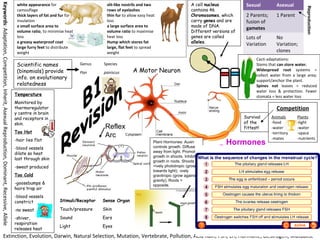
Biology: B1 Revision (AQA)
- 1. slit-like nostrils and two rows of eyelashes thin fur to allow easy heat loss a large surface area to volume ratio to maximise heat loss Hump which stores fat large, flat feet to spread weight white appearance for camouflage thick layers of fat and fur for insulation a small surface area to volume ratio, to minimise heat loss a greasy waterproof coat large furry feet to distribute weight Keywords:Adaptation,Competition,Inherit,AsexualReproduction,Dominant,Recessive,Allele A cell nucleus contains 46 Chromosomes, which carry genes and are made of DNA. Different versions of genes are called alleles. Extinction, Evolution, Darwin, Natural Selection, Mutation, Vertebrate, Pollution, Acid Rain, FSH, LH, Hormone, Oestrogen, Mutualist Competition Animals -food -water -territory -mates Plants -light -water -space -nutrients Sexual Asexual 2 Parents; fusion of gametes 1 Parent Lots of Variation No Variation; clones Cacti adaptations: Stems that can store water. Widespread root systems = collect water from a large area; support/anchor the plant. Spines not leaves = reduced water loss & protection. Fewer stomata = less water lossTemperature Monitored by thermoregulator y centre in brain and receptors in skin. Too Hot -hair lies flat -blood vessels dilate so heat lost through skin -sweat produced Too Cold -goosebumps & hairs trap air -blood vessels constrict -no sweat -shiver, respiration releases heat Scientific names (binomials) provide info. on evolutionary relatedness Genus Species Pan paniscus Survival of the fittest! Reproduction Stimuli/Receptor Sense Organ Touch/pressure Skin Sound Ears Light Eyes A Motor Neuron Reflex Arc Plant Hormones: Auxin controls growth. Diffuses away from light. Promotes growth in shoots. Inhibits growth in roots. Shoots = +ively phototropic (grow towards light); -ively gravitropic (grow against gravity). Roots = opposite. Hormones Gland > Secretion > Target organ
- 2. Theories of Evolution Evolution = random progressive change over long period of time Lamarck- inheritance of acquired characteristics Darwin- natural selection & survival of the fittest Fossils show how organisms have changed, but don’t often form and are usually fragmented Extinction due to…. •Changes in environment •New predators •New competitors •Disease Owls Blackbirds Caterpillars Oak tree Pyramids of Biomass Show amount of material at each stage Always a pyramid shape because energy & carbon is lost…. - Respiration: releases CO2, energy used in movement + heat production (mammals/birds) - Not all organisms eaten - Waste: faeces + urine The Carbon Cycle -Stored as CO2, or fats/proteins/carbs -Decay carried out by decomposers Food Chains Pyramids of numbers show the number of organisms at each level; not always a pyramid shape What is the source of all energy? 1. Mutation causes… 2. Variation, with 3. Some individuals better adapted 4. Better adapted survive and reproduce 5. Offspring inherit adaptation and also benefit E.g. Believed that the offspring of mice who had their tails chopped off would also have no tails…WRONG Electric shock to stimulate cell division Adult Cell CloningAdult cell cloning: new individual is an exact replica of just one parent Embryo transplant: two parents’ gametes, artificial insemination, embryo formed, split into several and each placed in a surrogate uterus What are the concerns with these procedures? Genetic Engineering Immune Response (1 of 3) White blood cells > produce antibodies > recognise foreign pathogens > faster response next time
- 3. Why does a person become malnoushired? Give two signs of malnourishment. Complete the table to evaluate the use of statins and cholesterol blockers for treating high cholesterol levels. What two nutrients do we need in small amounts to maintain good health. Use the information on the left to work out the BMI for the following people. What dietary and medical advice would you give to each? State three things that affect metabolic rate: Define metabolic rate Name the three major nutrient groups and state why we need each Name two factors that influence blood cholesterol levels. Name Mass (kg) Height (m) BMI Advice Mr X Miss P Mrs Q 70 65 54 1.90 1.43 1.74 19.4 31.8 17.8 What are statins and cholesterol blockers used for? Explain how each works. . Drug Advantages Disadvantages Statins Cholesterol blockers • . Name three important things in the body cholesterol is used for. BMI = mass in kg (height in m)2 Underweight <18 Normal 19-24 Overweight 25 - 29 Obese >30 Explain the link between cholesterol and heart disease. Name a source of: Saturated fat: Unsaturated fat: How can you change the fat intake in your diet to reduce cholesterol?
- 4. Why does a person become malnoushired? Their diet is not balanced Give two signs of malnourishment. Overweight / underweight Deficiency disesase Complete the table to evaluate the use of statins and cholesterol blockers for treating high cholesterol levels. What two nutrients do we need in small amounts to maintain good health. Vitamins Minerals Use the information on the left to work out the BMI for the following people. What dietary and medical advice would you give to each? State three things that affect metabolic rate: •Activity Levels •The ratio of fat to muscle in the body •Genes (inherited factors) Define metabolic rate is the rate at which all the chemical reactions in the cells of the body are carried out. Name the three major nutrient groups and state why we need each •Carbohydrate – energy source •Fat – energy, make hormones, insulation •Protein – build new cells Name two factors that influence blood cholesterol levels. Diet Genes Name Mass (kg) Height (m) BMI Advice Mr X Miss P Mrs Q 70 65 54 1.90 1.43 1.74 19.4 31.8 17.8 Healthy Obese –eat less fat and sugar; exercise more Underweight – increase calorie intake What are statins and chloesterol blockers used for? Explain how each works. Drugs that lower blood cholesterol. Statins block enzyme in liver. Cholesterol blockers reduce dietary absorption. Drug Advantages Disadvantages Statins Cholesterol blockers • Can lower cholesterol to zero • Good for people with high cholesterol due to genetics • Good for people with high cholesterol due to diet • Less side effects than • Need cholesterol to make hormones etc • Potentially fatal side effects • Can interact badly with other drugs. • Can cause diarrhoea. Name three important things in the body cholesterol is used for. Cell membranes Steroid hormones Bile BMI = mass in kg (height in m)2 Underweight <18 Normal 19-24 Overweight 25 - 29 Obese >30 Explain the link between cholesterol and heart disease. If you have a high ratio of LDLs to HDLs you have an increased risk of heart disease. This encourages cholesterol to be deposited in the walls of coronary arteries, Blockage prevents glucose and oxygen reaching the heart muscle so heart muscle cells cannot respire so die. Name a source of: Saturated fat: Meat, dairy, eggs Unsaturated fat: olive oil, peanuts, corn oil, sunflower oil, oily fish, margarine How can you change the fat intake in your diet to reduce cholesterol? Eat less saturated fats and more unsaturated
- 5. What 3 diseases does MMR vaccine protect from? Explain how the following make you ill: Bacteria Viruses How can the following drugs be used to treat disease? Painkillers Antibiotics Explain how vaccination works: Explain how white blood cells protect you from disease. What is a pathogen? . Outline the experiments carried out by Ignaz Semmelweiss and explain the contribution of these to modern medicine. Why can’t antibiotics be used to kill viruses? Why is overuse of antibiotics a problem? How can we reduce this problem? Why are antibiotics used in farming? Explain how antibiotic resistance develops in bacteria. What is a mutation? Why is mutatioin in pathogens problematic? What is a sterile culture. . Give 2 reasons it is important to keep cultures sterile. . List 4 precautions you must take when carrying out aseptic technique to grow a sterile culture 1. What temperature should we incubate cultures at in school and why? How does this compare to industry? .
- 6. What 3 diseases does MMR vaccine protect from? Measles Mumps Rubella Explain how the following make you ill: Bacteria Reproduce rapidly and produce toxins Viruses reproduce inside e cells and damage them How can the following drugs be used to treat disease? Painkillers relieve symptoms (don’t kill pathogen) Antibiotics Kill bacteria Explain how vaccination works: •Small amount of dead or inactive pathogen injected •Stimulates memory cells to form •Next time pathogen enters body white blood cells make antibodies faster and in greater numbers Explain how white blood cells protect you from disease. •Ingest pathogens (phagocytosis) •Produce antibodies – destroy specific bacteria or viruses •Produce antitoxins – neutralise toxins released by pathogens What is a pathogen? Microoganism that causes disease. Outline the experiments carried out by Ignaz Semmelweiss and explain the contribution of these to modern medicine. Noted death rates on maternity wards much lower when midwives delivered compared to doctors - realised doctors were transferring disease from surgery Encouraged use of chloride of lime to wash hands and kill bacteria - Death rates drastically fell Shows importance of handwashing to prevent spread of infection Why can’t antibiotics be used to kill viruses? Viruses replicate inside human cells so the antibiotic can’t reach them or would kill the human cell. Why is overuse of antibiotics a problem? Selects for antibiotic resistant bacteria to survive. These are hard to treat. How can we reduce this problem? Do not use antibiotics for minor infections Reduce use in agriculture Why are antibiotics used in farming? Help animals gain weight – less energy spent overcoming infection Increase profits – prevent spread of infection Explain how antibiotic resistance develops in bacteria. Bacteria mutate by chance Bacteria with mutation not killed by antibiotic These cells can survive to reproduce And pass the gene for resistance to their offspring – population of resistant bacteria increases What is a mutation? Change in a gene Why is mutatioin in pathogens problematic? Creates new strains that people have no immunity to or are resistant to antibiotics What is a sterile culture. Culture of only one type of microorganism. Give 2 reasons it is important to keep cultures sterile. . Other microbes would use up food resources Other microbes may produce dangerous toxins List 4 precautions you must take when carrying out aseptic technique to grow a sterile cuture 1. Sterilise petri dish and culture medium before use 2. Sterilise innoculating loop by passing through a flame 3. Tape lid to prevent contamination from air 4. Work near a flame What temperature should we incubate cultures at in school and why? How does this compare to industry? 25oC – to prevent growth of human pathogens. Industry higher – faster growth rate.
- 7. What is involved in phase two drugs testing? Complete the table to evaluate the use of cannabis What does phase one drug testing involve and why is it necessary? Why did the use of Thalidomide cause controversy? What is meant by A blind trial? Double blind trial? What would the placebo be if the real drug was: A tablet? An injection? Advantages Disadvantages What is a drug? What was Thalidomide originally developed as? What is it now used to treat? Give a negative effecs on the body of Smoking Drinking alcohol What is drug addiction? Name a very addictive drug.? What is the advantage of blind trials? Why is the overall impact of legal drugs on society greater than illegal drugs? What are withdrawal symptoms? Give an example. Why might an athlete take the following? •Anabolic steroid •Stimulants •Analgesics •Stimulants
- 8. What is involved in phase two drugs testing? Drug tested on healty volunteers Start with low dose – gradually increased until effective dose found Complete the table to evaluate the use of cannabis What does phase one drug testing involve and why is it necessary? Test drug on cells, tissues or animals Safety testing - check for toxicity and interaction with other drugs. Why did the use of Thalidomide cause controversy? Found to relieve morning sickness but had not been tested on pregnant animals – babies born with severe limb abnormalities. What is meant by A blind trial? Patients do not now who gets drug and who gets placebo Double blind trial? Neither doctor nor patient knows who gets drug or placebo What would the placebo be if the real drug was: A tablet? Sugar pill An injection? Saline injection Advantages Disadvantages Can be medicinal: glaucoma / MS / Cancer Relaxant Strong evidence suggesting causes mental illness Expensive May lead to use of more dangerous drugs What is a drug? Chemical that alters the way the body works. What was Thalidomide originally developed as? Sleeping Pill What is it now used to treat? Leprosy Some types of cancer Give a negative effecs on the body of Smoking Lung cancer / Low birth weight / Heart disease / Emphysema etc Drinking alcohol Liver cancer / cirrhosis etc What is drug addiction? Name a very addictive drug.? When your body becomes dependent on a drug due to frequent use– durg alters body chemistry so badly that you cannot function normally without it. Eg, heroin, cocaine What is the advantage of blind trials? Avoid bias Why is the overall impact of legal drugs on society greater than illegal drugs? More people use legal drugs What are withdrawal symptoms? Give an example. Unpleaseant side effects experienced when you stop taking an addictive drug. Eg. Tremors, palpitations, sweating, headaches etc Why might an althlete take the following? •Anabolic steroid increase muscle mass •Stimulants Liver cancer / cirrhosis etc •Analgesics relive pain •Stimulants make reactions faster
