Melden
Teilen
Empfohlen
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Was ist angesagt?
Was ist angesagt? (20)
Regulation of arterial blood pressure (The Guyton and Hall Physiology)

Regulation of arterial blood pressure (The Guyton and Hall Physiology)
Blood pressure by Pandian M, tutor, Dept of Physiology, DYPMCKOP,MH. This PPT...

Blood pressure by Pandian M, tutor, Dept of Physiology, DYPMCKOP,MH. This PPT...
Regulation of respiration (the guyton and hall physiology)

Regulation of respiration (the guyton and hall physiology)
Andere mochten auch
Andere mochten auch (19)
Osmoregulation (Urine Dilution & Concentration) - Dr. Gawad

Osmoregulation (Urine Dilution & Concentration) - Dr. Gawad
Power point the cardiovascular system - anatomy and physiology

Power point the cardiovascular system - anatomy and physiology
Ähnlich wie Cvs7
Ähnlich wie Cvs7 (20)
Physiological Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure.pptx

Physiological Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure.pptx
BibliographyHall, J. E. (2015). Guyton and Hall textbook of medic.pdf

BibliographyHall, J. E. (2015). Guyton and Hall textbook of medic.pdf
Maintaining homeostatic mean arterial blood pressure

Maintaining homeostatic mean arterial blood pressure
Mehr von Lawrence James
Mehr von Lawrence James (20)
Cvs7
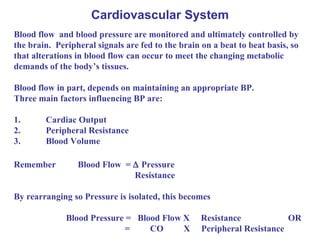
- 1. Cardiovascular System Blood flow and blood pressure are monitored and ultimately controlled by the brain. Peripheral signals are fed to the brain on a beat to beat basis, so that alterations in blood flow can occur to meet the changing metabolic demands of the body’s tissues. Blood flow in part, depends on maintaining an appropriate BP. Three main factors influencing BP are: 1. Cardiac Output 2. Peripheral Resistance 3. Blood Volume Remember Blood Flow = Pressure Resistance By rearranging so Pressure is isolated, this becomes Blood Pressure = Blood Flow X Resistance OR = CO X Peripheral Resistance
- 4. Cardiovascular System Neural Control of Peripheral Resistance aims to: 1. Alter blood distribution in response to specific demands. 2. Maintain appropriate MAP by changing vessel diameter. Neural Control of the cardiovascular system originates in the Cardiac Centres found in the Medulla. Cardio -Acceleratory Centre sends Sympathetic Neurones down the spine to between T1 and T5, where they exit to the periphery. Cardio - Inhibitory Centre originates with the Vagus Nucleus in the medulla and this Parasympathetic Nerve leaves the cranium as the Vagus (X) Nerve. Vasomotor Centre - is a cluster of sympathetic fibres in the Medulla. - transmits impulses via sympathetic vasomotor fibres from T1 to L2 to blood vessels (arterioles) Vasoconstriction is caused by increased frequency of impulses (Noradrenaline) Vasodilation is caused by decreased frequency of impulses.
- 5. Cardiovascular System Brainstem contains: Pons Medulla In the Medulla are the: Cardiac Acceleratory Centre Cardiac Inhibitory Centre Vasomotor Centre
- 9. Local mechanisms affect MAP:
- 11. The Baroreceptor Reflex Once signals have entered the medulla secondary signals inhibit the vasoconstrictor center and excite the vagal center. This results in vasodilation of the veins and arterioles throughout the systemic circulation and decreased heart rate and contractility. Therefore, stimulation of the baroreceptor reflex reduces blood pressure through a decrease in peripheral resistance and a decrease in cardiac output. Low pressure has the opposite effect Typical Carotid Sinus Reflex on Arterial Pressure Caused by Clamping Both Common Carotids
- 18. Cushing Reaction: If cerebro-spinal fluid pressure exceeds arterial pressure, arterial blood flow to the brain stops, this then triggers increased blood flow and pressure until blood flow returns to normal.
- 22. General control of MAP:
- 26. Comparison of Potency and Kinetics of Different Arterial Pressure Control Mechanisms at Different Time Intervals After the Onset of a Disturbance to the Arterial Pressure
