Asia: The World's Largest and Most Diverse Continent
- 2. ASIA Aegean word ASU which means sunrise Largest and most mountainous Covers almost a third of the earth’s total land area. In it, is the world’s highest peak, Mt. Everest.
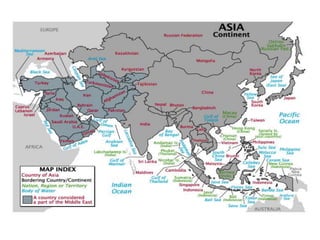
- 3. bounded on the N by the ARCTIC ocean to the S lies the INDIAN ocean with the Arabian sea, the Bay of Bengal and the South China sea. on the E is the Pacific ocean Southeastern part is made up of many islands.
- 4. on the W, Asia is joined to Europe: the Ural Mountains and the Caspian sea form the boundary between the two continents. in the SW Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea. It is linked to Africa by the narrow Isthmus of Suez, artificially cut by the Suez Canal.
- 5. Five Major Realms East Asia, including China, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Japan and Taiwan
- 6. Southeast: Myanmar (formerly known as Burma), Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Vietnam, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Brunei, East Timor and the Philippines
- 7. South Asia: India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives, Nepal, and Bhutan
- 8. West Asia: Afghanistan, Iran, Iraq, Turkey, Cyprus, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, and Kuwait.
- 9. North / Central: Area of Russia that lies east of the Ural Mountains (Russian Asia) and the states of Central Asia that were formerly part of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR). These states are Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan.
- 10. Facts about Asia Area : 17,176,102 sq.mi. (44,485,900 sq.km.) Population: estimate of 4 billion Highest Point: Mt. Everest, Tibet-Nepal (29,028 ft. above sea level) Lowest Point: Dead Sea, Israel-Jordan (1,312 ft. below sea level) Largest Country: (by area) Russia, excluding European portion, 4,845,580 sq.mi. Largest Country: (by population) China. Estimate of 1.2 billion Largest Metropolitan Area: (by population) Tokyo, Japan Bombay, India Shanghai, China Longest Rivers: Yangtze (Chiang Jiang); Yenisey-Angara (Russia) Largest Lakes: Caspian Sea (Asia-Europe),Lake Baikal(Russia) Largest Desert: Gobi Desert (China-Mongolia)
- 11. Asian Way of Life not only the largest but the most populous *Mongoloid people live in Eastern Asia and in most of Central Asia *Caucasoid people, related to the people of Europe, live in Southern Asia, Southwestern Asia and Siberia *Negroid people, similar to the peoples of Africa South of the Sahara, live in many of the islands of Southeastern Asia. Pygmies, called Negritos, live in Malaya and several of the largest of the islands.
- 12. > Asia also gave birth to all the world’s major religions. *Hinduism, main religion of India > Buddhism, developed in China and Japan *Confucianism, China’s other great religion *Shintoism, Japan’s traditional religion *Judaism, evolved among the ancient Israelites > Christianity > Islam
- 13. Mineral Resources Asia is so immense that it has a varied mineral and agricultural resources. But many of Asia’s mineral resources have not yet been fully exploited, and probably there are enormous mineral riches the locations of which are still unknown. Northern Asia – that is the Asiatic part of Russia – has a major coal deposits both in the E and in the W, and experts believe that there are vast untapped resources in the permafrost regions of the N. Oilfields are actively exploited to the N of the Caspian Sea and also on the long slender island of the Sakhalin, off the Pacific coast to the N of Japan
- 14. Other important minerals which the Russians are extracting include asbestos, chrome, cobalt, copper, gold, iron, mercury, manganese, nickel, tin, silver, uranium and vanadium. In addition, the major rivers have been harnessed as a source of energy, and several industrial regions are dependent on the hydro-electric power that they provide
- 15. > High performing Asian countries are mostly found in Eastern (Far and South) countries like: Japan, Hongkong, Taiwan, South Korea Singapore, Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand. > However, Asia has also both developing and poverty stricken countries like: Philippines, Bangladesh, Laos, and Kampuchea to name a few.
- 16. Side by side with economic boom in Asia is population increase. Most populous cities in the world are found in Asia. And by the next century, Asia will become regions of megacities. With the population problem, cities are characterized by slum areas, increasing urban crime and prostitution, severe cause of pollution, traffic, etc. This is the price the city folks of Asia’s tigers are paying to live where they are today.
- 17. And though megacities are sprouting in Asia, still 75% of the Asians live in the countryside. Asians way of life are still centered on the village, whether it is in the forest clearing, river valleys or upland plain.
- 18. Other important minerals which the Russians are extracting include asbestos, chrome, cobalt, copper, gold, iron, mercury, manganese, nickel, tin, silver, uranium and vanadium. In addition, the major rivers have been harnessed as a source of energy, and several industrial regions are dependent on the hydro-electric power that they provide
- 19. Eastern Asia is rich in coal, and is known to have small deposits of a great many metal ores, particularly those of antimony and tungsten. One of the most important resources in this region is iron ore, but surveys have so far indicated only small amounts of petroleum.
- 20. Southwestern Asia is rich in petroleum and coal. The area around the Persian Gulf is one of the world’s chief sources of oil and there is also coal in Iran and Turkey
- 21. Southern Asia is rich in iron ore and also has valuable supplies of coal, the chief concentrations being found in India. The region also has some petroleum and Pakistan and Bangladesh both possess natural gas deposits. But other minerals are scarce, though much of Southern Asia has yet to be surveyed.
- 22. Agricultural, Fisheries and Land Use Two Asians out of every three live by farming. Many have their own small holdings where they grow just enough food for themselves (Subsistence ) and for their families; in bad years they often grow hungry.
- 23. The best agricultural lands are in Southern Asia, Southeastern Asia, Eastern and the southwestern part of Siberia. The two chief subsistence crops are rice and wheat. The largest crops of rice are produced in China and the drier parts of India. Although improved agricultural methods and the use of better seeds have led to a larger crop yields in recent years, many parts of Asia do not manage to grow enough food to support their inhabitants if the weather is unfavorable and have to import wheat from North America.
- 24. A number of valuable crops are grown for export: Malaysia and Indonesia are major producers of rubber. Rubber trees are introduced to these countries from Brazil in the 1870’s. India, Sri Lanka and China produce most of the world’s tea. The island of the East Indies produce most of the world’s spices. Other important cash crops include cotton, citrus fruits, jute and tobacco.
- 25. Most of Central and Southwestern Asia is unsuitable for crop growing. But on the scanty pasture-lands of these regions, nomadic (wandering) herdsmen tend goats, sheep and cattle. They also raise camels which are important means of transport. In Southern Asia cattle are little use for food; in some countries they are protected for religious reasons and in other places they are protected because they represent wealth. But they are widely employed for ploughing and for drawing carts.
- 26. Forests still cover large parts of Asia, including the remote areas of Siberia. The Russians extract a great deal of softwood timber from those parts of the forests that lie near rivers or railways. In Southeastern Asia, there are thick teak forests that are exploited for timber, but most of the forests of the islands, including the Indonesian islands are not fully exploited.
- 27. Fish are important as food in the coastal lands and islands of eastern Asia. Both China and Japan possess large fishing fleets which roam the waters of the northern Pacific in search of catches.
- 28. Southern Asia, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and Burma all rely heavily on fish as an item of food. River and lake fishing are important in many parts of southeastern Asia, particularly in the deltas of the great rivers, such as the Mekong. China, too, has lakes and rivers in some areas that are well stocked with fresh water fish
- 29. Japan possesses a major whaling fleet, which hunts not only in home waters but also in the Antarctic Ocean. Edible sea weeds are collected by the Japanese, and some of these valuable foodstuff is exported.
- 30. Land use is very uneven in Asia. Half of the world’s people live in six Asian countries – China, India, Indonesia, Japan, Pakistan and Bangladesh. But huge areas of Central Asia and the Arabian Peninsula are almost uninhabited because they are desert or semi-desert.
