kbps • Z-wave provides connectivity for devices such as; lamps, switches, thermostats, garage doors. • Z-wave can be employed in the HAN segment of the smart grid
- 17. IEEE 802.11 - WiFi • Data rate of IEEE 802.11 standards range from 1 Mbps to 100 Mbps – It operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band • Wi-Fi is targeting Home Area Networks (HAN), Neighborhood Area Networks (NAN) and Field Area Networks (FAN) in the smart grid • Wi-Fi is already being used for municipal-scale network infrastructures outdoors
- 18. IEEE 802.16 - WiMAX • WIMAX uses the licensed bands of 10-66 GHz – The IEEE 802.16 standard also allows the use of license-exempt sub 11GHz bands • WIMAX can provide theoretical data rates up to 70Mbps communication range 50km for fixed stations and 5km for mobile stations • WIMAX can provide long range communications for the smart grid for automated reading WMAR wireless automatic meter Reading. • Real Time pricing: based on real time Energy Consumption. • Outage detection and Restoration: 2 way communication in Wi-MAX fast outage detection can be implemented. • Challenges: WiMax tower is Expensive.High frequency cannot penetrate obstacles while low frequecy licensed.
- 19. LTE and LTE-A • The peak data rates for LTE is around 300Mbps at the downlink and 80Mbps at the uplink with 20MHz channel bandwidth and 4x4 MIMO antennas – LTE-A’s targeted peak downlink transmission rate is 1Gbps and the uplink transmission rate is 500Mbps • A typical LTE cell has a diameter of 4km – By relaying technique, range can be extended
- 20. IEEE 802.22 –Cognitive Radio • Cognitive Radio (CR) provides access to unlicensed users to the spectrum that is not utilized by licensed users – A CR has the ability to sense unused spectrum, use it and then vacate as soon as a licensed user arrives • The bands that are planned to be used by 802.22 are the UHF/VHF bands between 54 and 862 MHz and their guard bands
- 21. Power Line Communications • Power Line Communications (PLC) use the low voltage power lines as the communication medium • PLC has been already used by some utilities for load control and remote metering – It can be integrated to the smart metering system since the power lines already reach the meter • As the PLC does not have external cabling cost, it is considered to be convenient for HANs, NANs and FANs in the smart grid
- 22. IEEE P1901/Broadband over Power Lines • BPL has high data rates exceeding 100 Mbps using frequencies below 100 MHz • P1901 workgroup has selected two physical layers for the standard – Wavelet OFDM-based PHY – FFT OFDM-based PHY. • These PHY techniques aim to improve the communication over the noisy power lines
- 23. ITU-T G.hn • G.hn standard is developed for communication in residential premises, offices, hotels, etc. • G.hn is able to operate over all types of in-home wiring including phone line, power line, coaxial cable, and Cat-5 cable – It uses a windowed OFDM-based PHY with a programmable set of parameters • G.hn can support bit rates up to 1Gbps • G.hn devices aim to be interoperable with power line devices that use the IEEE P1901 standard
- 24. ANSI/CEA-709 • ANSI/CEA-709 series of standards have been developed for home control and automation • ANSI/EIA 709.1 is also known as Lonworks – Lonworks platform is a proprietary technology – Lonworks operates in the 115-132MHz band – Data rates of Lonworks can reach up to a few kbps • NIST has included Lonworks as a candidate standard along with IEEE P1901 and ITU G.hn
- 25. 3G/4G Cellular • Range 824-894/1900 MHz. • Licensed frequency band hence Costly. • Mobile can receive data over serial/Ethernet interface and transmit over second interface. • Advantage: 1. SCADA interface for remote distribution. CDMA for power system SCADA provides cellular communication between RTU and SCADA Server.
- 26. 3G/4G cellular continued 2. Monitoring and metering of remote DERs. Non critical information exchange using SMS monitoring application using GPRS. Challenges: Call establishment indefinite time delay.Call dropout affect large data Exchange. High monthly fees hence Expensive.
- 27. Mobile Broadband Wireless Access (MBWA) or MobileFi • High bandwidth, high mobility and low latency in the licensed frequency bands below 3.5 GHz, by utilizing the positive features of both IEEE 802.11 WLANs and IEEE 802.16 WMANs. • Used for wireless backhaul for electric grid monitoring and broadband communication for plug-in electric vehicles .
- 28. Fiber Optic Communications • Fiber optics is already used in the power grid to connect utility head offices and substations • Fiber optics is not impacted by electromagnetic interference • It is ideal for the high voltage operating environment • Its major drawback of fiber is high deployment cost • Optic Ethernet can be also utilized in the smart grid • It is also possible to employ a combination of the wireless and wired communication technologies in the smart grid
- 29. Comparison of Communication Standards
- 30. Communication Enabled Smart Grid Applications • Direct Load Control (DLC) • Wireless sensor network (WSN)-based demand management • iPower • Sensor web services for energy management • Machine-to-machine (M2M) communications based demand management • Energy saving applications on appliances • Electric vehicle demand management
- 31. Direct Load Control (DLC) • DLC means passing the control of several appliances to the utility or an aggregator – Appliances that can be remotely controlled are pool pumps and the heating/cooling appliances – A pilot study in Australia has shown that cycling air conditioners have resulted in 17% of peak load reduction • DLC requires simple communications between the consumers and the utility – Utility commands can be delivered to the customers through smart meters • Zigbee or one of the PLC standards can be a suitable option for DLC
- 32. Wireless Sensor Network (WSN)- based Demand Management • in-Home Energy Management (iHEM) is a non- intrusive, interactive demand management scheme • Energy Management Unit and appliances communicate wirelessly over the WSN • iHEM aims to shift consumer demands to off-peak hours • Unlike, DLC, iHEM suggests convenient start times for the appliances
- 33. Intelligent and Personalized energy conservation system by wireless sensor networks (iPower) • iPower: – Implements an energy conservation application for multi- dwelling homes and offices – Employs a WSN, a control server, power-line control devices and user identification devices – Sensor nodes are deployed in each room and they monitor the rooms with light, sound and temperature sensors – They form a multi-hop WSN and send their measurements to the gateway when an event occurs • iPower combines wireless and power line communication technologies
- 34. Sensor web services for energy management Energy management application is a suit of three energy management modules: The first module enables users to learn the energy consumption of their appliances while they are away from home The second module is a load shedding application for the utilities • Load shedding is applied to the air conditioning appliances when the load on the grid is critical The third module offers an application for energy generating customers • Customers can monitor and control the amount of energy stored and energy sold back to the grid while they are away from home These applications utilize sensor web services
- 35. Machine-to-machine (M2M) communications based demand management • M2M communications have been implemented in the Whirlpool Smart Device Network (WSDN) • WSDN consists of HAN, the Internet and AMI • WSDN utilizes several technologies together – Wi-Fi connects the smart appliances and forms the HAN – ZigBee and PLC connect the smart meters in the AMI – Broadband Internet connects consumers to the Internet • It enables remote access to appliance energy consumption • It also provides load shedding capabilities to utilities during critical peaks
- 36. Energy saving applications on appliances • An appliance-to-appliance communication protocol for energy saving applications • Energy management protocol allows consumers to set a maximum consumption value • Based on this threshold, the residential gateway is able to turn off the appliances that are in standby mode once these limits are exceeded
- 37. Electric vehicle demand management Home Gateway and Controller (HGC) communicates with the PHEV Controls its charging and discharging profile based on • Status of the roof-top solar power generation unit • Demands of the smart appliances HGC also communicates with the other HGC devices in the neighborhood and coordinates PHEV loads
- 38. Challenges in Smart Grid Communications • Wireless channels are • Prone to interference due to the populated ISM bands • Have lower bandwidth than wired communication technologies • Do not penetrate well through concrete construction • Their range is limited • The impact of harsh smart grid environment on wireless communications is not explored well • Powerline communications suffer from • Noisy channel conditions • Channel characteristics that vary depending on the devices plugged in • Electromagnetic interference (EMI) due to unshielded power lines • Poor isolation among units
- 39. Security in Smart Grid Communications • The potential security risks identified by NIST: – Increased complexity causing device misconfiguration based errors – Increased number of interconnections increase the risks of denial of service attacks, injection of malicious software and compromised hardware – Increased number of network nodes increase the number of entry points and paths that might be exploited by adversaries – Increased amount of data increase the risk of compromising data and violating user privacy
- 40. Privacy in Smart Grid Communications • Consumer privacy may be violated if high resolution electricity consumption data is made available to malicious users – By looking at the consumption, it is possible to obtain information on absence or presence, the number of individuals in the property, sleep cycles, meal times, etc. – A PHEV’s location can be tracked from its charging location • Sophisticated attacks may benefit from data leakage from consumer premises
- 41. NAN Challenges and solution • Problem: radio coverage to 100% of service area. NAN devices are fixed wireless Terminals interacting with smart meter inside house (may have low SNR). • Solution : Radio Mesh network based NAN using 6loWPAN(IPv6 Low power personal Area network). IEEE 802.15.4 with neighborhood discovery functions.
- 42. Technologies For NAN • Power Line Carrier PLC architecture: Cheap but slow. meter reading data transmitted over electric line but not optimum other factor as well transformer electromagnetic interference. • GSM Global satellite for Mobile: Expensive but good coverage, telecom systems are built to scale. • SMS for exchange messages between grid. • 3G/4G, LTE Wimax: better choice due to high level of reliance and accessibility. • Weakness in Infrastructure network plugged by Short range radio based 6LoWPAN (mesh network) with low cost and Energy requirements.
- 43. Smart meter requirement • QoS : requirement relaxed. • Latency: low latency • Reliability: All data packets must be delivered to controller. • Last mile connectivity between residence and control utility IP technology outweighs Zigbee and Wireless HART as IP is attached to NAN. • 6lowWPAN based on IPv6 not limited in IP address space also secure options in header.
- 46. Analytics For AMI mathematical prediction algorithms it is possible to predict how many standby generators need to be used, to reach a certain failure rate Random fuse networks or Percolation theory fuse or diode: smoothen high low current density Neural networks: Grid management Markov processes: offline wind demand supply, pricing, mathematical model Maximum entropy : network congestion, game theory.
- 47. Key drivers For Utility Services Architecture Safety Reliability Security Stability Robustness (environment) Cost, automated efficiency Vs privacy. Vendor capability on stack (lockin Vs flexibility) Ubiquity
- 49. Gateway interaction with WAN TLS connections provide authentication , encryption and integrity to data transmitted. Stored data at gateway is encrypted and access control restrict access to data and functionality.
- 50. Data Analytics requirement in Smart Meter • Data modeling Understand energy consumption patterns – Build user behavioral models from data – Is current data enough to get new knowledge? – Which sources to fuse? • Data collection Understand architectural needs – Fusion, where and how? – Scalability and hierarchy – Which users of new knowledge?
- 51. Analysis Real Time data from Smart meter Architectural Consideration
- 52. Hadoop Ecosystem
- 54. Model needs on Consumer Behavior • Demand-Response decision support – How far can behavioral adaptation go? – How far can decision support go? • Active controller for peak shifting – Spot price vs. load in home – Appliances and smart plugs – Simple user control for decision support, schedule and policy-based actuation – Prioritized load groups in home • Scale up a demonstration model home – Simulation-based study for large-scale effect
- 55. Model needs on Consumer Behavior • Capitalize on model of behavioral profiles – Give advise to move between profiles – Compare trends with current profile • Improved model – Fuse with additional data sources – Improved real-time and alarms • Innovative user interface – Leverage the involvement, multi-modal? • Added services – Sub-meter installations for refined profiling – Better CR for Utility companies
- 56. Scenario BPM for Smart meter 56 CreatedMeterReading (Send) CreatedMeterReading (Receive)
- 57. Advanced Metering Infrastructure AMI Components Collector Collectors • Various Vendors • Neuhaus is just an example of a Multi Utility Controller (MUC) Support Head-end side • GPRS • Ethernet (Web Interface) • WLAN • WiMAX Support Meter side • Wired Serial (RS-485) • Wired M-Bus • ZigBee • Wireless M-Bus
- 58. Smart Meter Electricity Meters • Various Vendors • Kamstrup is just an example Interfaces • Optical • Wired Interfaces • GPRS • ZigBee • Wireless M-Bus Functionality • Meter reading • Pre-payment • Tariffs • Disconnect
- 59. M-Bus Protocol
- 60. Compare Protocol used by Application on top of AMI. Protocol CoAP XMPP RESTful HTTP MQTT Transport UDP TCP TCP TCP Messaging Request/Respo nse Publish/Subscri be Request/Respo nse Request/Respo nse Publish/Subscri be Request/Respo nse 2G, 3G, 4G Suitability (1000s nodes) Excellent Excellent Excellent Excellent LLN Suitability (1000s nodes) Excellent Fair Fair Fair Compute Resources 10Ks RAM/Flash 10Ks RAM/Flash 10Ks RAM/Flash 10Ks RAM/Flash Success Storied Utility Field Area Networks Remote management of consumer white goods Smart Energy Profile 2 (premise energy management/h ome services) Extending enterprise messaging into IoT applications
- 62. Cisco Field Area Network (FAN)
- 64. Smart Meter BI • Decision-making action framework • Analysis of multiple device events to detect – Tampering – Outages • Can be combined with multi-device detection for transformer and substation outage detection – Other abnormal situatiosn • BI Analysis to detect patterns in comsumption related to misconfiguration, tampering or technical malfunction – Using Business Intelligence for Utilities
- 65. Converged Infrastructure Issues Water Electricity Gas Other Utilities Water Converged Services Platform on Smart Meter IP Network Collectors , Aggregators and Collection Component (SCADA system) Network Providers/Telecom Operators (GSM,3G,LTE,WiMax)
- 66. AMI defense in Depth 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Layered Defense Framework (Defense in Depth) Corporate Perimeter - Defines the separation between the public and corporate domains. Remote Access – Methods and controls used to manage access to assets located within the corporate perimeter from locations external to that perimeter. Corporate Network – Equipment and topology used to provide the general employee population access to corporate computer resources. Host Device Security – Operating Systems, access accounts, network services, community strings and removable media capabilities. Applications – All non-operating system software. Communications – Technology and protocols used to communicate outside of a security perimeter. AMI – Contains Head-End system, Meter Data Management Systems Electronic Security Perimeter – Device(s) used to control data flow between two security zones. Definitions: Source: http://smart-grid.tmcnet.com
- 67. Security Standards • NIST guidelines for Control systems. http://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublicat ions/NIST.SP.800-82r1.pdf • ANSI C12.20 standards for smart meter http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_C12.20 • IEC 61107 is a communication protocol for smart meters • Open Metering System
- 68. Recommended ICS DID Architecture
- 69. Smart Meter Internal • Data at rest : Microcontrollers, memory, Radios • Data In Motion: MCU to Radio, MCU to MCU, MCU to memory, Board to Board, IR to MCU
Hinweis der Redaktion
- AMI is polled most important application of smart grid by municipalities in US.
- Source: GridPriv: A Smart Metering Architecture Offering k-Anonymity – by Mark Stegelmann∗ and DoganKesdogan∗,HAN Home Area network: enables the Gateway to communicate with user interfaces and with controllable local systems CLS.WAN Wide Area Network: communicating with service provider.NAN :LMW Local meteorological Network : used by customer meter to report reading.Gateway: Firewall + intermediate storage and processing unit. Gateway interacts with various service providers. (GSM, CDMA, Wimax, LTE ) operators. (TSP) Telecom service providers.Smart meter: cryptographic component (storing key) is compulsory variations are allowed in other components†∗Centre for Quantifiable Quality of Service in Communication SystemsNorwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, NorwayEmail: mark.stegelmann@q2s.ntnu.no†Research Group for IT Security, FB5, University of Siegen, 57068 Siegen, GermanyEmail: kesdogan@uni-siegen.de
- unique blend of radio access (macro cells, small cells and Wi-Fi), advanced IP backhaul/transport, - See more at: http://www2.alcatel-lucent.com/techzine/lte-the-best-thing-to-happen-to-wireless-networks/#sthash.1EKF1Fjh.dpufRefine Topicslowers the total cost of ownership of the network reduces power consumption and footprint, delivering a greener sustainable solution offers an order of magnitude increase in capacity and flexibility to manage growthintegrates seamlessly with the existing network paving the way for faster migration to 4G and enriched user experiences See more at: http://www2.alcatel-lucent.com/techzine/lte-the-best-thing-to-happen-to-wireless-networks/#sthash.1EKF1Fjh.dpufUnlike 3G, LTE is all IP. In fact, it’s based on IPv6 which supports massive numbers of additional IP addresses and provides other improvements over IPv4. And it opens up access to new market segments like machine-to-machine. With IP across the radio access network (RAN), backhaul network, packet core network and backbone, operators benefit from a simpler, more scalable and cost-effective architecture. - See more at: http://www2.alcatel-lucent.com/techzine/lte-the-best-thing-to-happen-to-wireless-networks/#sthash.1EKF1Fjh.dpuf-LTE provides a converging path for all wireless technologies. According to the GSA, LTE is the natural migration choice for GSM, HSPA, CDMA and WiMAX operators - See more at: http://www2.alcatel-lucent.com/techzine/lte-the-best-thing-to-happen-to-wireless-networks/#sthash.1EKF1Fjh.dpuf
- HART (Highway Addressable Remote Transducer Protocol)
- voice, data, video
- Availability required for Utility infrastructure but may not be important for Smart Meter.
- he process map for telecommunication But only limited to the description of processes, not set to implement. [7, 8, 9] Figure # 4 Structure of SID Source: Scheible, L. 2005 TAM Map Telecommunication Application (TAM) defines a clear set objective and applications with which operators must provide the service. Allows a clear integration between information, processes and systems involved. It provides a benchmark for the industry, enables software vendors to define where your application will be framed in relation to the horizontal processes defined in eTOM. A service providers allows them to organize and catalog their current applications. TAM acts as a bridge between eTOM and SID, by providing operational systems that group functions and processes information flowing through them, within recognized Systems Operation Support (OSS) and Systems Support business (BSS).As shown in Figure # 5 is consistent with structure ETOM and SID. It is also divided into domains, representing the applications that must operate in each. These domains are:. Market / Sales, Product, Customer Management, Service Management, Resource Management, Management of Suppliers / Partners, Business Management As eTOM and SID which must be defined only applications, but no details as have to be developed. [6, 9, 10] Figure # 5 Structure of Telecom Applications Map Source: Scheible, L. 2005 TNA Technology Neutral Architecture (TNA) is a guide to the definition of a general infrastructure for applications, data and processes which must work together in systems operator. Some of the TNA requirements: Must have reusable software entities that provide their services through well-defined interfaces open, known as contracts . All external dependencies must be explicitly defined has to be . characterized by a gap in the services provided by constituent components of software that automates business processes have to endure a common communication mechanism, such as,. Java Message ServiceITIL Many of the services offered by companies Telecommunications are supported by the Information Technology. This increasing dependence has resulted in a growing need for quality IT services that match business objectives and to meet the requirements and customer expectations. To achieve this requires on the one hand, that the processes are defined by eTOM and secondly, that the services of information technology are managed. To do a standard widely used is called Infrastructure Library Information Technology (ITIL) can be mapped to eTOM. Datang Software Technologies Co., Ltd TAM used which provides an abstraction of the structure of a delivery system service, which includes service design, resource allocation, configuration and service activation, further illustrates the function in detail. Specifically used parts: Application service management and application integration infrastructure. Also taken by reference to TNA to determine the technical architecture of the system. groups China Telecom who have used the system have reduced the time of provision of end to-end service, have improved the degree of automation of this process and have decreased the time required for the introduction of a new service and thus have greatly increased satisfaction and customer loyalty.
- GSM, 3G, LTE Smart meter Log analysis
- Hadoop Common: The common utilities that support the other Hadoop modules.Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS™): A distributed file system that provides high-throughput access to application data.Hadoop YARN: A framework for job scheduling and cluster resource management.HadoopMapReduce: A YARN-based system for parallel processing of large data sets.Other Hadoop-related projects at Apache include:Ambari™: A web-based tool for provisioning, managing, and monitoring Apache Hadoop clusters which includes support for Hadoop HDFS, HadoopMapReduce, Hive, HCatalog, HBase, ZooKeeper, Oozie, Pig and Sqoop. Ambari also provides a dashboard for viewing cluster health such as heatmaps and ability to view MapReduce, Pig and Hive applications visually alongwith features to diagnose their performance characteristics in a user-friendly manner.Avro™: A data serialization system.Cassandra™: A scalable multi-master database with no single points of failure.Chukwa™: A data collection system for managing large distributed systems.HBase™: A scalable, distributed database that supports structured data storage for large tables.Hive™: A data warehouse infrastructure that provides data summarization and ad hoc querying.Mahout™: A Scalable machine learning and data mining library.Pig™: A high-level data-flow language and execution framework for parallel computation.Spark™: A fast and general compute engine for Hadoop data. Spark provides a simple and expressive programming model that supports a wide range of applications, including ETL, machine learning, stream processing, and graph computation.ZooKeeper™: A high-performance coordination service for distributed applications.
- Based on architecture Discussed in previous slide
- Smart adv metering infrastructure (can send commands to meter): Distributed SystemConsumer DMZHead End (MDM Metering device management) patch management, firmware update, sending commands to metersWAN –Collector,router, Firewall multi utility connector (MUC)Collector (interface with Electricity, Gas, Water meter ) port for GPRS, W-MBUS Antenna , Antenna( Kamstrup )Connected devices Admin panel can track after keys are keyed in.Interfaces To medium: (Optical,Wired Interfaces, GPRS, ZigBee, Wireless M-BusFunctionality: Meter reading, pre-payment, Tariff setting, DisConnectmeter send information to collector,meter to relay to controllerNAN
- The Wireless M-Bus standard (EN13757-4:2005 and 2012) specifies the RF communication link between water, gas, heat, and electric meters and the data collecting devices and is becoming widely accepted in Europe for smart metering or Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) applications. Wireless M-Bus was originally targeted to operate only in the 868 MHz band, which gives a good trade-off between RF range and antenna size. Recently two new bands (169MHz and 433MHz) have been added to the wM-Bus specification as well, introducing narrow-band solutions with much higher link budget and thus providing longer range solutions than at 868MHz.
- Some Good practices:The Wireless M-Bus standard (EN13757-4:2005 and 2012) specifies the RF communication link between water, gas, heat, and electric meters and the data collecting devices and is becoming widely accepted in Europe for smart metering or Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) applications. Wireless M-Bus was originally targeted to operate only in the 868 MHz band, which gives a good trade-off between RF range and antenna size. Recently two new bands (169MHz and 433MHz) have been added to the wM-Bus specification as well, introducing narrow-band solutions with much higher link budget and thus providing longer range solutions than at 868MHz.Evaluation of Wireless Smart Metering Technologies in Realistic Indoor Channels Nils Langhammer, and RuedigerKays, Member, IEEE Communication Technology Institute TU Dortmund University Dortmund, Germany {nils.langhammer | ruediger.kays}@tu-dortmund.de
- Cisco FANCapEx Private network OpEX Public network
- Single head End For deploying, managing, and trouble shootSingle RBAC Authenticate AND authorize all field devicesProtocol Translation:SCADA devices and protocols (Require Non IP network to traverse over IP network)Scalability: Network services to all different kind Utility devices (in Ubiquitous manner).Encryption: Utility Network Network Layer Encrption between head end router and DA gateway.Flex VPN scale to 1000 devicesUnified Field Architecture.
- New services billing in expanding role of smart meter to include many utilities hence billing component As shown fig 4, the AE has features such as Collection, Correlation, Aggregation. The collection receives the billing information. The correlation is used when a service manage the various service equipment. The correlation gathers different equipment's service information into one service according to relative information character. The aggregation receives the billing information from Service Function and Transaction Function with reference of the information of user in User ProfileSCADA System
