three phase inverter
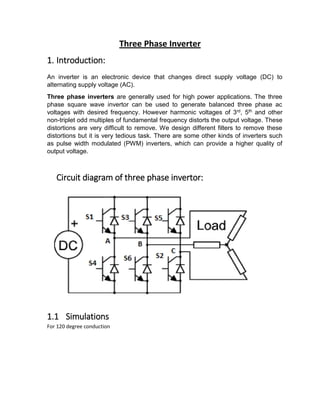
- 1. Three Phase Inverter 1. Introduction: An inverter is an electronic device that changes direct supply voltage (DC) to alternating supply voltage (AC). Three phase inverters are generally used for high power applications. The three phase square wave invertor can be used to generate balanced three phase ac voltages with desired frequency. However harmonic voltages of 3rd, 5th and other non-triplet odd multiples of fundamental frequency distorts the output voltage. These distortions are very difficult to remove. We design different filters to remove these distortions but it is very tedious task. There are some other kinds of inverters such as pulse width modulated (PWM) inverters, which can provide a higher quality of output voltage. Circuit diagram of three phase invertor: 1.1 Simulations For 120 degree conduction
- 2. Phase voltages will be as Phase difference will be as
- 3. Line voltage will be as
- 4. Line voltage difference will be as For 180 degree Conduction
- 5. Line voltage will be as Line difference will be as
- 6. Phase voltage will be as Phase difference will be as
- 7. 2. Modes of conduction: There are two modes of conduction: i. 180 degrees’ conduction ii. 120 degrees’ conduction 2.1 180o conduction: In this mode of operation each switch conducts for half cycle. At any instant of time three switches are ON. When S1 is ON, the terminal A gets connected to the positive terminal of input DC source, at the same time its complementary switch S4 remains off. Similarly, when S4 is ON, terminal A gets connected with the negative terminal of the DC source. These combinations are same for S3, S6 (terminal B) and S5, S2 (terminal C). There are six possible modes of operation in a cycle and each is of 60 degree. Equivalent circuit For Y-connected resistive load for step1 (0-60 degree), others are similar to this:
- 8. For step 1 (0-60 degree) S1, S6, S5 will conduct A and B will be connected with positive terminal of DC source and C will be connected with negative terminal of DC source. Equivalent resistance is equal to 𝑅𝑒𝑞 = 𝑅 + 𝑅 ∗ 𝑅 𝑅 + 𝑅 𝑅 + 𝑅 2 = 3𝑅 2 Current can be calculated as 𝑖 = 𝑉𝑔 𝑅𝑒𝑞 = 2𝑉𝑔 3𝑅 Phase Voltages can be calculated as 𝑉𝑎𝑛 = 𝑉𝑐𝑛 = 𝑅 2 3𝑅 2 ∗ 𝑉𝑔 = 1 3 𝑉𝑔 𝑉𝑏𝑛 = 𝑅 3𝑅 2 ∗ 𝑉𝑔 = −2 3 𝑉𝑔 Line to line voltages can be calculated as 𝑉𝑎𝑏 = 𝑉𝑎𝑛 − 𝑉𝑏𝑛 = 𝑉𝑔 𝑉𝑏𝑐 = 𝑉𝑏𝑛 − 𝑉𝑐𝑛 = −𝑉𝑔 𝑉𝑐𝑎 = 𝑉𝑐𝑛 − 𝑉𝑎𝑛 = 0
- 9. We can calculate voltages for other steps by following same procedure. 2.1.1 Waveforms There waveforms are shown of phase voltages and line to line voltages are shown: For line to line voltages between A & B For Phase voltages
- 10. RMS value of phase voltage: √2 3 𝑉𝑔 RMS value of line voltage: √ 2 3 𝑉𝑔 2.2 1200 conduction: In 120-degree conduction mode, only two switches conduct at the same time; one upper switch and one lower switch. Each switch conducts for a duration of 1200 in one period of 3600 of the output voltage. The gating signal for each switch is maintained for 120-degree. There are six sub-intervals of 600 each. The operation of invertor during one cycle of input voltage can be explained in six different steps. I have explained only on, others are similar to this. In step 1 (0-60 degree) S6 and S1 is conducting as figure becomes: Equivalent circuit For Y-connected resistive load for step1 (0-60 degree)
- 11. Phase voltages can be calculated as: 𝑉𝑎𝑛 = 𝑉𝑔 2 𝑉𝑏𝑛 = − 𝑉𝑔 2 𝑉𝑐𝑛 = 0 𝑉𝑎𝑏 = 𝑉𝑔 𝑉𝑏𝑐 = 𝑉𝑐𝑎 = −𝑉𝑔 2 2.2.1 Waveforms For phase voltages
- 12. For line to line voltages between A & B RMS value of phase voltage: 6 sV RMS value of line voltage: 2 sV 3. Hardware
- 14. Waveforms Across Phase voltage Phase voltage (phase) difference Line Voltage
- 15. Line voltage Phase difference After Passing through Filter